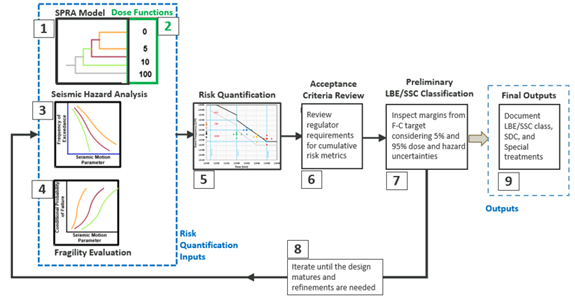
Figure showing the nine steps of the demonstration example’s RIPB design process.
Hanford crews break up concrete and remove contaminated soil near the site’s former K Area reactors in 2023. (Photo: DOE)
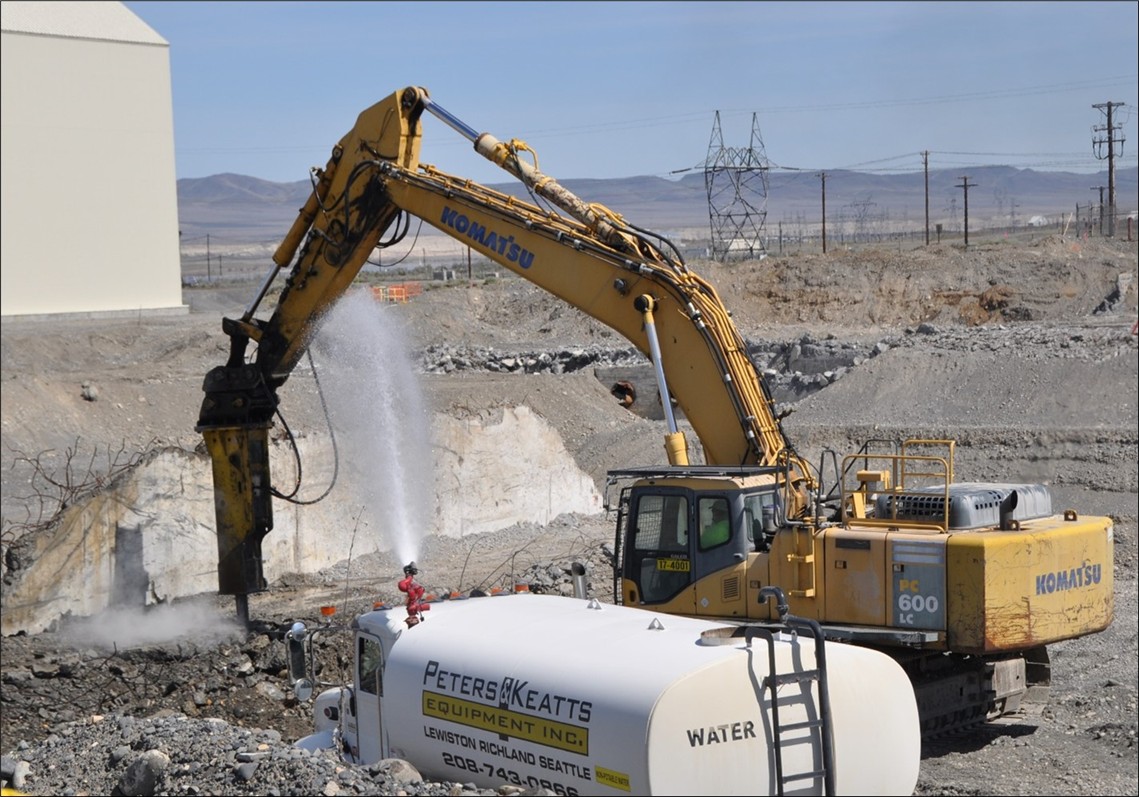
The cost to complete the cleanup of the Department of Energy’s Hanford Site in Washington state could cost as much as $589.4 billion, according to the 2025 Hanford Lifecycle Scope, Schedule, and Cost Report, which was released by the DOE on April 15. While that estimate is $44.2 billion lower than the DOE’s 2022 estimate of $640.6 billion, a separate, low-end estimate has since grown by more than 21 percent, to $364 billion.
The life cycle report, which the DOE is legally required to issue every three years under agreement with the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency and Washington State Department of Ecology (Ecology), summarizes the remaining work scope, schedule, and cost estimates for the nuclear site. For more than 40 years, Hanford’s reactors produced plutonium for America’s defense program.
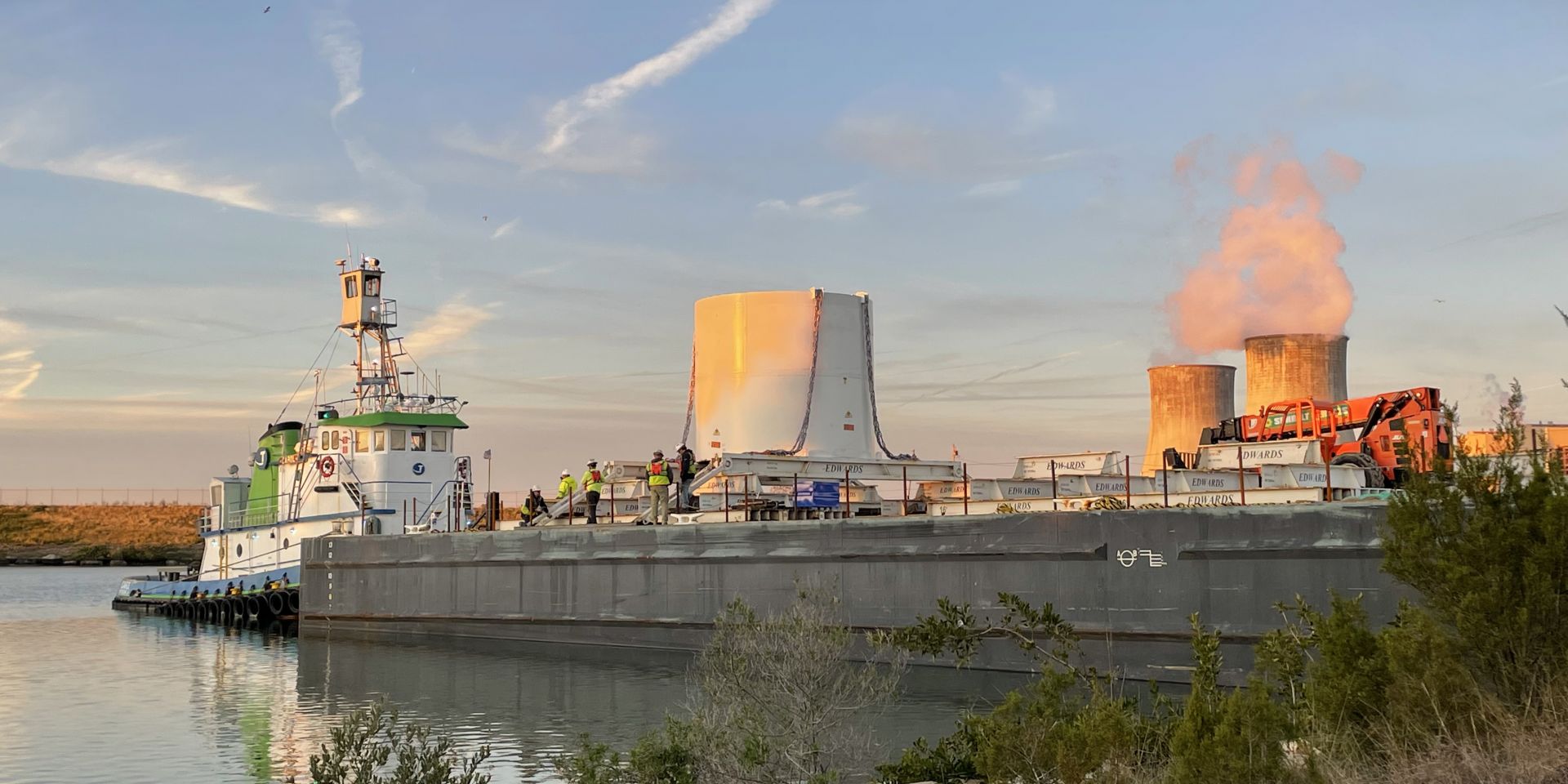
April 16, 2025, 3:39PMRadwaste SolutionsRichard “Ricky” Furr, Larry McDougal, and John Mayer The CR-3MP is loaded on the barge at the Crystal River-3 site in Florida on January 17, 2024. (Photos: Orano DS)
The Optimized Segmentation process patented by Orano Decommissioning Services was successfully implemented for the first time at the Crystal River Unit 3 (CR-3) decommissioning project in Florida [1]. Using this approach, Orano was able to avoid the time- and resource-intensive process of packaging components into numerous standardized waste containers and significantly reduced the required segmentation activities.
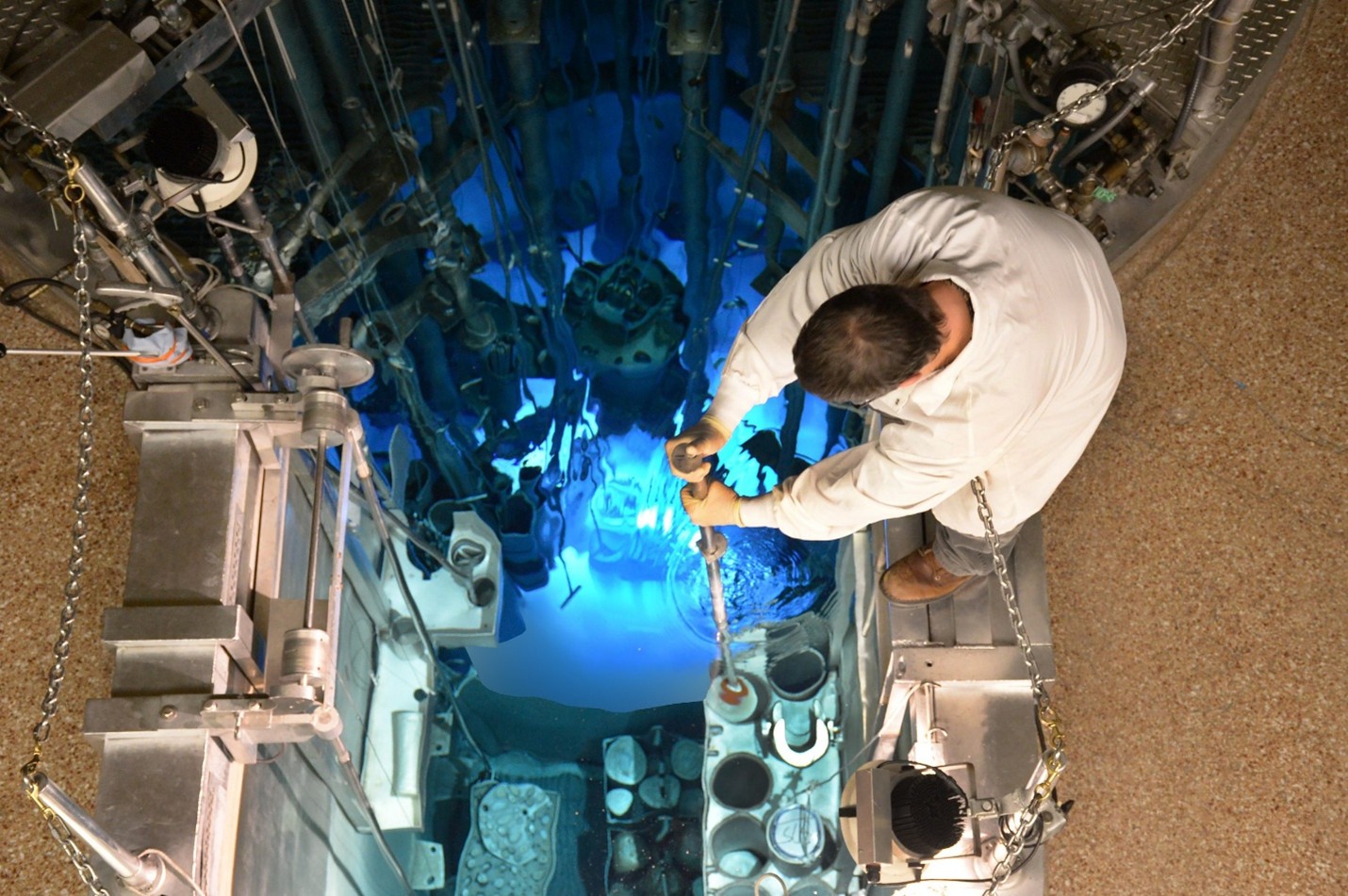
A reactor operator retrieves a sample can from the MURR, as seen from above. (Photo: University of Missouri)
The University of Missouri announced today that it has signed a $10 million contract for the initial design phase of the $1 billion-plus state-of-the-art NextGen MURR research reactor project.
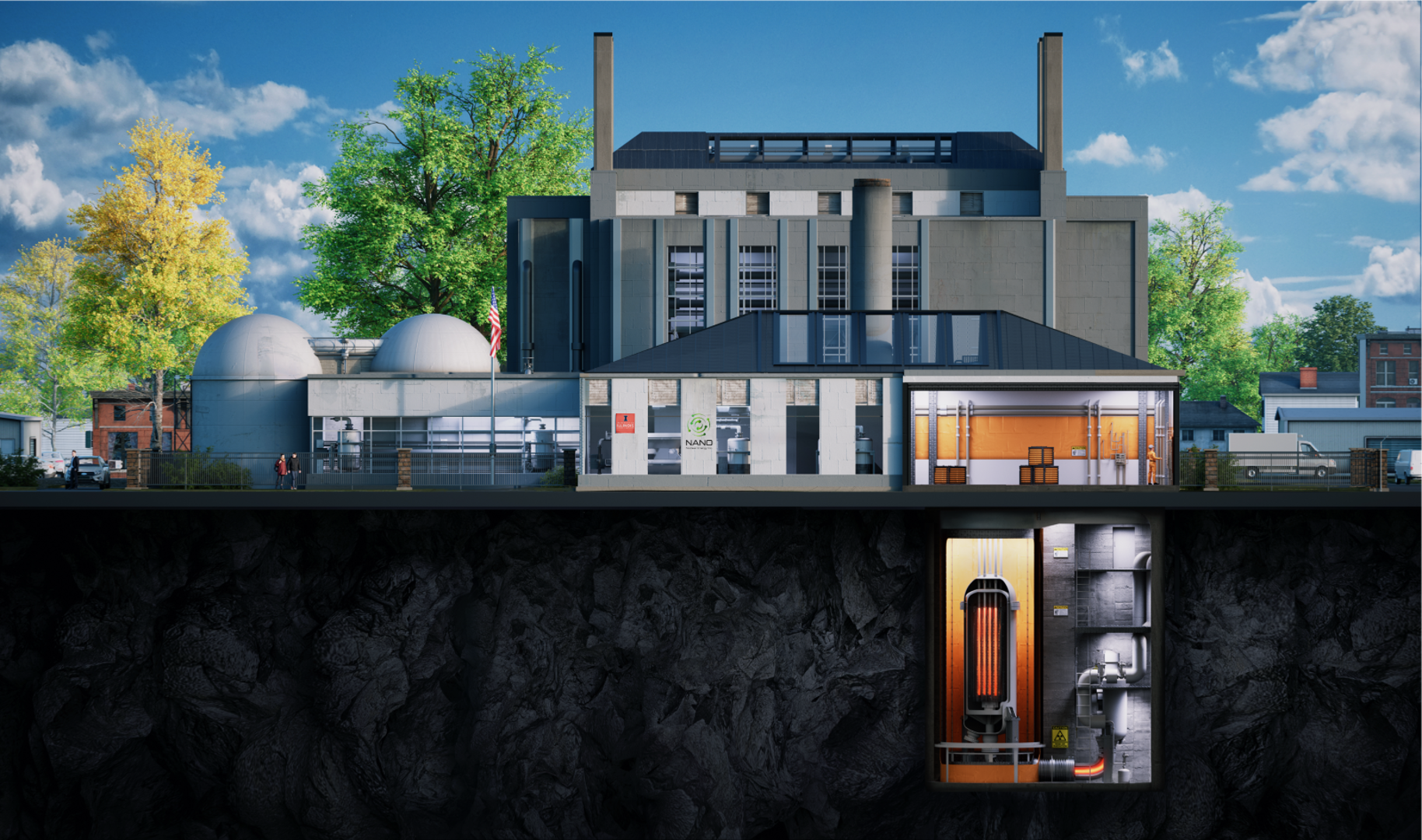
Concept art of NANO Nuclear’s KRONOS MMR research reactor that UIUC plans to operate on its campus in Champaign, Ill. (Image: NANO Nuclear)
Plans to bring a university research reactor like no other to the campus of the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign (UIUC) were punctuated last fall by the news that Ultra Safe Nuclear, the developer of the gas-cooled reactor technology selected for the Illinois Microreactor Project, had declared bankruptcy.
A worker replaces the end jig used to collect fuel debris samples from the damaged Fukushima reactor. (Photo: TEPCO)
Tokyo Electric Power Company is scheduled this week to begin retrieving a second sample of nuclear fuel debris from Unit 2 of Japan’s damaged Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant. This second retrieval comes after TEPCO improved the telescopic device used to gather samples.
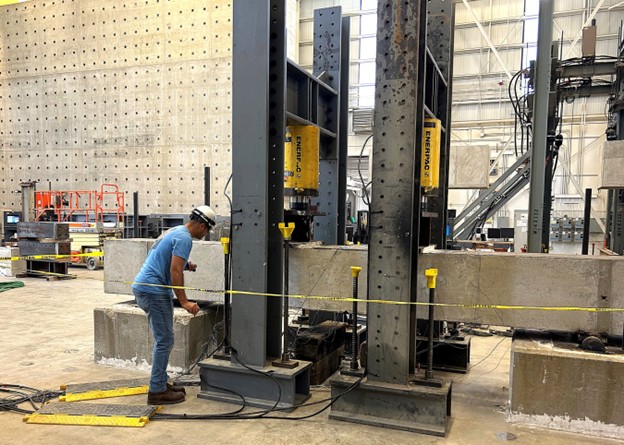
DPSC blocks undergo testing at Purdue University’s Bowen Laboratory. (Photo: Idaho National Laboratory)
Researchers at GE Hitachi Nuclear recently completed a successful test on potential new building blocks made of steel-concrete composite.
ANS President Lisa Marshall (second from left) attended the LAS/ANS Symposium in July 2024. (Photo: LAS/ANS)
The 50th anniversary of the founding of the Latin American Section of the American Nuclear Society is today: April 14, 2025! LAS/ANS was created with the goal of representing the interests of the nuclear professionals of Latin America.
Historic nuclear plant restart could happen in 2025.
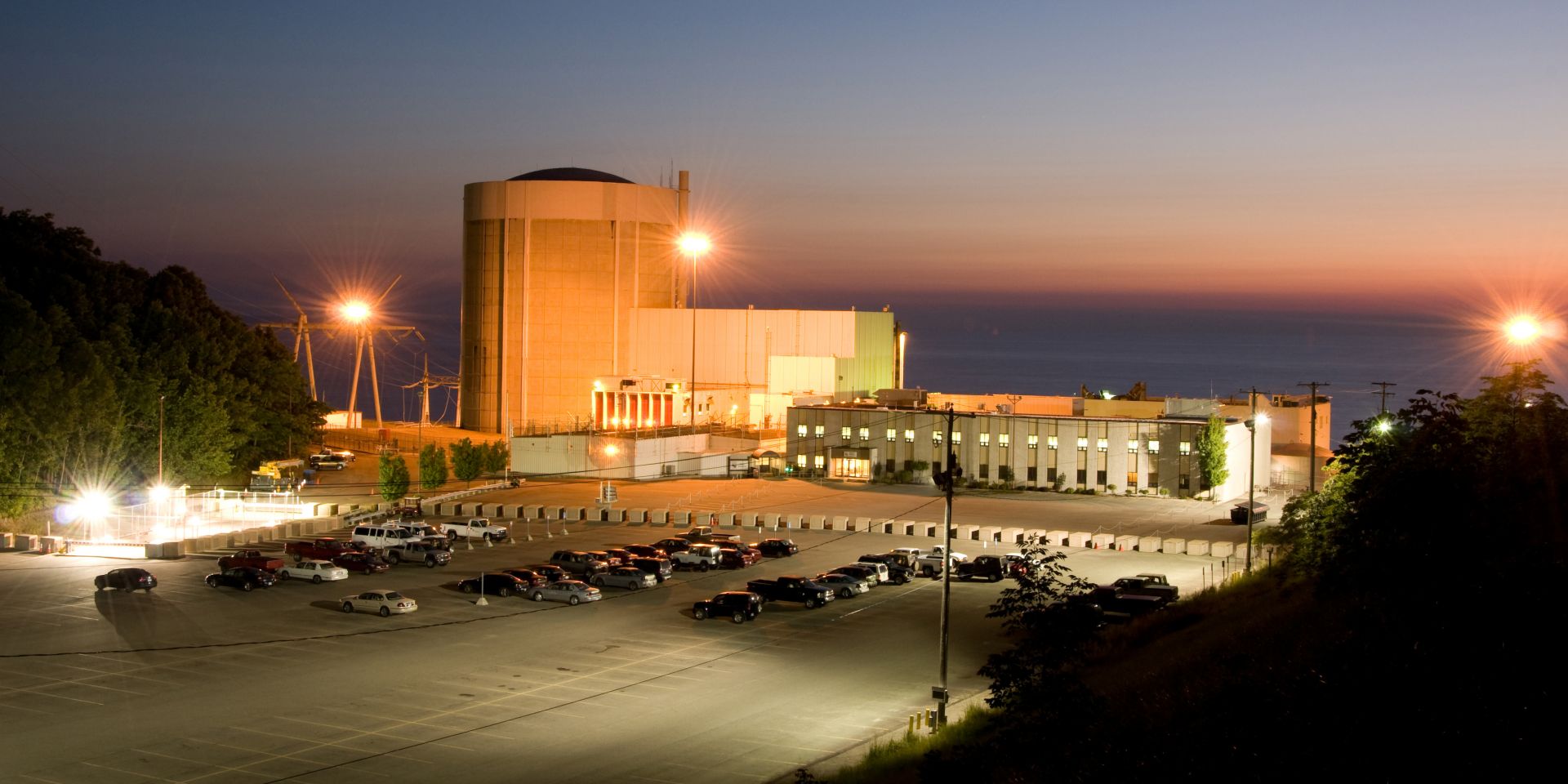
Palisades nuclear power plant on Lake Michigan, at night. (Photo: Holtec)
Mike Mlynarek believes in this expression: “In the end it will be OK; and if it’s not OK, it’s not the end.”
As the site vice president at Palisades nuclear power plant in Covert Township, Mich., Mlynarek is overseeing one of the most exciting projects in the United States nuclear power industry. If all goes according to plan, Holtec’s Palisades plant will be splitting atoms once again by the end of 2025 and become the first U.S. nuclear facility to restart after being slated for decommissioning.
Industry's first lead test assemblies with U-235 enriched up to 6 percent were loaded into Vogtle-2. (Photo: Southern Nuclear)
Southern Nuclear recently loaded nuclear fuel with uranium-235 enriched up to 6 percent—higher than the usual 3–5 percent enrichment—into Vogtle-2 to test it through irradiation.