The EBR-II sodium fast reactor at Idaho National Laboratory began operations in 1964 and generated electricity for decades. Soon it will serve as a National Reactor Innovation Center test bed for future advanced reactor demonstrations. (Source: ANL)
At the box office or streaming at home, it’s fear, not truth, that sells. The laws of physics are swept aside, apocalypse is inevitable, and superpowered heroes wait until the last possible second to save the universe. It can make for great entertainment, but in the real world we need to stick with science over science fiction and be wowed by engineering, not special effects.
The truth is, science and innovation are incredible in their own right. From communications and machine learning to space travel and medical advances, technology is evolving in hyperdrive to solve real problems. With climate change and global warming here on earth, we don’t have to go looking for trouble in a galaxy far, far away.
A rendering of the VTR facility. (Image: INL)
The Department of Energy announced in 2020 its approval of Critical Decision 1 for the Versatile Test Reactor (VTR) project, a one-of-a-kind scientific user facility that would support research and development of innovative nuclear energy and other technologies. The decision was well received by the nuclear energy community—after all, the DOE’s Nuclear Energy Advisory Committee had studied and reported on the need for the VTR and found strong support for the project among reactor developers, federal agencies and national laboratories, and university researchers.
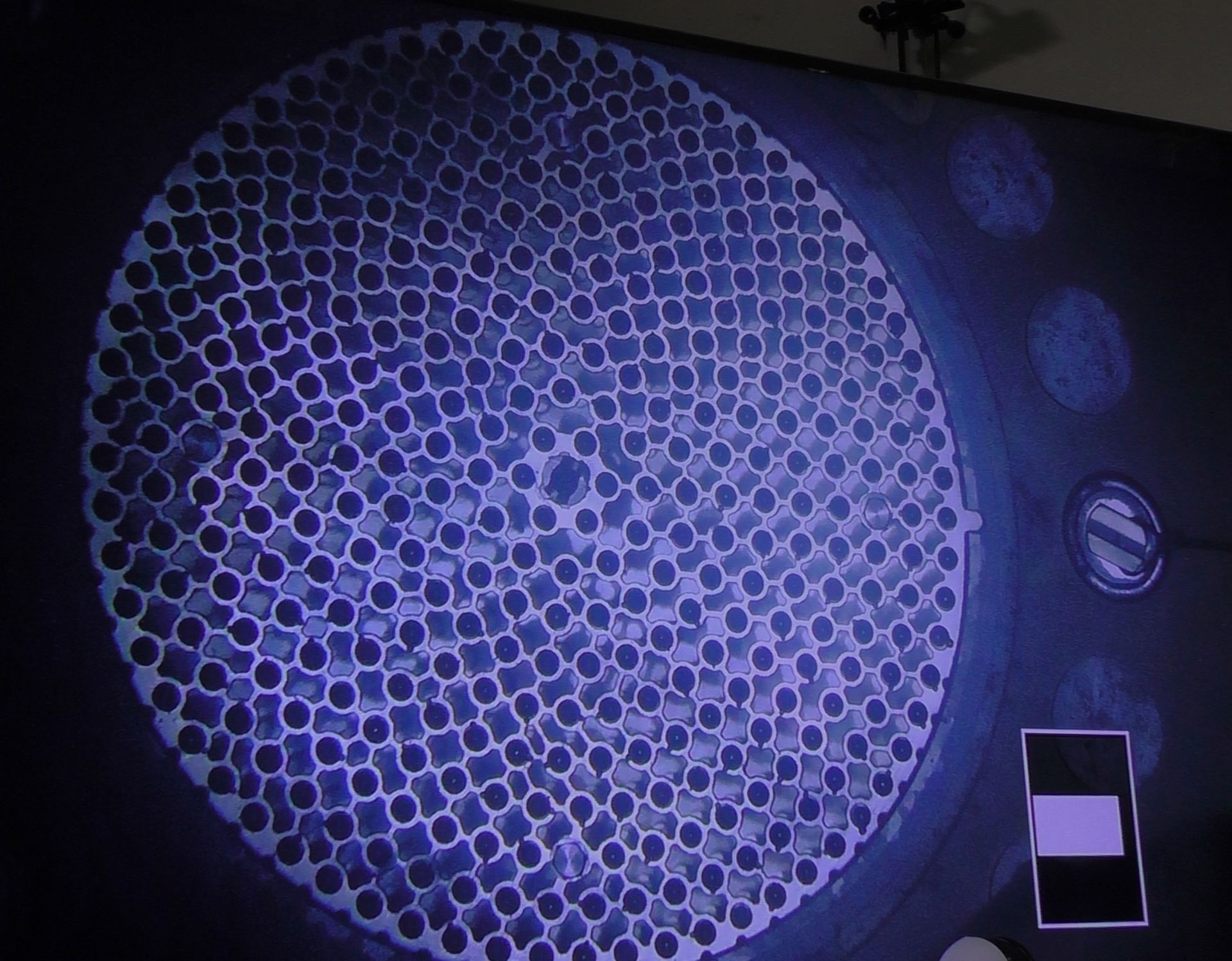
This image shows the individual pins in a full-core nuclear reactor simulation. (Image: ANL)
Coolant flow around the fuel pins in a light water reactor core plays a critical role in determining the reactor’s performance. For yet-to-be-built small modular reactors, a thorough understanding of coolant flow will be key to successfully designing, building, and licensing first-of-a-kind reactors.
The 40-year effort to make research reactors safer and more secure has led to the conversion of 71 reactors worldwide from HEU fuel to LEU.
The Ghana Research Reactor-1, located in Accra, Ghana, was converted from HEU fuel to LEU in 2017. Photo: Argonne National Laboratory
In late 2018, Nigeria’s sole operating nuclear research reactor, NIRR-1, switched to a safer uranium fuel. Coming just 18 months on the heels of a celebrated conversion in Ghana, the NIRR-1 reboot passed without much fanfare. However, the switch marked an important global milestone: NIRR-1 was the last of Africa’s 11 operating research reactors to run on high-enriched uranium fuel.
The 40-year effort to make research reactors safer and more secure by replacing HEU fuel with low-enriched uranium is marked by a succession of quiet but immeasurably significant milestones like these. Before Africa, a team of engineers from many organizations, including the U.S. Department of Energy’s Argonne National Laboratory, concluded its conversion work in South America and Australia. Worldwide, 71 reactors in nearly 40 countries have undergone conversions to LEU, defined as less than 20 percent uranium-235. Another 31 research reactors have been permanently shut down.






 The Gateway for Accelerated Innovation in Nuclear (GAIN) announced that three nuclear technology companies—Radiant, Oklo, and Lightbridge—will receive GAIN nuclear energy vouchers to accelerate the innovation and application of advanced nuclear technologies.
The Gateway for Accelerated Innovation in Nuclear (GAIN) announced that three nuclear technology companies—Radiant, Oklo, and Lightbridge—will receive GAIN nuclear energy vouchers to accelerate the innovation and application of advanced nuclear technologies. 


 The ANS Young Members Group (YMG) is offering a series of live webinars—Spotlight on National Labs—to highlight the missions, key projects, and rising stars of the Department of Energy’s national laboratories. Recently it was Argonne National Laboratory’s turn to shine.
The ANS Young Members Group (YMG) is offering a series of live webinars—Spotlight on National Labs—to highlight the missions, key projects, and rising stars of the Department of Energy’s national laboratories. Recently it was Argonne National Laboratory’s turn to shine.