A schematic illustration of a deep borehole repository assuming disposal into a bedrock. (Image: Sandia National Laboratories via IAEA)
The International Atomic Energy Agency is launching a new Coordinated Research Project (CRP) to increase international knowledge and drive progress toward testing deep borehole disposal for intermediate- and high-level radioactive waste.
PCAT is prepared for transport from INL to Pennsylvania for testing. (Photo: INL)
As global concerns about climate change and energy sustainability intensify, the need for cleaner and more efficient energy sources is more critical than ever. Nuclear power consistently emerges as an important part of the solution, driving the development of innovative technologies. While numerous fission technologies were built and proven in the early days of nuclear energy, times and regulations have changed. Between the 1950s and mid-1970s, Idaho National Laboratory built 52 reactors—then paused for five decades. Can this nation return to the frontier once again, embarking on new fission technologies? With a mature regulatory environment and increasing public support, how quickly can a new non–light water system be deployed in modern times?
A new IAEA peer review service demonstrates the proper management of disused sealed radioactive sources. (Photos: IAEA [left] and TINT [right])
The International Atomic Energy Agency has carried out the first mission of its Disused Sealed Radioactive Sources Technical Centre peer review service, or DSRS TeC, at the Thailand Institute of Nuclear Technology (TINT) in Bangkok. Held July 18–21, the inaugural mission was supported by funds from the United States.
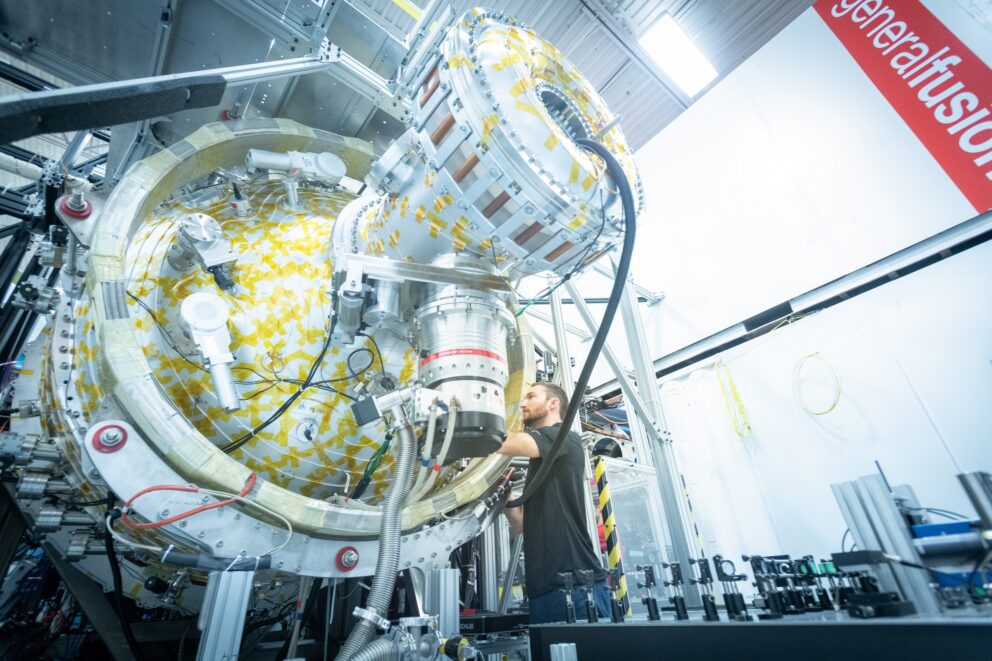
General Fusion’s current plasma injector (PI3) is the 25th in a series of prototypes developed by the company. (Photo: General Fusion)
General Fusion announced on August 9 that it will build a fusion machine called Lawson Machine 26 (LM26) at the company’s new headquarters in the city of Richmond, British Columbia, near Vancouver. The machine is intended to achieve fusion conditions of over 100 million degrees Celsius by 2025 and progress toward scientific breakeven by 2026 to support the company’s vision of commercial fusion energy by the early to mid-2030s.
K-9 officer Dee and her partner, Patrol Officer Manny Rodriguez, during a training exercise. (Photo: DOE )
The Department of Energy’s Hanford Site has introduced its newest team members, Dee and Freda, two highly skilled explosive-detecting K-9 officers. The police dogs will work with Richland Operations Office contractor Hanford Mission Integration Solutions to help ensure the safety and security of the legacy nuclear reservation near Richland, Wash.
The Oskarshamn nuclear power plant in Sweden. (Photo: Daniel Kihlgren)
The Swedish Radiation Safety Authority (SSM) has issued a final report to the Swedish government regarding its investigation into how the regulatory framework for the country’s nuclear power might be improved.
SRS reached a landmark achievement with the placement of 2,000 double-stacked canisters of vitrified HLW. (Image: DOE)
To expand interim storage of vitrified high-level radioactive waste at the Savannah River Site, the Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management and its liquid waste contractor Savannah River Mission Completion (SRMC) have double stacked 2,000 canisters in one of the site's two glass waste storage buildings (GWSB). GWSB 1 consists of a below-grade, seismically qualified concrete storage location containing support frames for the vertical storage of 2,262 10-foot-tall canisters.
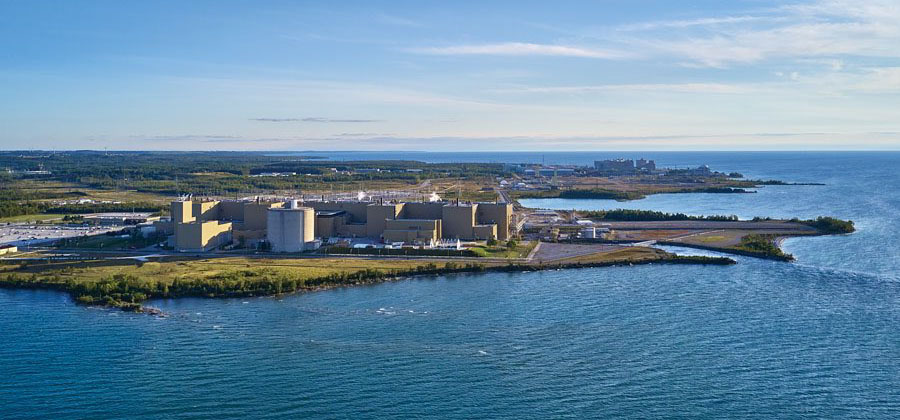
The Bruce nuclear power plant in Ontario, Canada. (Photo: Bruce Power)
Unit 6 at the Bruce nuclear power plant in Kincardine, Ontario, achieved a sustained fission chain reaction over the weekend—a key step in returning the 817-MWe CANDU reactor to commercial operation, Bruce Power announced yesterday.
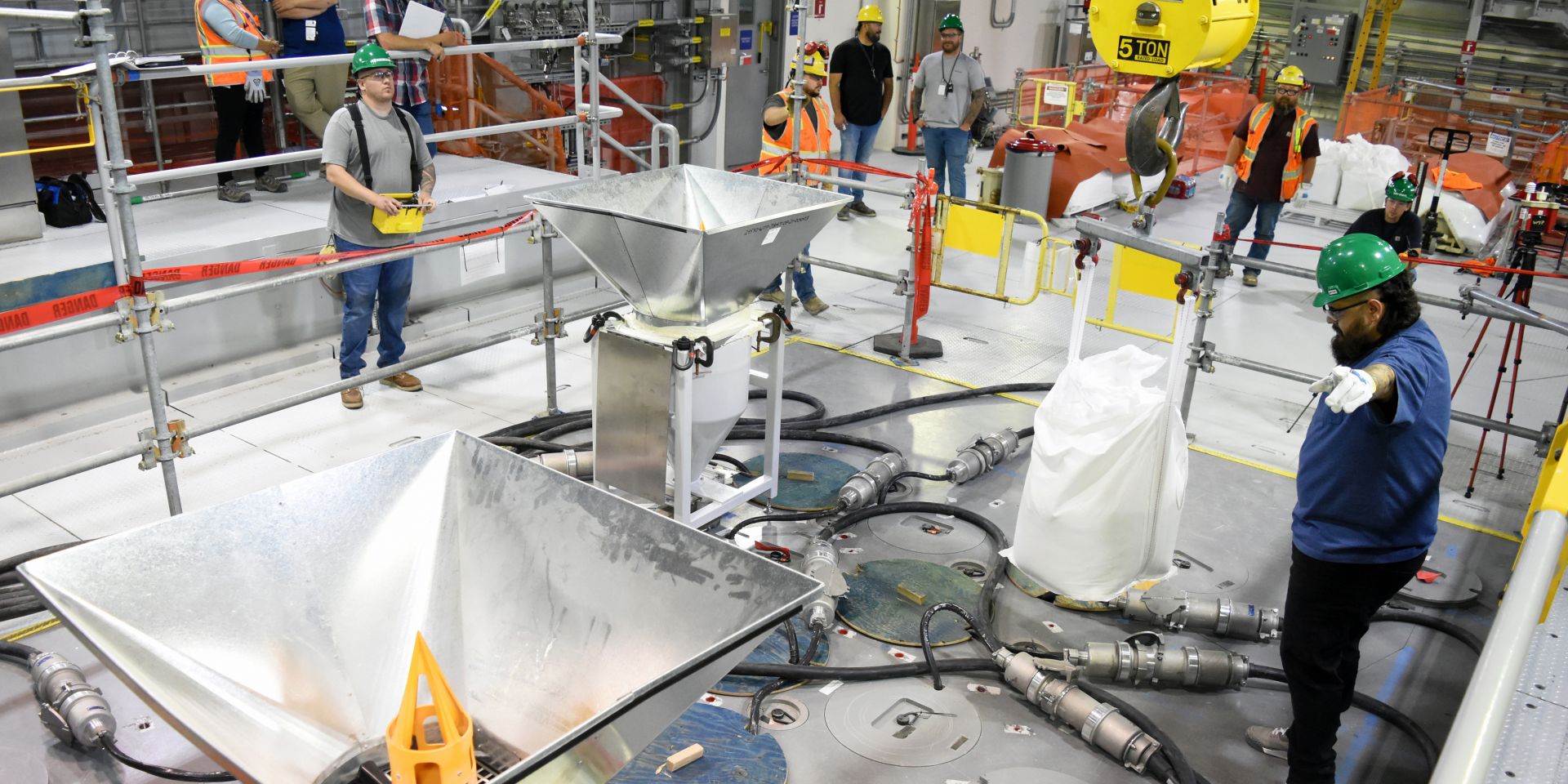
A 300-pound bag of frit is in position to be poured into the melter at Hanford’s LAW Facility. (Photo: Bechtel National)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management announced that the first batches of glass-forming beads, called frit, were poured last week into a melter at the Hanford Site’s Waste Treatment and Immobilization Plant (WTP), also known as the Vit Plant. The melter, which has been heated to 2,100ºF, will be used to immobilize Hanford’s radioactive and chemical tank waste, turning it into a stable glass form through vitrification.
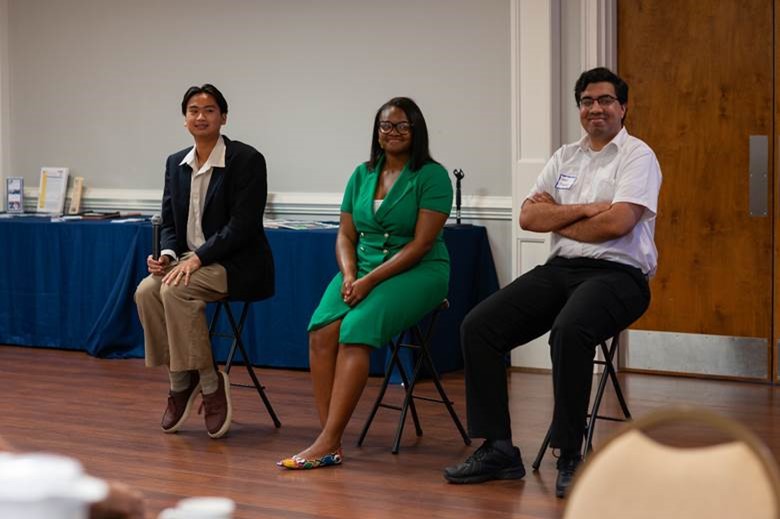
From left, interns Justin Vu Le (SRMC), Zaire Shaw (SRNL), and Neal Thakkar (SRNS) were the featured speakers at an Up & Atom breakfast. (Photo: CNTA)
Three college interns from the Savannah River Site were the keynote speakers at a recent Up & Atom Breakfast hosted by Citizens for Nuclear Technology Awareness (CNTA). The breakfast was held at Newberry Hall in Aiken, S.C.
Some of the participants of the recent SRNL-Hanford Analytical Knowledge Sharing Workshop pause for a photo. (Photo: DOE)





 The
The 



 (002) 2x1.jpg)





