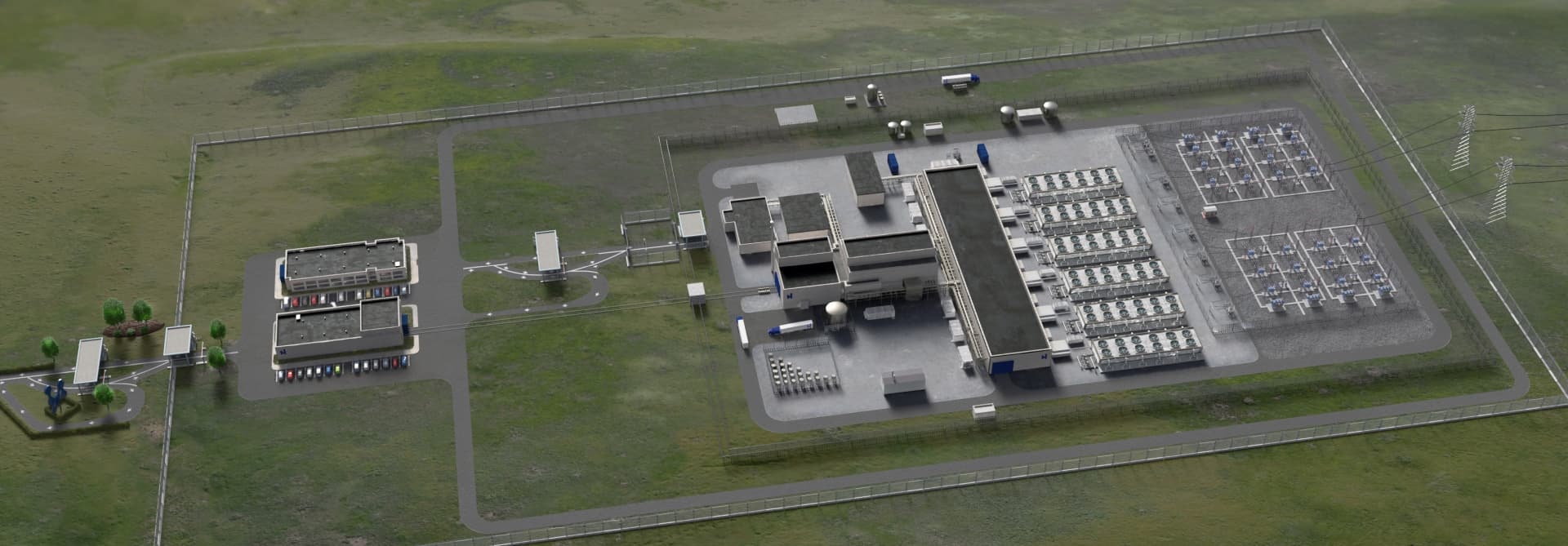
Concept art of the six-module CFPP at INL, terminated before construction could begin. (Image: NuScale)
Utah Associated Municipal Power Systems (UAMPS) and NuScale Power announced November 8 that they have mutually agreed to end the Carbon Free Power Project (CFPP)—a plan to build a set of 77-MWe pressurized water reactors, called NuScale Power Modules, at Idaho National Laboratory. The reactors were intended to provide power to INL and UAMPS customers in Utah and surrounding states with an anticipated start date of 2029.
Concept art of the six-module Carbon Free Power Project, to be sited at INL. (Image: NuScale)
CFPP LLC, the limited liability company established by Utah Associated Municipal Power Systems (UAMPS) in 2020 to bring its Carbon Free Power Project to fruition, has applied to the Nuclear Regulatory Commission for a limited work authorization (LWA) to permit certain early project construction activities prior to the issuance of a combined license (COL). In a July 31 news release, CFPP said that should its application be approved, early-scope construction on the small modular reactor project would likely begin in mid-2025.
A rendering of a NuScale VOYGR plant. (Image: NuScale)
NuScale Power, the Portland, Ore.–based small modular reactor developer, announced last week that it has placed the first upper reactor pressure vessel (RPV) long-lead material (LLM) production order with South Korea’s Doosan Enerbility.
A rendering of the six-module Carbon Free Power Project planned for construction in Idaho. (Image: NuScale)
NuScale Power announced October 20 that the Nuclear Regulatory Commission’s Advisory Committee on Reactor Safeguards (ACRS) issued a letter the previous day agreeing with NRC staff’s approval of NuScale’s methodology for determining the plume exposure pathway emergency planning zone (EPZ). As approved, the methodology would permit a smaller EPZ—dependent on site-specific conditions, including seismic hazards—that provides the same level of protection to the public as the 10-mile radius EPZs used for existing U.S. nuclear power plants.
A still image from a three-part video tour of NuScale’s facilities. (Photos: NuScale Power)
When Utah Associated Municipal Power Systems (UAMPS) in 2015 announced its plan to develop the Carbon Free Power Project (CFPP) using NuScale Power’s modular light water reactor design, it envisioned the construction of a dozen 50-MWe modules for a plant that could produce a total of 600 MWe. The CFPP’s target output later rose to 720 MWe, when UAMPS opted to scale up to 60-MWe modules. In late June, the plans changed once again, as UAMPS participants chose to build 77-MWe modules but downsize the plant from 12 units to six, which would yield 462 MWe—about 64 percent of the 720 MWe that could have been generated from 12 of the 60-MWe modules.