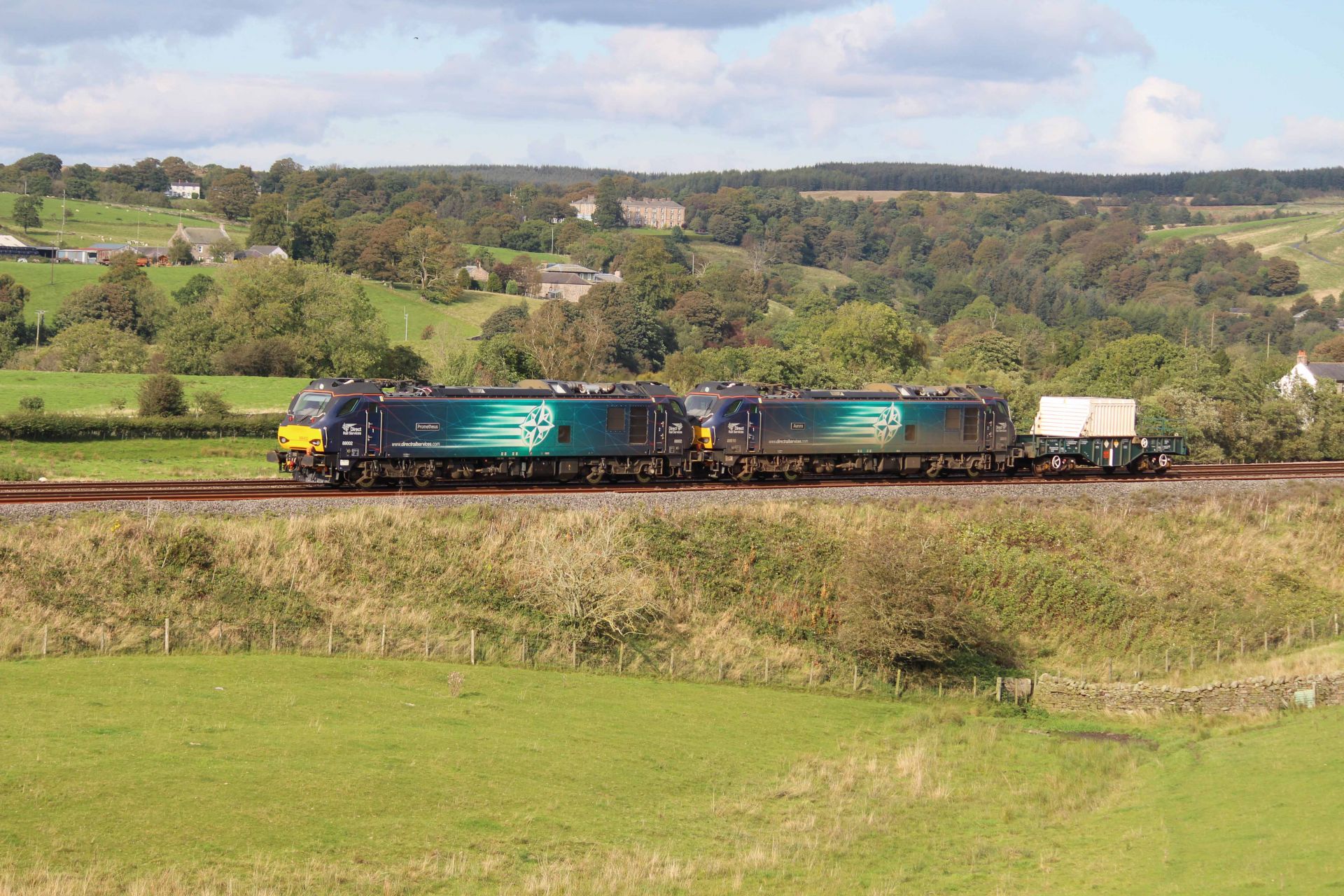
Two British Class 88 locomotives transport a nuclear waste flask wagon across Great Britain. (Photos: NTS)
Since its formation in 2005, the United Kingdom’s Nuclear Decommissioning Authority (NDA) has been tasked with ensuring that the U.K.’s nuclear legacy sites are decommissioned and cleaned up safely, securely, cost-effectively, and in ways that protect the people and the environment.
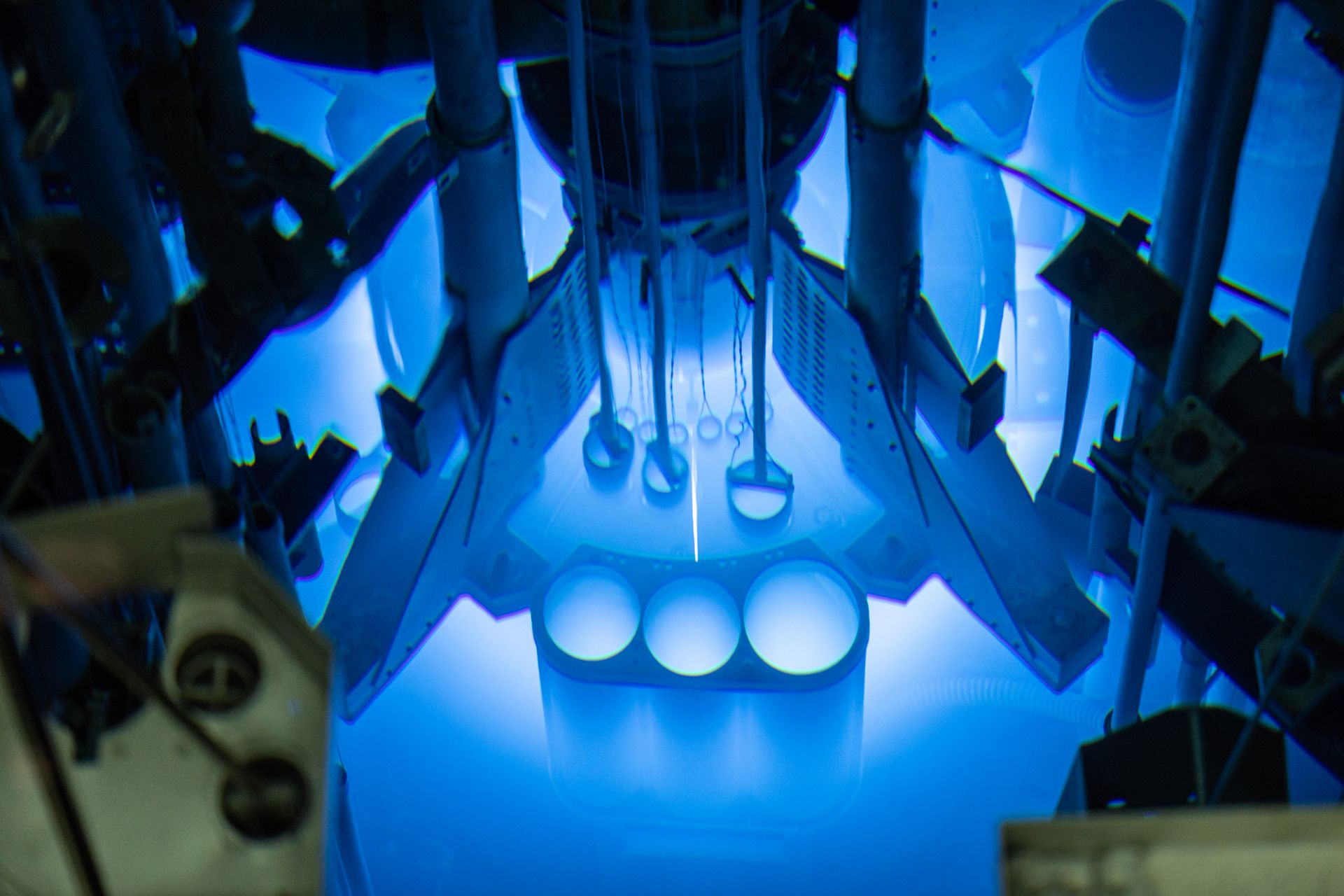
Situated in a 30-foot-deep pool, the 10 MW core of MURR is used to irradiate samples and produce isotopes for medical radiopharmaceuticals and research. (Photo: University of Missouri)
The University of Missouri intends to build a new, larger research reactor to produce medical radioisotopes, announcing that it intends to issue a request for qualification/request for proposal (RFQ/RFP) in April to solicit interest from qualified parties to provide preliminary designs and industry partnerships for the new reactor project, called NextGen MURR.
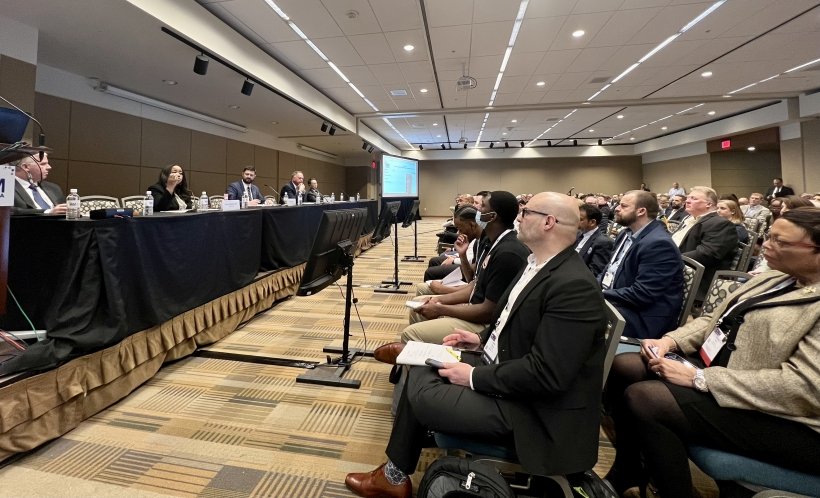
Panelists speak at the 2023 Waste Management Symposia “Hot Topics” session. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (EM) has made great progress in accomplishing its cleanup of legacy radioactive waste but has yet to tackle its most challenging tasks, including the treatment of liquid tank waste at the Hanford, Idaho, and Savannah River sites. That was the consensus of the DOE-EM officials who took part in a panel session of the 2023 Waste Management Symposia, held February 26–March 2 in Phoenix, Ariz.
A technical collaboration agreement was signed by (seated from left) Jay Wileman, GEH; Jeff Lyash, TVA; Ken Hartwick, OPG; and Rafał Kasprów, SGE; and was observed by dignitaries and an audience both in-person and online. (Photo: TVA)
“I’m glad you came to our party!” said GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy (GEH) chief nuclear officer Nicole Holmes as she prepared to announce that Wilmington, N.C.–based GEH will develop a standard design for its BWRX-300 boiling water small modular reactor with not one but three power producers representing three countries: Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA), Ontario Power Generation (OPG), and Synthos Green Energy (SGE). Celebration was a theme throughout the March 23 event held in Washington, D.C., which was flush with dignitaries representing the United States, Canada, and Poland.
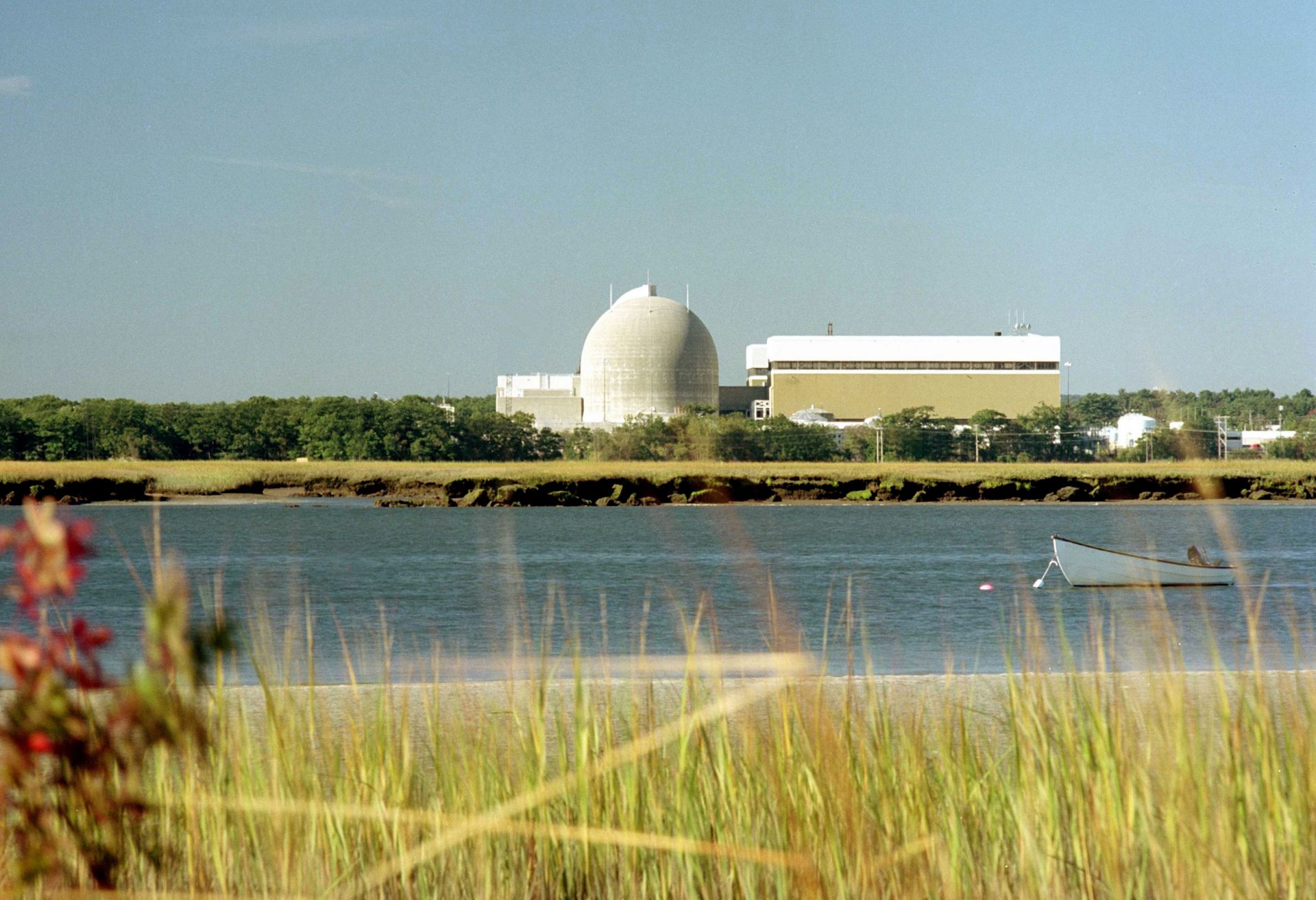
Seabrook nuclear power plant, located in southern New Hampshire. (Photo: NextEra Energy)
According to a new study conducted by the economics consulting firm Analysis Group, “Massachusetts utilities could save their customers $880 million to more than $2 billion by 2032 by entering into a long-term power purchase contract with the Seabrook Station nuclear plant.” The study, Economic and Environmental Benefits to Massachusetts from the Operation of the Seabrook Nuclear Plant, also found that operation of the plant through 2032 is expected to contribute as much as $2.9 billion to the state’s economy and reduce regional greenhouse gas emissions by 5 million tons per year.
A loaded MP197HB cask is prepared for departure from the Vermont Yankee decommissioning site to West Texas. (Photos: Orano TN)
The rapid changes in the nuclear energy industry over the last decade, driven in part by fluctuating energy market prices and an aging fleet of reactors, have led to the closure of multiple reactors in the United States and other countries. These closures have increased the need for larger and more efficient ways to manage low-level radioactive waste processing and transport capacities. The safe transport of radioactive material is a key component of the overall nuclear industry reliability. Though sometimes perceived as a bottleneck and costly, it is necessary to send waste material to disposal.
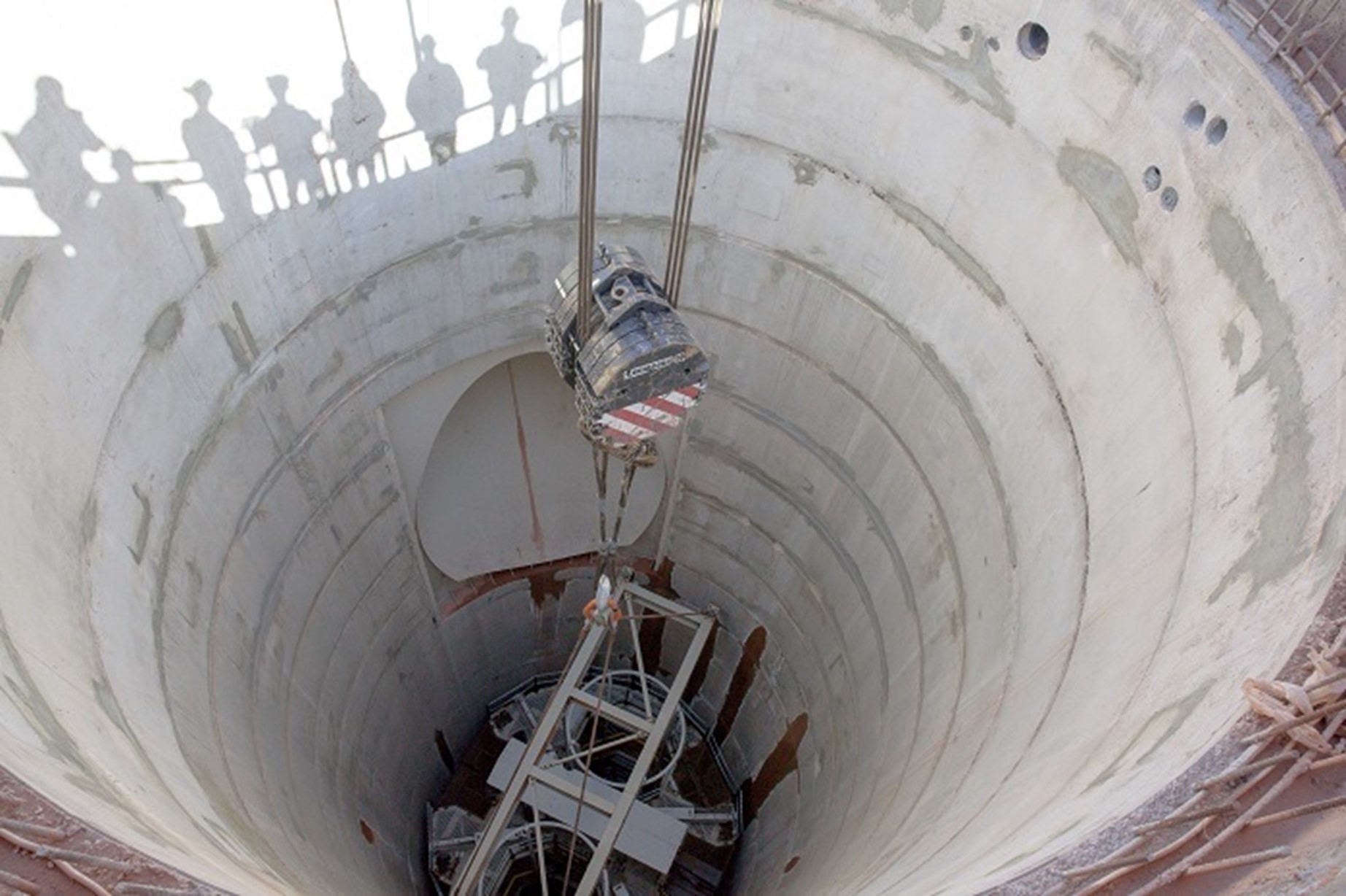
The Galloway is lowered into the utility shaft at WIPP. (Photo: DOE)
Progress continues on a new utility shaft at the Department of Energy’s Waste Isolation Pilot Plant in New Mexico as shaft-sinking crews recently surpassed the midway point at a depth of 1,076 feet. When complete, the full shaft depth will be 2,275 feet, with the team now halfway to the WIPP repository depth of 2,150 feet.
The UKAEA will provide novel fusion materials to be irradiated in ORNL’s HFIR facility over the next four years. Pictured (from left) are Kathy McCarthy, director of the U.S. ITER Project; Jeremy Busby, ORNL’s associate lab director for fusion and fission energy and science; Mickey Wade, ONRL Fusion Energy Division director; Ian Chapman, chief executive officer of the UKAEA; Cynthia Jenks, ORNL’s associate lab director for physical sciences; and Yutai Kato, ORNL Materials Science and Technology Division interim director.
The Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) and the U.K. Atomic Energy Authority (UKAEA) have formed a strategic research partnership to investigate how different types of materials behave under the influence of high-energy neutron sources. The five-year partnership was announced by ORNL and by the UKAEA on March 13.
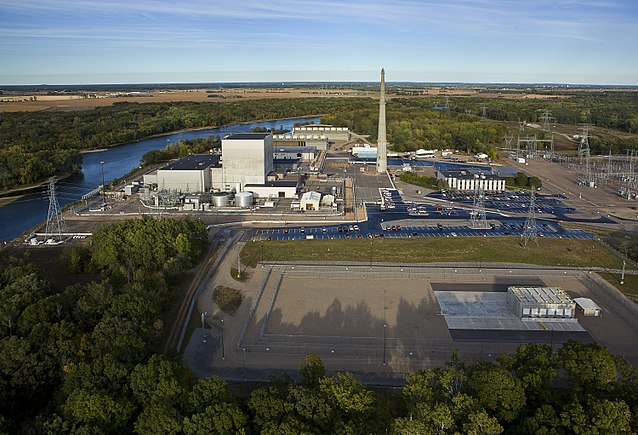
The Monticello nuclear power plant. (Photo: NRC)
An Xcel Energy news release issued last week regarding the leak of some 400,000 gallons of tritium-containing water at Minnesota’s Monticello nuclear power plant in 2022 has sparked a flood of news stories over the past few days—in large part because the general public had previously been unaware of the leak. (A low-level beta emitter, tritium is a common byproduct of nuclear reactor operation.)










 The International Atomic Energy Agency is
The International Atomic Energy Agency is 

.jpg)