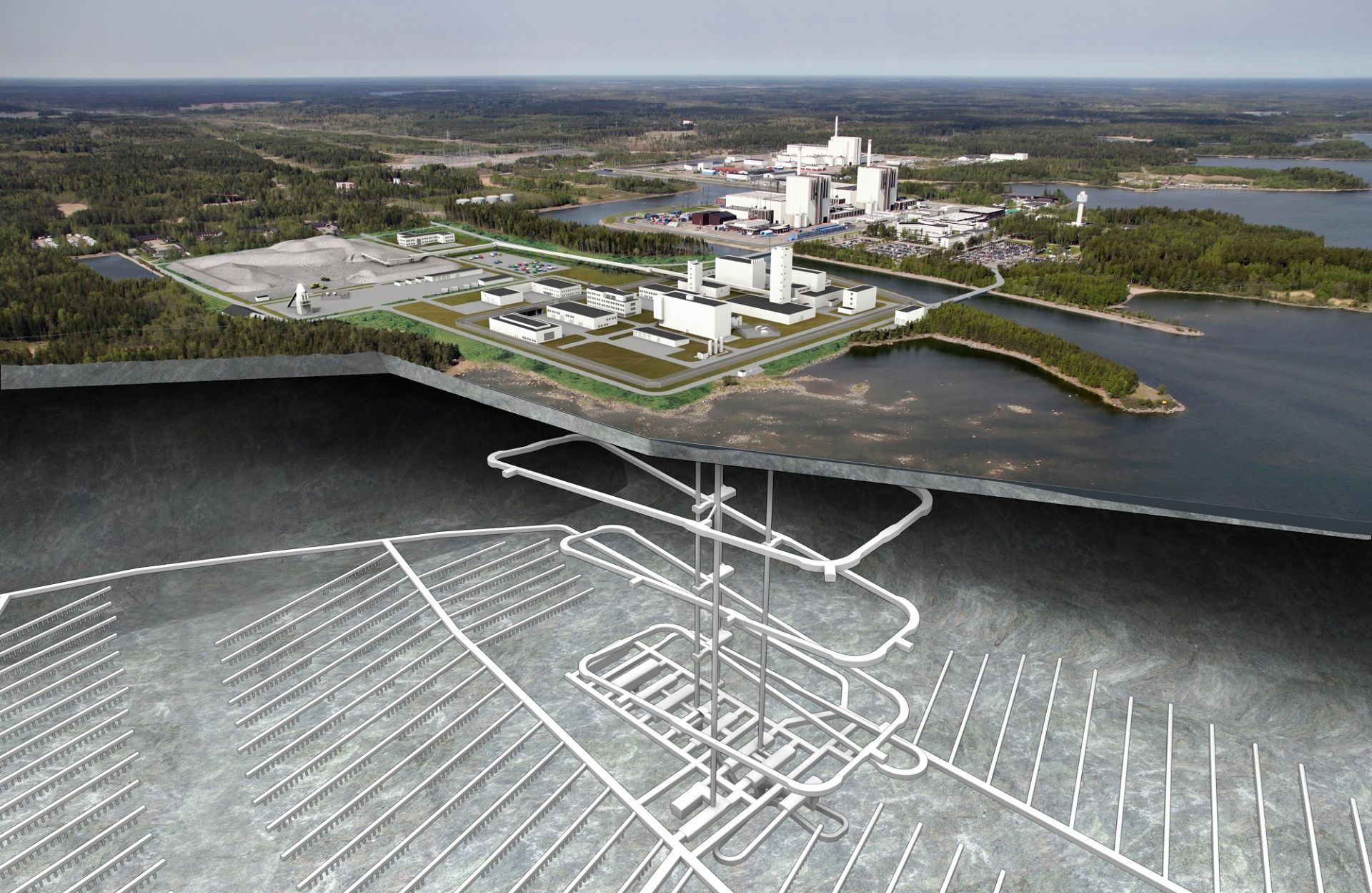
Rendering of the Forsmark geologic repository for spent nuclear fuel in Sweden. (Image: SKB)
Sweden’s Land and Environmental Court has granted the Swedish Nuclear Fuel and Waste Management Company (Svensk Kärnbränslehantering AB, or SKB) an environmental permit to build and operate a geologic repository for the country’s spent nuclear fuel near the Forsmark nuclear power plant, about 86 miles north of Stockholm. The permit also includes the building of a spent fuel encapsulation plant at the central interim storage facility for spent nuclear fuel at Oskarshamn, about 200 miles south of Stockholm.
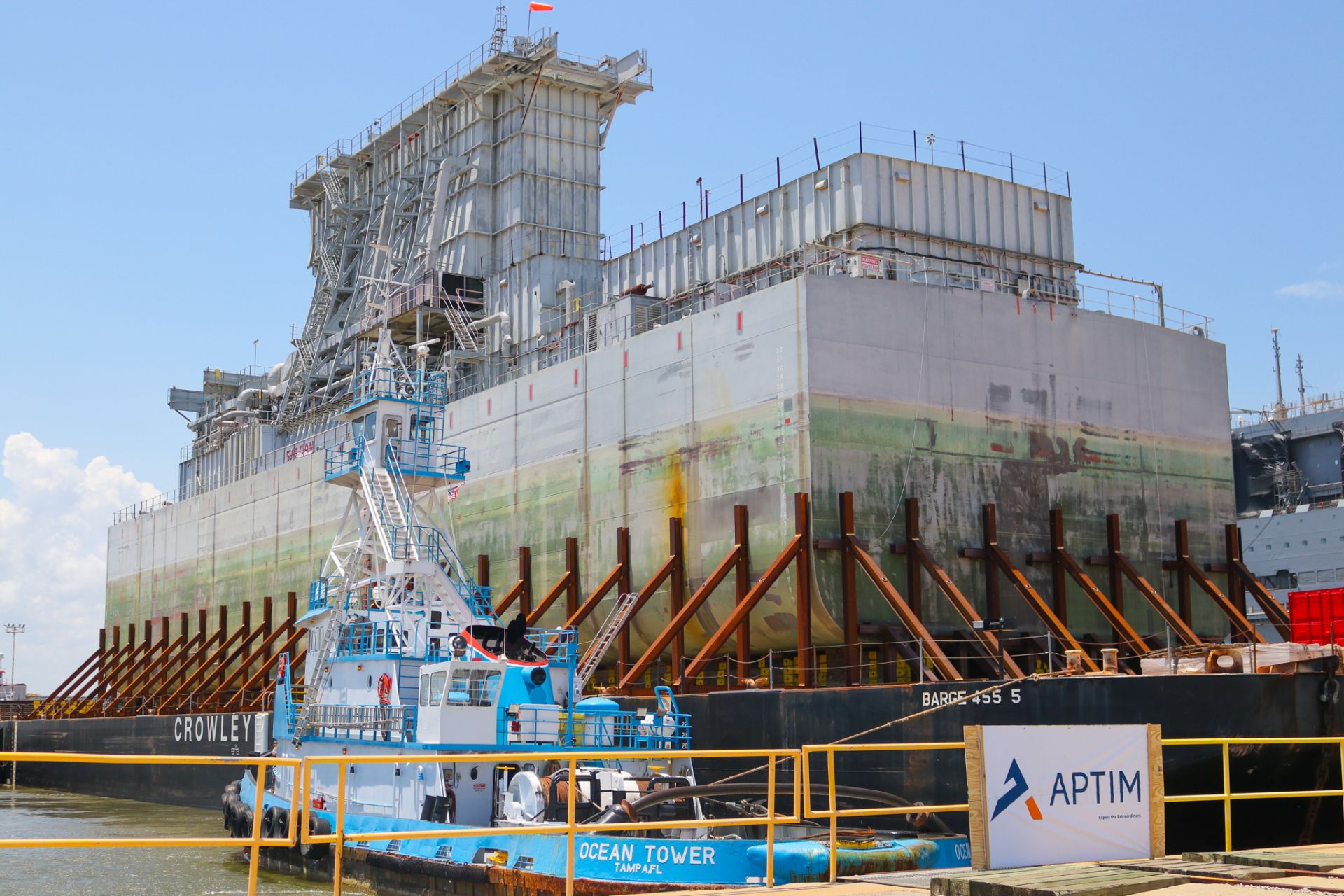
October 29, 2024, 7:03AMRadwaste SolutionsBruce Fox, David Lowe, Jack Reust, and Sean McCutcheon The U.S. Navy’s Surface Ship Support Barge arrives in Mobile, Ala., for demolition after being towed by sea from Virginia. (Photos: APTIM)
The U.S. Navy’s Surface Ship Support Barge, converted in the 1960s from a WWII T2 tanker to a support barge to accept spent nuclear fuel during the refueling of nuclear aircraft carriers, was dismantled and disposed of by the nuclear decommissioning company APTIM as a first-of-its-kind vessel dismantlement project for the Navy. The project was executed under contract with Naval Sea Systems Command; however, regulatory oversight was accomplished through an interagency framework agreement between the U.S. Navy and the Nuclear Regulatory Commission.
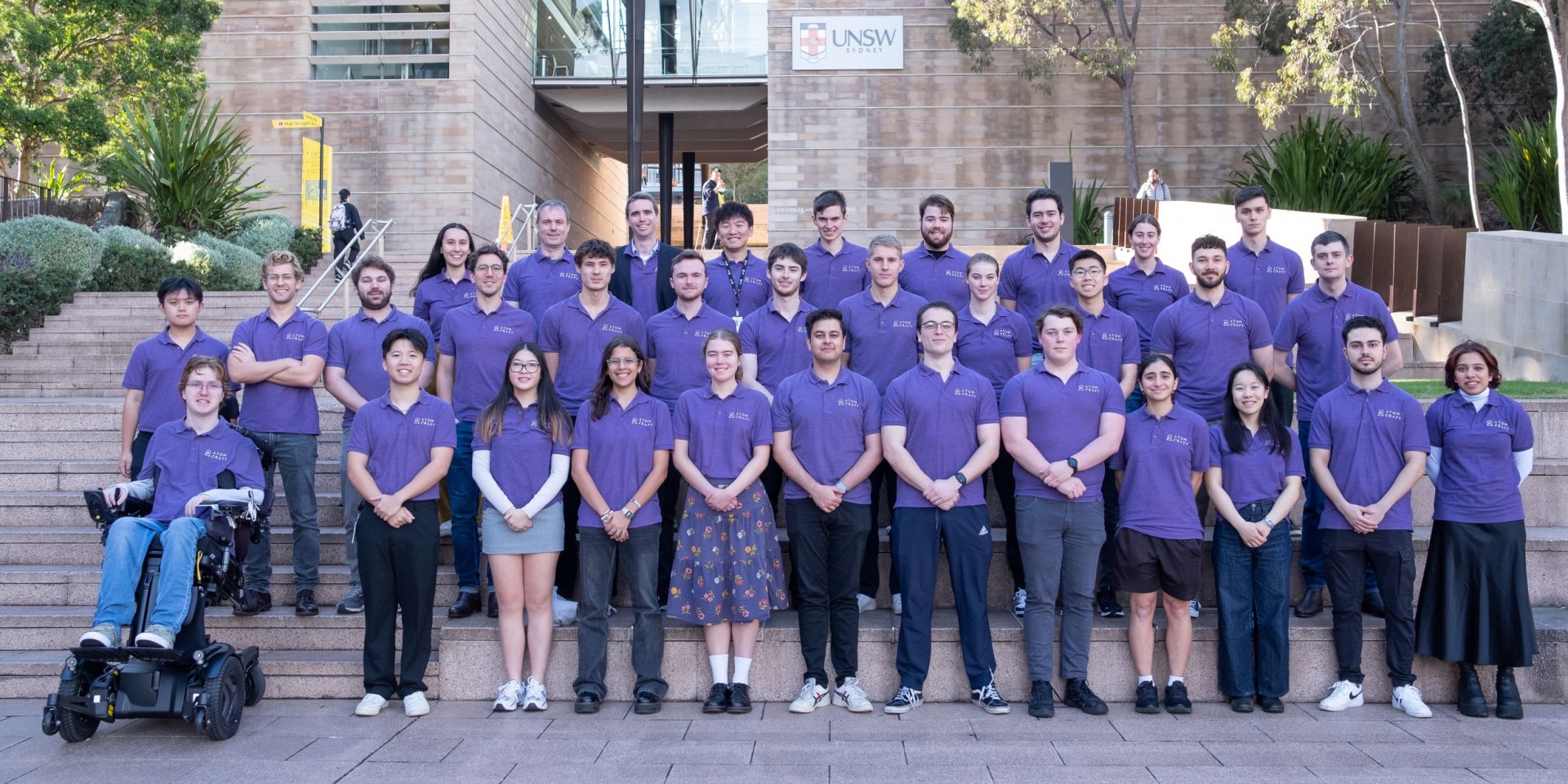
The cross-disciplinary AtomCraft team. (Photo: University of New South Wales)
Commercial nuclear power is illegal in Australia, and it has been since the 1990s. This past June, however, the country’s main opposition party announced plans to build seven commercial nuclear reactors in the 2030s and 2040s on sites presently occupied by aging coal-fired plants—should the party’s Liberal–National Coalition win power in federal elections next year. This statement has reignited a public debate regarding the potential role of nuclear energy in Australia.
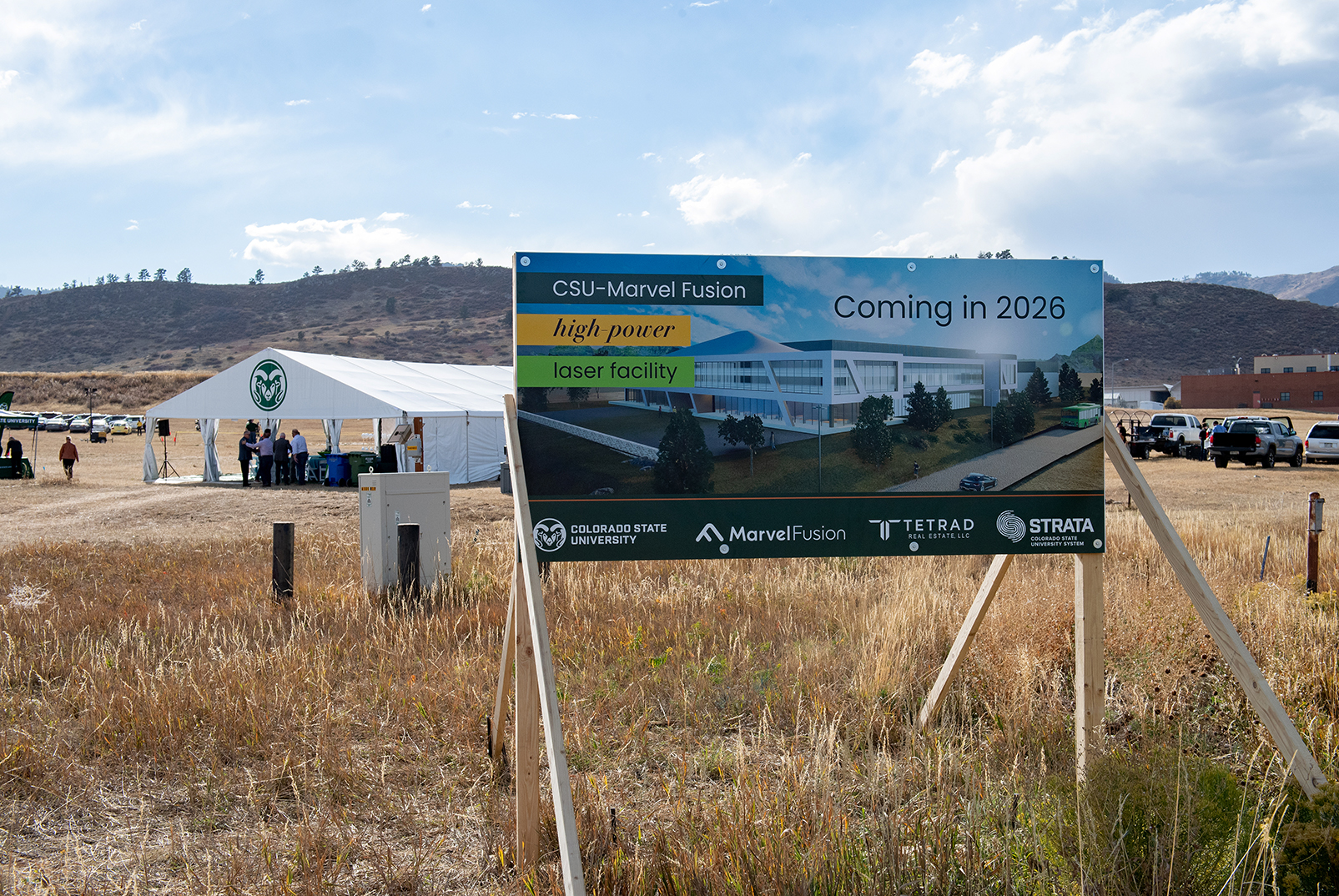
Colorado State University hosted a ground-breaking event for a new laser research facility being built in partnership with Marvel Fusion at the university’s Foothills Campus. (Image: CSU)
In the foothills of the Rocky Mountains on the outskirts of Fort Collins, Colo.—home to Colorado State University—work began this month on a new laser facility funded by a public-private partnership. The private portion is $150 million from Marvel Fusion, announced in August 2023, while $12.5 million—the latest funding for CSU from the Department of Energy’s Office of Fusion Energy Sciences (FES)—will support the new facility as part of LaserNetUS, a laser research network operated by DOE-FES to provide access to laser facilities for multidisciplinary researchers from the United States and abroad.
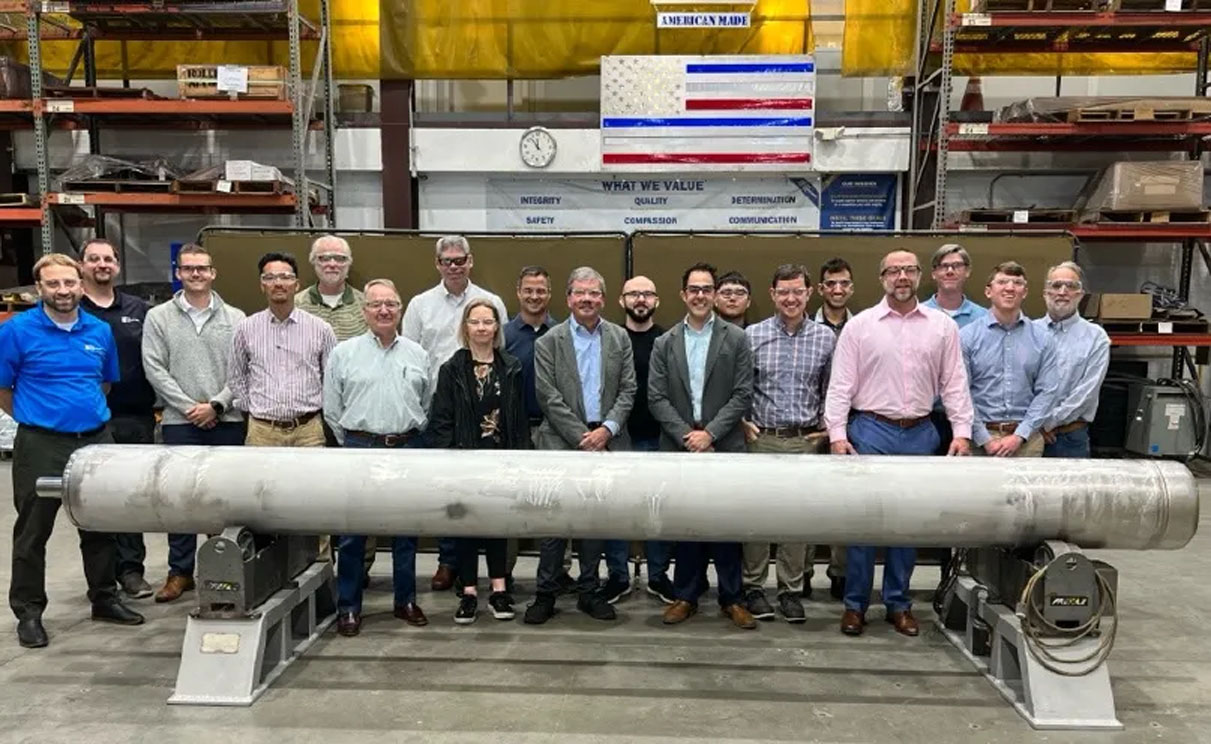
Members of the UPWARDS technical advisory committee stand in front of a prototype universal canister system. (Photo: Deep Isolation)
Deep Isolation announced that it hosted its third technical workshop for the UPWARDS project, a Department of Energy Advanced Research Projects Agency-Energy (ARPA-E) initiative aimed at developing a universal canister system (UCS) for the disposal of radioactive waste streams from advanced reactors. The workshop, held at R-V Industries in Honey Brook, Pa., focused on the large-scale manufacturing and commercialization of the UCS.
October 25, 2024, 2:58PMNuclear NewsGeoffrey Campbell and Christopher Koehler The clevis bolt replacement team working in parallel off of the refueling bridge. This team is working directly on the reactor vessel clevis with a first-of-a-kind docking station. (Photo: Westinghouse)
Unit 2 at the Prairie Island nuclear power plant near Red Wing, Minn., underwent an outage in fall 2023, which included extensive work on the reactor vessel using a novel approach to replace baffle-former bolts and lower radial clevis insert bolts. The work relied on extensive analysis beforehand to determine which bolts to replace such that only the new bolts were structurally credited for performance of their safety function. This proactive approach eliminated the need for costly contingencies associated with inspections.
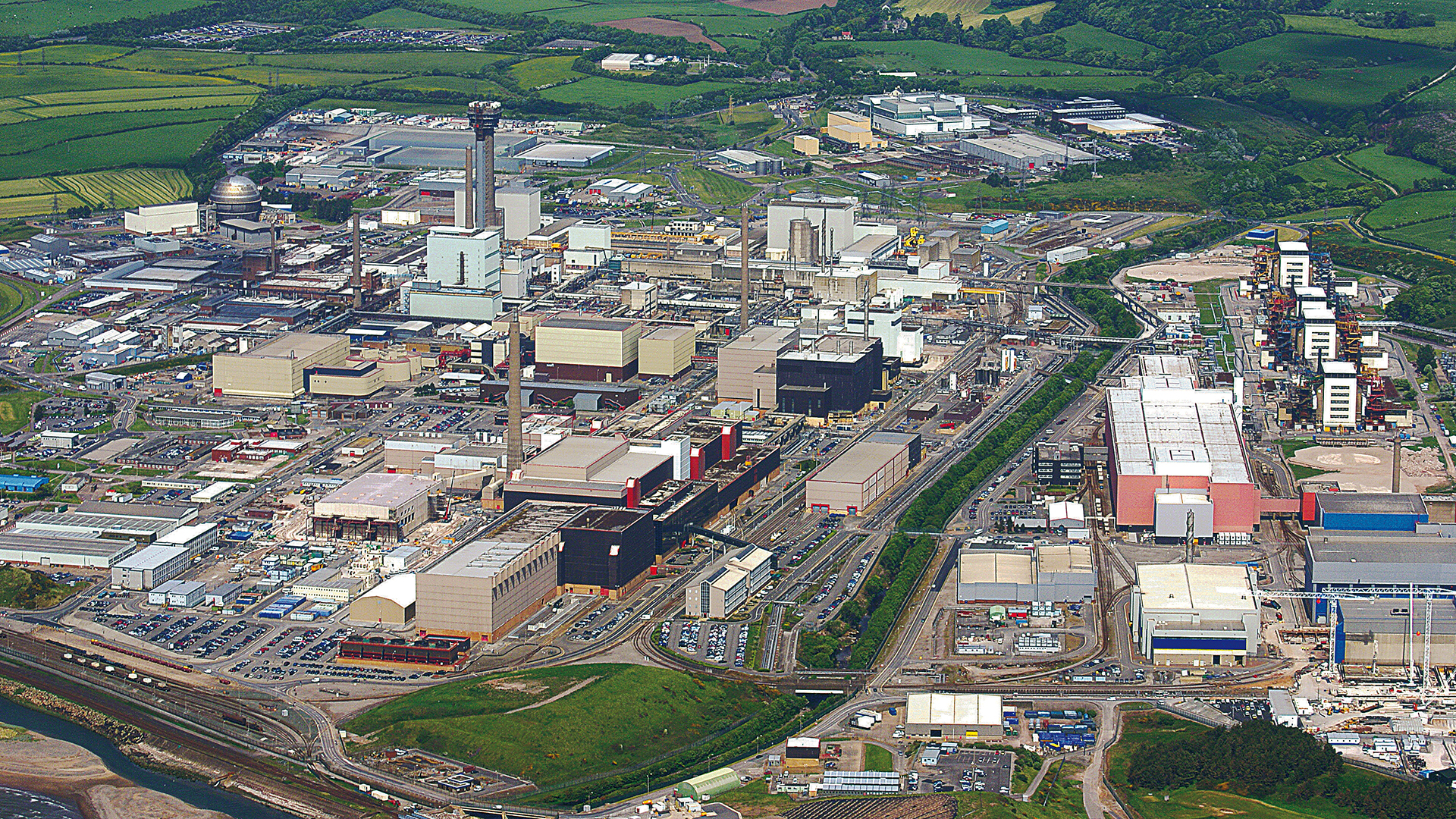
The Sellafield nuclear site in Cumbria, England. (Photo: NEA/OECD)
Despite progress made over the past years, the United Kingdom’s Nuclear Decommissioning Authority (NDA) has not seen an adequate return on investment in cleaning up the Sellafield nuclear site on England’s Cumbria coast, according to a new report by the U.K.’s National Audit Office, which scrutinizes government spending.
Framatome’s GAIA Protect EATF assembly. (Photo: Framatome)
Framatome’s enhanced accident tolerant fuel assemblies recently completed a third 18-month fuel cycle at Southern Nuclear’s Vogtle-2 plant—the first of this type of fuel to reach this milestone in the U.S., the company said.
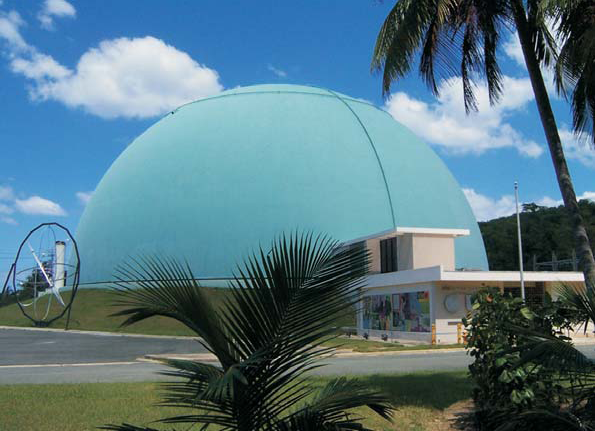
The BONUS nuclear power plant. (Photo: DOE)
An article on the Huffington Post examines the prospects for re-establishing nuclear energy in Puerto Rico, uncovering a mix of positive and negative attitudes toward nuclear power in the U.S. territory.
Officials of the ABS and INL gathered at a forum, where rules for floating nuclear power plants were unveiled. (Photo: INL)
A comprehensive set of rules and guidelines for floating nuclear power plants, Requirements for Nuclear Power Systems for Marine and Offshore Applications, has been released by the American Bureau of Shipping (ABS). According to the document, which, according to ABS, is the first of its kind for floating power plants, the rules and guidelines have been “developed for classification requirements specific to design, construction, and survey of vessels fitted with nuclear power systems whose generated power is transferred or distributed to onboard industrial or adjacent facilities.”
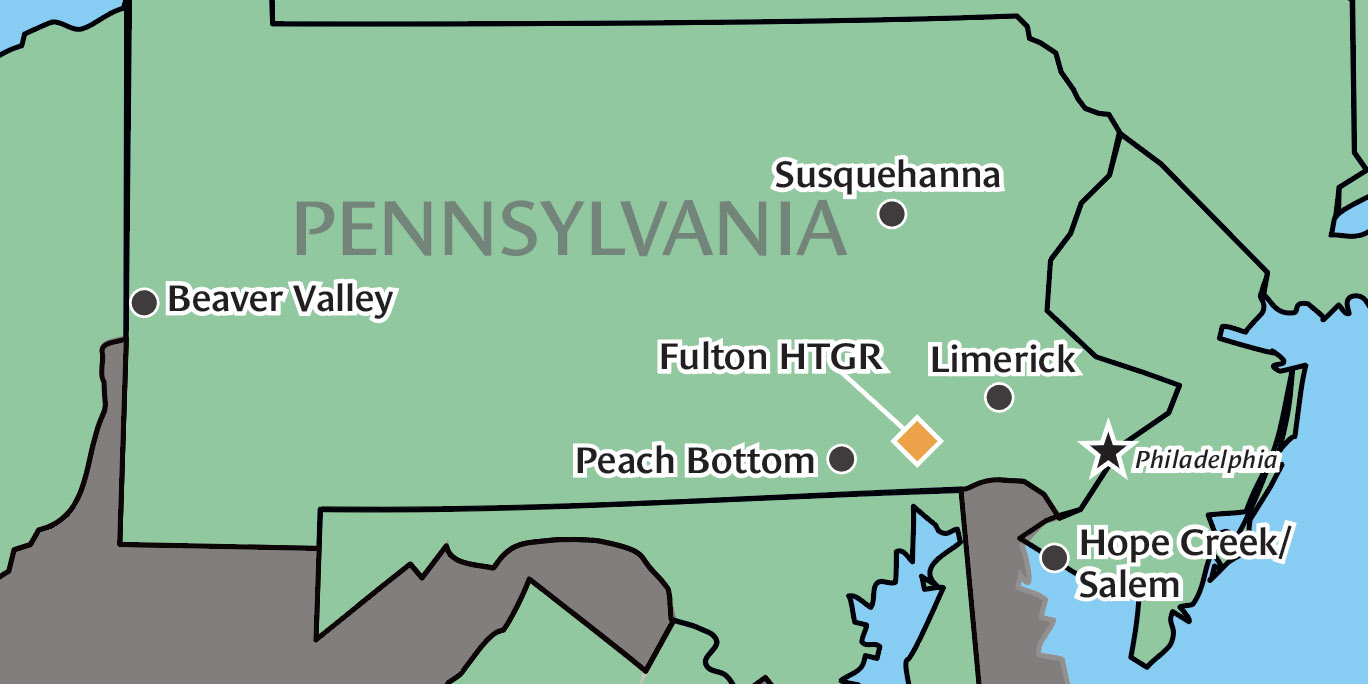
The once-proposed location of the Fulton HTGR, in relation to modern-day operating nuclear power plants.
Fulton Station was to be a two-unit high-temperature gas-cooled reactor that was originally planned to start commercial operation in 1981 for Unit 1 and in 1983 for Unit 2. Each reactor was to provide 1,160 MWe of power. The nuclear steam supply system (NSSS) and fuel were to be developed by General Atomics (GA), and engineering firm Stone & Webster was charged with handling the construction. The Philadelphia Electric Company (PECO) had big plans for Fulton Station, but ultimately, the plant was never built.











 The 2024 edition of
The 2024 edition of 

.png)