An NRC diagram of a LLW waste disposal site.
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission will integrate two separate rulemaking activities concerning the disposal of low-level radioactive waste, issuing a “re-proposed” rule that consolidates updates to 10 CFR Part 61, “Low-Level Radioactive Waste Disposal,” and proposed changes to the requirements for the near-surface disposal of greater-than-Class C (GTCC) waste.
A robot called Lyra was used to survey an underground radioactive ventilation duct in Dounreay’s redundant laboratories. (Photo: NDA)
Dounreay Site Restoration Ltd. (DSRL) and the Robotics and Artificial Intelligence in Nuclear (RAIN) Hub, a consortium of universities led by the University of Manchester, are working together on the development of robots capable of accessing areas that are inaccessible or unsafe for humans to work in. The robots will be used to inspect and characterize Dounreay’s laboratories, buildings, and structures as the United Kingdom prepares to decontaminate and decommission the nuclear site.
The Kewaunee nuclear power plant in Carlton, Wis.
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission has approved the transfer of the operating license of the shutdown Kewaunee nuclear power plant from Dominion Energy to EnergySolutions. The transfer, which includes the general license for the Wisconsin site’s spent fuel storage facility, is contingent upon approval by the Wisconsin Public Service Commission.
EnergySolutions entered into an agreement with Dominion in May 2021 to acquire the Kewaunee site for decommissioning.
Waste packages are loaded with contaminated soil during remediation work at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory. (Photo: PermaFix)
Depending on the size and complexity of a decommissioning project, the transportation and disposal of radioactive waste will have an oversized impact on planning, schedule, and budget. The scope of decommissioning a site contaminated with radioactive material begins and ends with the proper and safe packaging of waste and subsequent transportation from the site to the final disposal location. Once all of the waste is gone from the site, the compliance exercise can be completed and the site released from controls (i.e., the radioactive materials license is terminated and the site is decommissioned).
An aerial view of the Radioactive Waste Management Complex at the Idaho National Laboratory site. (Photos: DOE)
Idaho Gov. Brad Little, attorney general Lawrence Wasden, Idaho legislators, county and city representatives, and the Department of Energy’s cleanup program management staff gathered at the Idaho National Laboratory site on March 30 to mark the completion of a cleanup project that helps protect the Snake River Plain Aquifer and fulfills a commitment with the State of Idaho.
NS Savannah at Pier 13 in Baltimore, Md., in 2012.
Utah-based EnergySolutions is joining Radiation Safety and Control Services (RSCS) in the decommissioning of NS Savannah, the world’s first nuclear-powered merchant ship, currently berthed at the Port of Baltimore in Maryland. EnergySolutions announced on March 29 that a joint venture of the two companies, Nuclear Ship Support Services, is conducting the final phases of decommissioning the ship’s reactor, which was defueled in 1975 but remains in place.
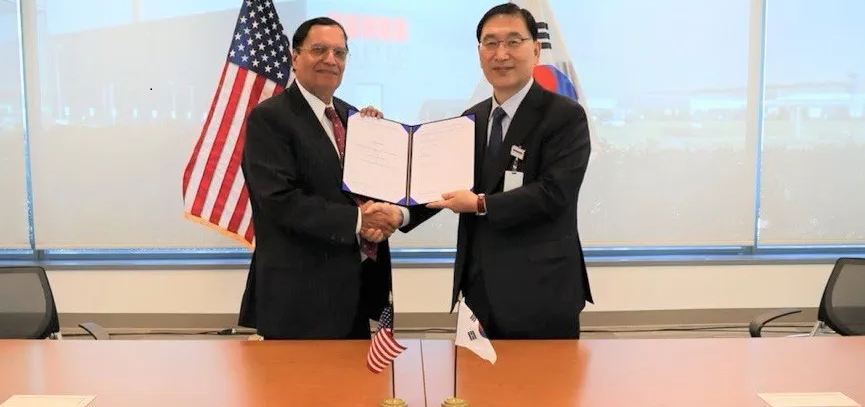
Holtec president and chief executive officer Kris Singh (left) and Hyundai E&C president and CEO Yoon Young-Joon at the teaming agreement signing ceremony. (Photo: Holtec)
Holtec International and Hyundai Engineering & Construction have signed an agreement to cooperate in the area of nuclear plant decontamination and decommissioning.
Under the teaming agreement, Hyundai E&C will participate in D&D activities at Holtec-owned decommissioning sites in the United States to build its capabilities and experience in preparation for decommissioning projects in South Korea, which will be undertaken by the two companies. The agreement also provides for the two companies to further expand their cooperation internationally.
A view of the village of Min Kush in central Kyrgyzstan. (Photo: EBRD)
The remediation of two former Soviet-era uranium mining sites in Kyrgyzstan has been completed on schedule and below budget, despite difficulties caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD) announced on March 28.
Sandia National Laboratories researchers Melissa Mills, left, and Kristopher Kuhlman peer through a WIPP salt sample.
Last fall, scientists from Sandia, Los Alamos, and Lawrence Berkeley national laboratories began the third phase of a years-long experiment to understand how salt and very salty water behave near hot nuclear waste containers in a salt-bed repository. Initiated in 2017, the Brine Availability Test in Salt (BATS) project is part of a spent nuclear fuel research campaign within the Department of Energy’s Office of Nuclear Energy (DOE-NE).
UCOR workers remove waste from the Alpha-2 building at the Y-12 National Security Complex in Oak Ridge. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy recently awarded $24.7 million to Oak Ridge cleanup contractor UCOR for its work at the Oak Ridge site in Tennessee from April 2021 through October 2021, amounting to 98 percent of the available fee for the evaluation period.
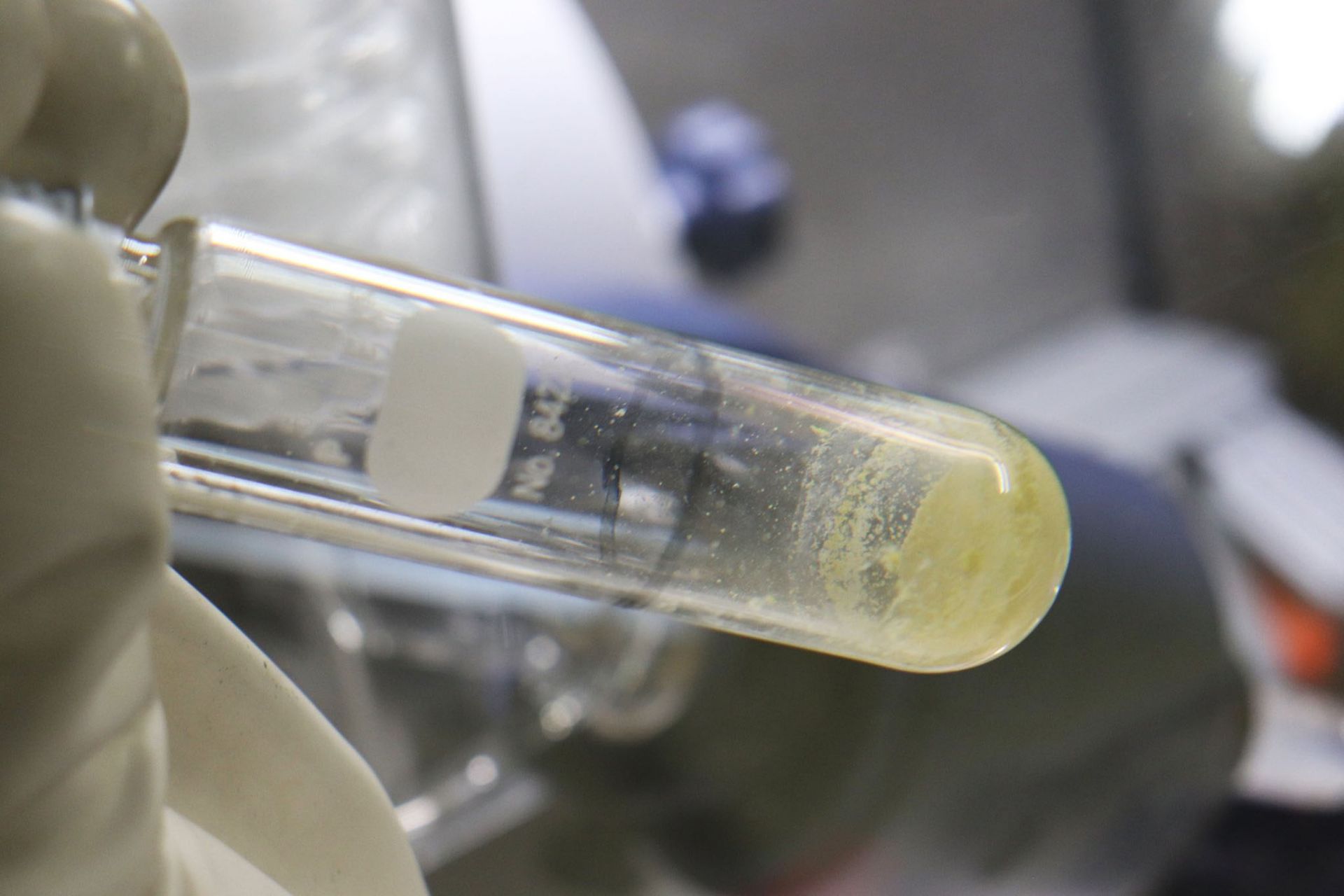
The DOE and a contractor recently succeeded in disposing of Oak Ridge’s low-activity U-233, but not before recovering Th-229 from the material.
A vial containing Th-299 extracted from uranyl nitrate.
This past October, the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge Office of Environmental Management (OREM) and its contractor Isotek successfully completed processing and disposing the low-dose inventory of uranium-233 stored at Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL), ending a two-year effort that has eliminated a portion of the site’s legacy nuclear material and provided rare nuclear isotopes for next-generation cancer treatment research.
Workers construct a new ventilation system's filter building last year at WIPP. (Photo: DOE)
Without a plan for addressing issues in completing construction projects at the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant in New Mexico, the Department of Energy cannot ensure that further cost increases and schedule delays will not continue, according to a report by the Government Accountability Office. In particular, the GAO said, the DOE has not developed a corrective action plan to address root causes identified for the rising cost and the delay in building a new ventilation system at the transuranic waste repository.
Bulk Processing Unit at the Perma-Fix Northwest waste treatment facility. (Photo: Perma-Fix)
Westinghouse Electric Company and nuclear waste management company Perma-Fix Environmental Services plan to jointly develop a state-of-the-art advanced materials treatment facility in the United Kingdom. During the 2022 Waste Management Symposia, held last week in Phoenix, Ariz., the two companies signed a nonbinding agreement to cooperate on a facility that will provide low-level radioactive waste treatment services to the European market.
An artist’s rendering of the K East Reactor safe-storage enclosure. (Photo: DOE)
Preparations are being made to enclose, or “cocoon,” the K East Reactor, the seventh of nine former reactors at the Department of Energy’s Hanford Site. The cocooning project is expected to be completed by the end of the year.
Watch this video for more on the project.
Spent nuclear fuel handlers move the last ATR fuel to an awaiting cask in the CPP-666 basin. (Photo: DOE)
The last spent nuclear fuel elements from Idaho National Laboratory’s Advanced Test Reactor (ATR) have been retrieved from a water-filled storage basin and transferred to a nearby dry-storage facility in accordance with a 1995 agreement with the State of Idaho, the Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (EM) announced this week.







.png)






 The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (EM) has issued EM Strategic Vision 2022-2032, a blueprint for planned nuclear-related cleanup efforts over the next decade. The document outlines environmental cleanup priorities for 2022–2032, focusing on safety, innovation, and improved performance.
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (EM) has issued EM Strategic Vision 2022-2032, a blueprint for planned nuclear-related cleanup efforts over the next decade. The document outlines environmental cleanup priorities for 2022–2032, focusing on safety, innovation, and improved performance.