The Integrated Waste Treatment Unit at the Idaho National Laboratory Site. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (EM) said that the Integrated Waste Treatment Unit (IWTU), the radioactive liquid waste treatment facility at the Idaho National Laboratory Site, began its final heat-up in December prior to initiating radiological operations, planned for early this year.
IWTU crews were to follow a prescribed incremental process as the facility transitions from simulant to sodium-bearing waste (SBW), according to EM.
An aerial view of Hanford’s Plutonium Uranium Extraction plant, showing the main facility (at center), the 211-A chemical storage area, and (in foreground) the 203-A acid storage area. (Photo: DOE)
Work crews at the Department of Energy’s Hanford Site in Washington state are performing risk-reduction activities at the Plutonium Uranium Extraction (PUREX) plant to prepare it for eventual disposition.
“It will be a yearslong effort to get this large facility ready for disposition, and I’m encouraged by the progress to safely and efficiently advance this work,” said Andy Wiborg, the DOE’s Projects and Facilities Division team lead for Hanford’s Central Plateau cleanup project.
A radiological control technician checks radiation readings on waste containers at WIPP. (Photo: WIPP)
The New Mexico Environment Department (NMED) is adding several conditions to the operating permit for the Department of Energy’s Waste Isolation Pilot Plant (WIPP) near Carlsbad, N.M. The permit changes, which would prioritize the disposal of transuranic (TRU) waste generated in the state and limit the repository’s capacity, are contained in a fact sheet the NMED.
A tanker holding 6200 gallons of leachate unloads at a backup load-in station at the Hanford Site’s ETF. (Photo: DOE)
Construction of a backup load-in station has been completed at the Hanford Site’s Effluent Treatment Facility (ETF) in Washington state.
“We broke ground on the backup facility about a year ago,” said Rob Wood, project manager for Washington River Protection Solutions, the Department of Energy’s tank operations contractor at the site. “I am proud of the team for completing this portion of the load-in expansion project and doing it safely. In phase two, expansion of the main load-in station will prepare us for 24/7 operations on the Hanford Site.”
Watch a time-lapse video of the backup load-in station construction here.
Workers walk down a passageway in Panel 8 at the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant in November. (Photo: DOE)
Employees have begun emplacing defense-related transuranic (TRU) waste in Panel 8 of the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant (WIPP) in New Mexico, the Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (EM) announced in November. TRU waste is permanently disposed of at WIPP in rooms mined in a Permian salt bed 2,150 feet below the surface.
Crews completed the teardown of Oak Ridge’s Bulk Shielding Reactor (Building 3010), once used for research as part of the federal Aircraft Nuclear Propulsion Program. (Photos: DOE)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (EM) said its cleanup contractor UCOR recently completed the first-ever demolition of a reactor in the central campus area at the Oak Ridge National Laboratory in Tennessee.
Demolition and disposal shifted into high gear this spring at the DOE’s former uranium enrichment plant in Ohio.
In the 1950s, the U.S. Department of Energy constructed the Portsmouth Gaseous Diffusion Plant in rural southern Ohio to enrich uranium, alongside two other federally owned and managed facilities in Oak Ridge, Tenn., and Paducah, Ky. The Cold War-era plant was built as a self-sufficient industrial city with more than 400 buildings and facilities centered around three massive gaseous diffusion process buildings that could enrich the level of the uranium-235 isotope for nuclear fuel in the defense and energy sectors.
A screenshot from the Local 12 report. (Image: WKRC/Sinclair)
In May 2019, Zahn’s Corner Middle School in Pike County, Ohio, located within four miles of the former Portsmouth Gaseous Diffusion Plant (PORTS), was closed after local officials reported enriched uranium and transuranic radionuclides were detected inside the school and at outside air monitors.
Now, Cincinnati’s WKRC Local 12, a news affiliate of Sinclair Broadcast Group, is reporting that a private house in Lucasville, Ohio, 10 miles from the PORTS site, has been contaminated with enriched uranium.
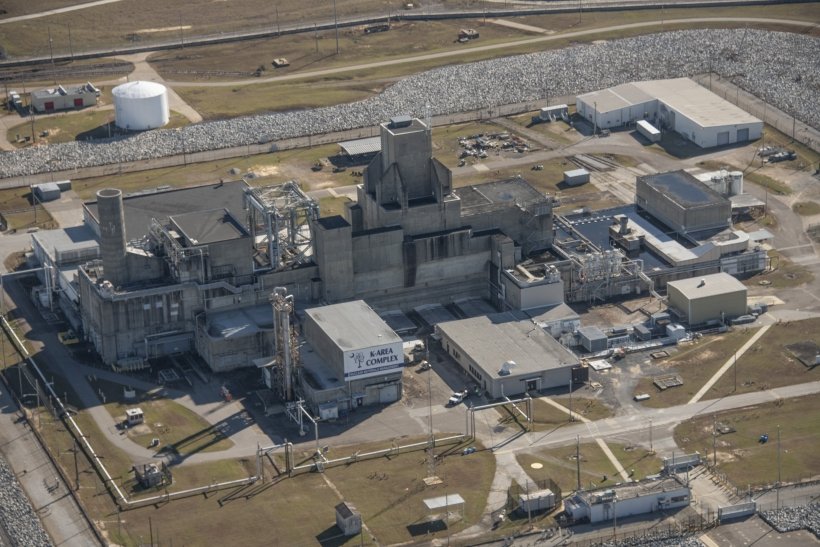
A view of Savannah River’s K Area, where employees began downblending plutonium in 2016. (Photo: DOE)
Contractor employees at the Department of Energy’s Savannah River Site in South Carolina recently exceeded their plutonium downblending goal for 2022 ahead of schedule as part of the ongoing activities to remove Pu from the state, the DOE’s Office of Environmental Management (EM) announced.
Nicholas Spivey, left, an SRNL mechanical engineer, and Kurt Gerdes, director of EM’s Office of Technology Development, use virtual reality simulation of an EM worksite during meetings held at the IHMC in Pensacola, Fla. (Photo: DOE)
For the first time since forming in 2020, more than 40 members of a Department of Energy team met in person to evaluate technologies, including exoskeletons and wearable robotic devices, that could be adapted to the cleanup mission of department’s Office of Environmental Management (EM), helping improve the safety and well-being of its workers.
DOE contractor CPCCo recently completed construction of a protective cocoon over the former K East Reactor building at Hanford. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (EM) announced that construction of Hanford’s K East Reactor cocoon has been completed ahead of schedule and under budget. Cocooning of K East—enclosing it in a protective steel structure while the reactor’s radioactivity naturally decays—was one of EM’s key construction priorities for 2022.
Workers install one of 18 startup heaters into Melter 1 of Hanford’s Low-Activity Waste Facility. (Photo: Bechtel National)
Heating of the first waste vitrification melter at the Department of Energy’s Hanford Site was paused after operators identified an “abnormal condition with the startup heater power supplies,” the DOE’s Office of River Protection (ORP) said. Heat-up of the 300-ton melter, which will be used to vitrify Hanford’s low-level radioactive tank waste, was initiated on October 8.
The decommissioning of ORNL’s aging research reactors is clearing the stage for future missions at the site.
An aerial photograph of Oak Ridge National Laboratory’s “Reactor Hill,” with, from left to right, reactor buildings 3042, 3005, and 3010. The DOE and its contractors are removing these excess contaminated facilities to eliminate risks and clear land for future research missions. (Photos: UCOR)
The Department of Energy and its environmental cleanup contractor United Cleanup Oak Ridge (UCOR) are poised to meet critical milestones as they continue to move to the next generation of cleanup at Oak Ridge National Laboratory in Tennessee. On ORNL’s main campus, crews on “Reactor Hill”—so named because of the four remaining reactor facilities on that hillside—and at the Experimental Gas-Cooled Reactor (EGCR) just east of the campus continue rigorous schedules as they enter a new phase of progress in the cleanup program.
A view of the Savannah River Site’s H Area. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (EM) announced on October 18 that it has begun the process of transferring primary authority of South Carolina’s Savannah River Site (SRS) to the National Nuclear Security Administration, with the transfer expected to be completed in 2025.
DRUM program members and others visit mine sites in the Navajo Nation during the spring of 2022. (Photo: DOE-LM)
The Department of Energy’ Office of Legacy Management (LM) will be conducting verification and validation work at abandoned uranium mines in the Navajo Nation of northeastern Arizona during the fall field season, which runs from mid-October to mid-December.
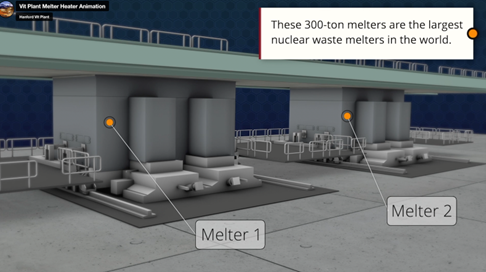
A screenshot from a 3D animation showing the heat-up of Hanford’s melters. (Image: DOE)
Crews at the Department of Energy’s Hanford Site, near Richland, Wash., have begun heating up the first of two 300-ton melters that will be used to vitrify mixed low-level radioactive and chemical tank waste. According to the DOE’s Office of Environmental Management (EM), initiating and completing the heating of the melter is a critical step to commissioning Hanford’s Waste Treatment and Immobilization Plant (WTP), which will treat and stabilize the site’s 56 million gallons of tank waste by immobilizing it in glass through the vitrification process.