Micro-scale nuclear prototype showcased in D.C.
Energy startup Last Energy took an opportunity last week to showcase a prototype of its micro-scale nuclear reactor outside a convention center in Washington, D.C.

Energy startup Last Energy took an opportunity last week to showcase a prototype of its micro-scale nuclear reactor outside a convention center in Washington, D.C.

Sean Doherty
The most important thing the nuclear community can do to support space nuclear applications is the same thing we must focus on for terrestrial nuclear science: developing the trust of the American public.
Americans are widely supportive of NASA, and space has long captivated our imaginations. Recently, the publicity surrounding the new U.S. Space Force and the popularity of commercial rocket launches have drawn the public eye skyward. We don’t need to convince people that space is important and exciting, but we do have a long way to go in promoting nuclear power to the public.

The mission of the Department of Energy’s Office of River Protection (ORP) is to complete the safe cleanup of waste resulting from decades of nuclear weapons development. One of the most technologically challenging responsibilities is the safe disposition of approximately 56 million gallons of radioactive waste historically stored in 177 tanks at the Hanford Site in Washington state.
ORP has a clear incentive to reduce the overall mission duration and cost. One pathway is to develop and deploy innovative technical solutions that can advance baseline flow sheets toward higher efficiency operations while reducing identified risks without compromising safety. Vitrification is the baseline process that will convert both high-level and low-level radioactive waste at Hanford into a stable glass waste form for long-term storage and disposal.
Although vitrification is a mature technology, there are key areas where technology can further reduce operational risks, advance baseline processes to maximize waste throughput, and provide the underpinning to enhance operational flexibility; all steps in reducing mission duration and cost.

The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management has issued a request for qualifications for interested parties and prospective offerors looking to enter into a realty agreement for carbon-pollution-free electricity (CFE) projects at the department’s Waste Isolation Pilot Plant site in southeastern New Mexico.
Investment banking on higher demand for SMR and large nuclear reactors
BWX Technologies announced today plans to expand and add advanced manufacturing equipment to its manufacturing plant in Cambridge, Ontario, Canada.
A $36.3 million USD ($50M CAD) expansion will increase the plant’s size by 25 percent—to 280,000 square feet—and another $21.7 million USD ($30M CAD) will be spent on new equipment to increase and accelerate its output of large nuclear components. The investment will increase capacity and create more than 200 long-term jobs for skilled workers, engineers, and support staff, according to the company.

Framatome and Korea Hydro & Nuclear Power (KHNP) have announced the signing of a memorandum of understanding to explore the possibility of producing the medical isotope lutetium-177 at KHNP’s Wolsong nuclear power plant in South Korea. The companies also will investigate the feasibility of using the plant to support Korean production of medical radioisotopes in the future.

French nuclear developer Framatome is slated to deliver key equipment for Sizewell C Ltd.’s two large reactors planned for the United Kingdom’s Suffolk coast.
The agreement, reportedly worth multiple billions of euros, was announced this week and will involve Framatome from the design phase until commissioning. The company also agreed to a long-term fuel supply deal. Framatome is 80.5 percent owned by France’s EDF and 19.5 percent owned by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries.

The Office of Nuclear Energy is awarding $59.7 million to 25 U.S. colleges and universities, two national laboratories, and one industry organization to support nuclear energy research and development and provide access to world-class research facilities, the Department of Energy announced on April 15.
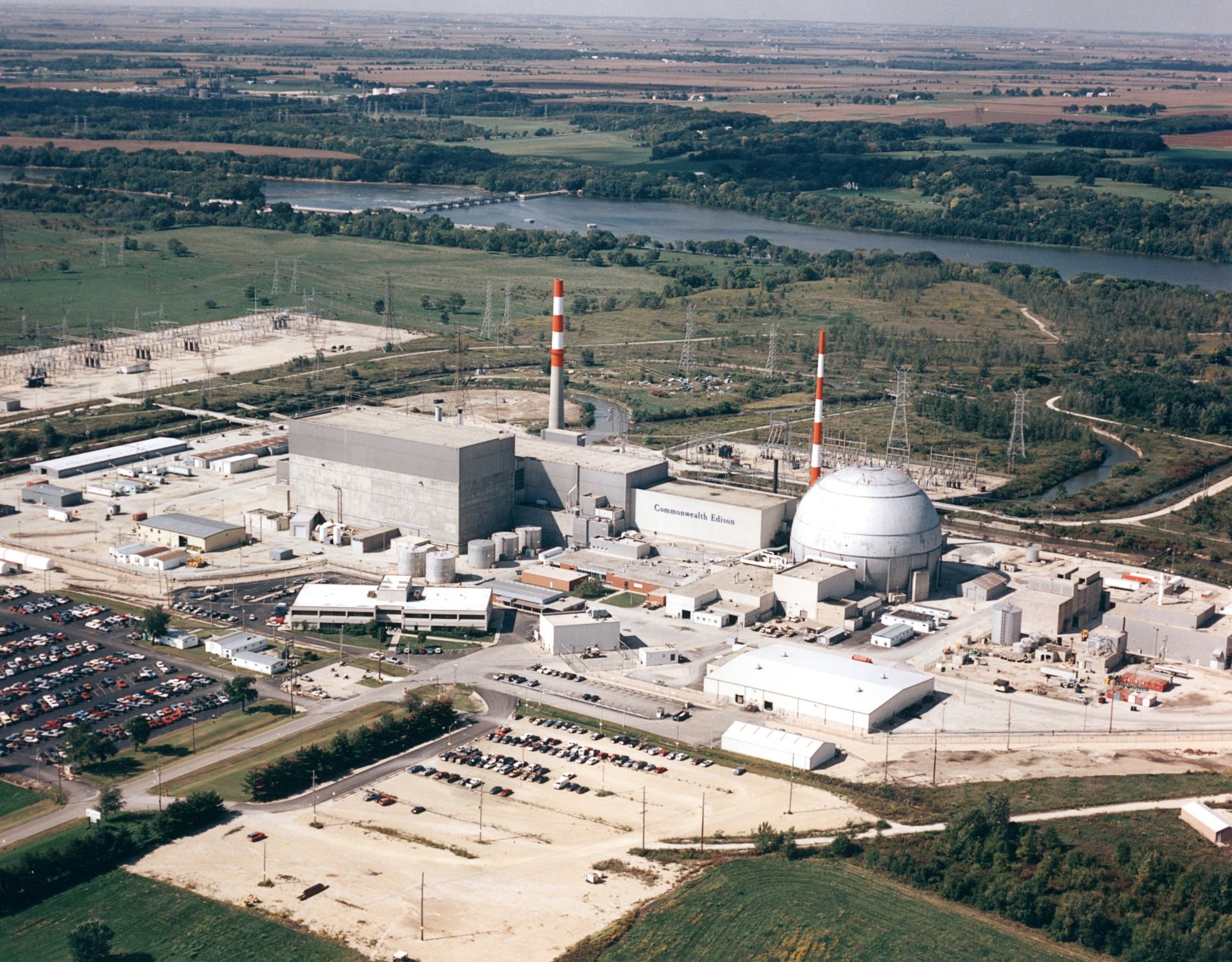

Constellation Energy has filed with the Nuclear Regulatory Commission for a subsequent license renewal for its Dresden nuclear power plant in Illinois. The extension would allow Dresden to run through 2051.
The filing begins a comprehensive, multiyear review by the NRC. Unit 2 is currently licensed to operate through 2029 and Unit 3 through 2031. The facility’s license was first renewed by the NRC in 2004.
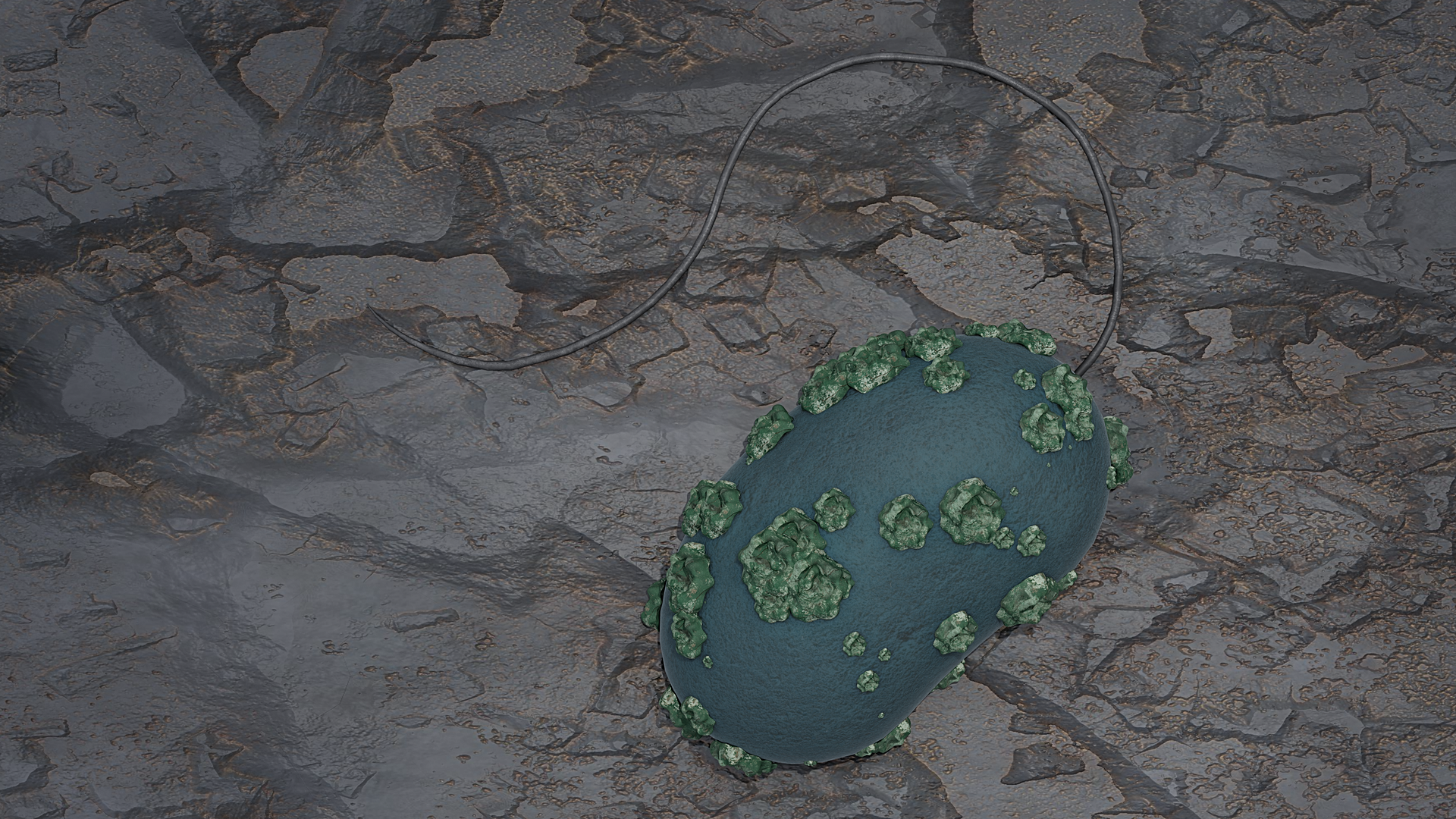
Researchers at the Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf (HZDR) research laboratory in Germany have investigated a microorganism capable of transforming water-soluble hexavalent uranium [U(VI)] to the less-mobile tetravalent uranium [U(IV)]. The researchers found that the sulfate-reducing bacterium Desulfosporosinus hippei, a relative of naturally occurring microorganisms present in clay rock and bentonite, showed a relatively fast removal of uranium from clay pore water.

Crane
Exelon announced that Chris Crane, the company’s former chief executive, passed away on Saturday in Chicago at the age of 65.
Crane served as the company’s president and CEO from 2012 until his retirement in December 2022. During his tenure, he steered the energy company through several transformational milestones, including the successful mergers with Constellation Energy in 2012 and Pepco Holdings in 2016, creating the largest utility business by customer count in the United States.
In 2022, with the spin-off of Constellation as the generation and retail side of energy business (with the largest U.S. nuclear fleet), Crane led the creation of a stand-alone transmission and delivery energy company.
A recent drone attack at Ukraine’s Zaporizhzhia nuclear power plant prompted an emergency meeting by the International Atomic Energy Agency Board of Governors, during which the agency again called for the immediate removal of Russian military and personnel from the site.
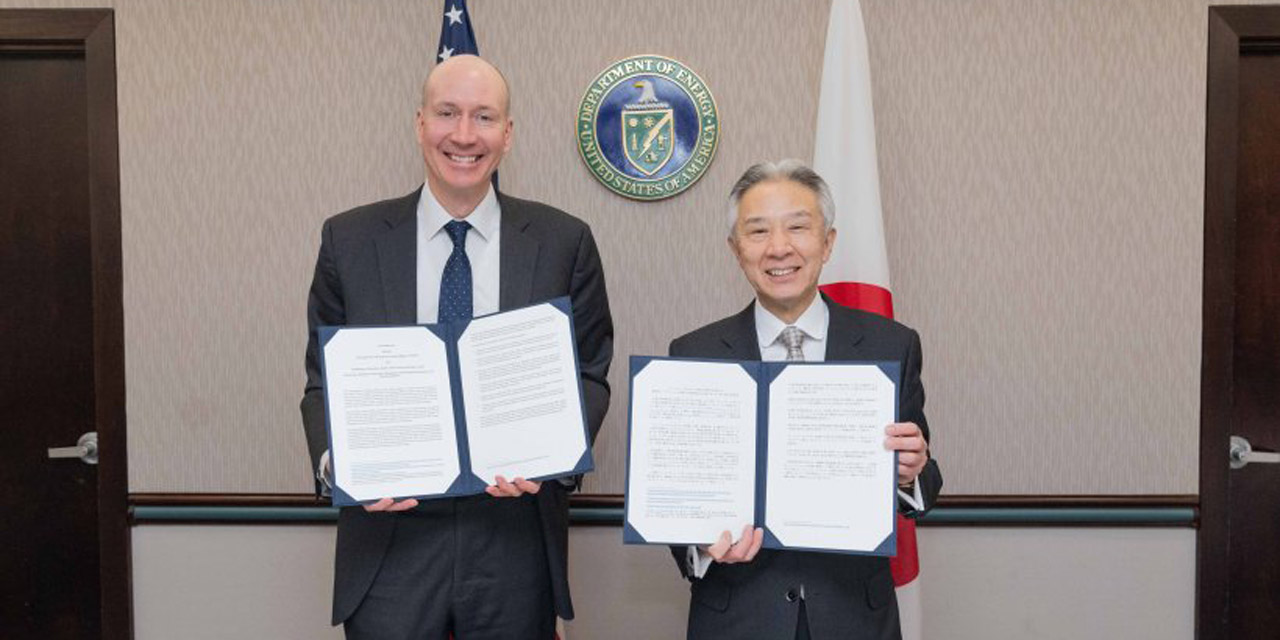

During a state visit to the White House by Japanese prime minister Fumio Kishida on April 10, the Department of Energy announced that U.S. and Japanese agencies had cooperated to remove all high-enriched uranium (HEU) from the Japan Materials Testing Reactor Critical Assembly (JMTRC) of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) two years ahead of schedule.
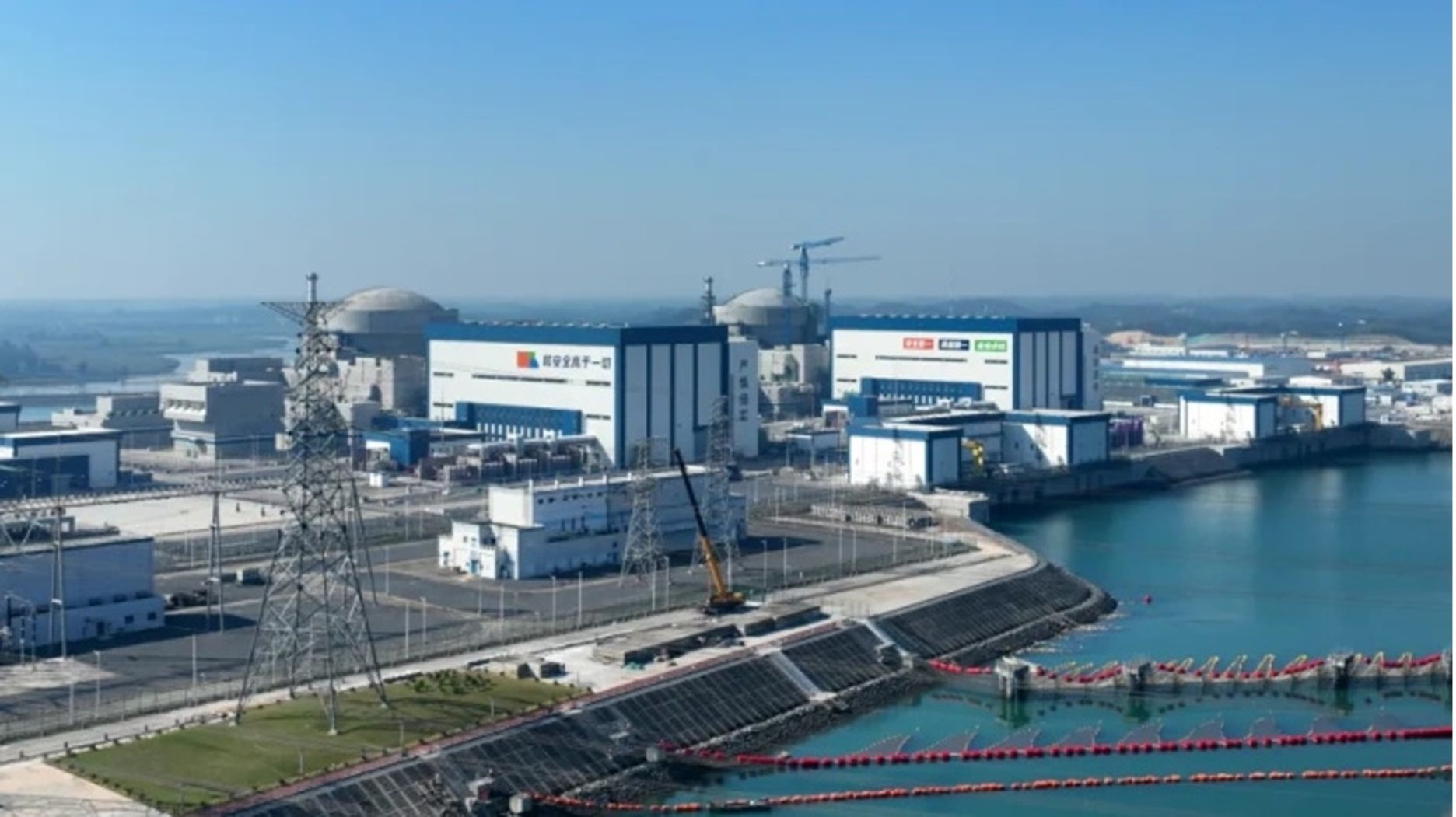

China’s second demonstration reactor—Fangchenggang Unit 4—connected to the grid on April 9, China General Nuclear Power Group has announced. Located in the autonomous region of Guangxi, the reactor achieved first criticality April 3.

In discussing how to counter global warming, it’s pretty easy to argue that nuclear should be the major electricity source and heat producer to replace fossil fuels. At 6 grams per kilowatt-hour, it has the lowest carbon emissions of any energy source, according to the United Nations, and is objectively the safest form of energy for humans and the environment alike, again from a recent UN report.
Spring marks the passing of the torch for American Nuclear Society leadership. During this election cycle, ANS members voted for the newest vice president/president-elect, four members-at-large for the Board of Directors, and one Young Member director for the Board. New professional division leadership was also decided on in the election, which opened on February 20 and closed on April 9. About 22 percent of eligible members voted—a similar turnout to last year.
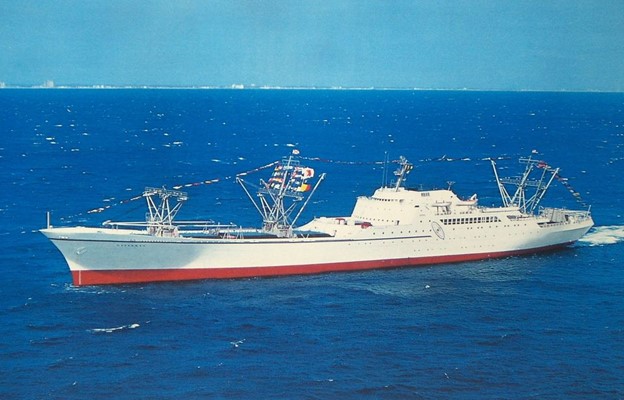

The Nuclear Regulatory Commission will hold a public meeting on May 8 to discuss the license termination process for the retired nuclear-powered merchant ship, the NS Savannah. During the meeting, NRC staff will discuss the license termination process and receive public comments on the remaining cleanup activities described in the license termination plan for the historic ship, which may see a second life as a floating museum.
Is a new generic repository standard on the horizon?
Funding in President Biden’s proposed fiscal year 2025 budget may signal movement toward the promulgation of a new generic Environmental Protection Agency standard for high-level nuclear waste repositories in the United States.

Huff
After serving two years as the Department of Energy’s assistant secretary for Nuclear Energy, Kathryn Huff will vacate that position on May 3 and return to teaching. Huff had started at the DOE in May 2021, serving for one year as the principal deputy assistant secretary for Nuclear Energy.
“Serving in this capacity has been an unparalleled privilege, and I’m immensely grateful for the opportunity to have worked alongside you--the dedicated and talented public servants in Nuclear Energy, in DOE, and across the Biden-Harris Administration,” Huff wrote in an email announcement to colleagues last week. “I chose this timing to enable the smoothest transition back to my professorship at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign where my beloved research, students, husband, and dog await.”
Clean Core Thorium Energy (Clean Core) has announced that its ANEEL fuel is ready to begin irradiation testing and qualification at Idaho National Laboratory. The fuel, made of thorium and HALEU, was developed by Clean Core for use in pressurized heavy water reactors, including CANDU (Canadian deuterium-uranium) reactors. Irradiation of the fuel samples in INL’s Advanced Test Reactor (ATR) is set to begin this month.