The Bruce Power nuclear power plant. (Photo: Bruce Power)
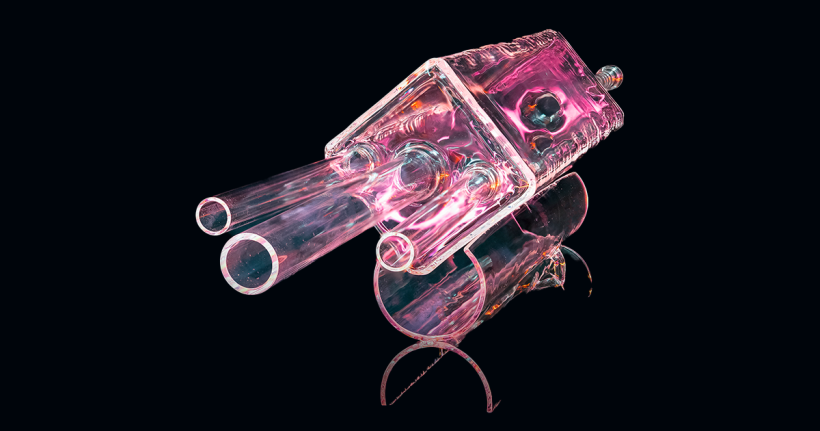
A glass test cell that was fabricated to visualize noble gas behavior in a stagnant molten salt column. (Photo: ORNL)
Transparency is one advantage of certain molten salts that could serve as both a coolant and fuel carrier in an advanced reactor. For scientists studying molten salt chemistry and behavior at the laboratory scale, it helps if the test vessel is transparent too. Now, Oak Ridge National Laboratory has created a custom glass test cell with a 1-liter capacity to observe how gases move within a column of molten salt, the Department of Energy announced August 5.
NRC accepting hearing requests on Holtec’s restart plans
The Department of Energy has signed off on a $1.5 billion loan guarantee to Holtec Palisades LLC to support initial work needed to restart the Michigan nuclear plant.
AI-generated concept image. (Image: DARPA)
Nuclear power already has an energy density advantage over other sources of thermal electricity generation. But what if nuclear generation didn’t require a steam turbine? What if the radiation from a reactor was less a problem to be managed and more a source of energy? And what if an energy conversion technology could scale to fit nuclear power systems ranging from miniature batteries to the grid? The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) Defense Sciences Office (DSO) is asking these types of questions in a request for information on High Power Direct Energy Conversion from Nuclear Power Systems, released August 1.
Southeast Asian nation considering deployment of first nuclear energy
U.S. secretary of state Antony Blinken (left) with Singapore foreign minister Vivian Balakrishnan. (Photo: X/@SecBlinken)
The United States and Singapore have signed a civil nuclear cooperation agreement, commonly known as a 123 Agreement.
U.S. secretary of state Antony Blinken and Singapore’s minister of foreign affairs Vivian Balakrishan met on July 31 to formalize the agreement, which outlines a comprehensive framework for peaceful nuclear collaboration between the two nations based on a mutual commitment to nuclear nonproliferation.
Dresden nuclear power plant. (Photo: Constellation Energy)
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission is hosting several public meetings this month to discuss the Dresden nuclear power plant and its request for subsequent license renewal.
The Golfech nuclear power plant. (Photo: Theanphibian)
Électricité de France reduced power production by 1 gigawatt on Friday at its Golfech nuclear plant, citing high water temperatures on the Garonne River.
The ALCF AI Testbed includes the AI systems represented in this collage: Cerebras, Graphcore, Groq, and SambaNova. (Image: Argonne National Laboratory)
Generative artificial intelligence paired with advanced diagnostic tools could detect potential problems in nuclear power plants and deliver a straightforward explanation to operators in real time. That’s the premise of research out of the Department of Energy’s Argonne National Laboratory, and just one example of the DOE’s increasing exploration of AI applications in nuclear science and technology research. Training and restraining novel AI systems take expertise and data, and the DOE has access to both. According to a flurry of reports and announcements in recent months, the DOE is setting out its plans to ensure the United States can use AI to its advantage to enhance energy security and national security.
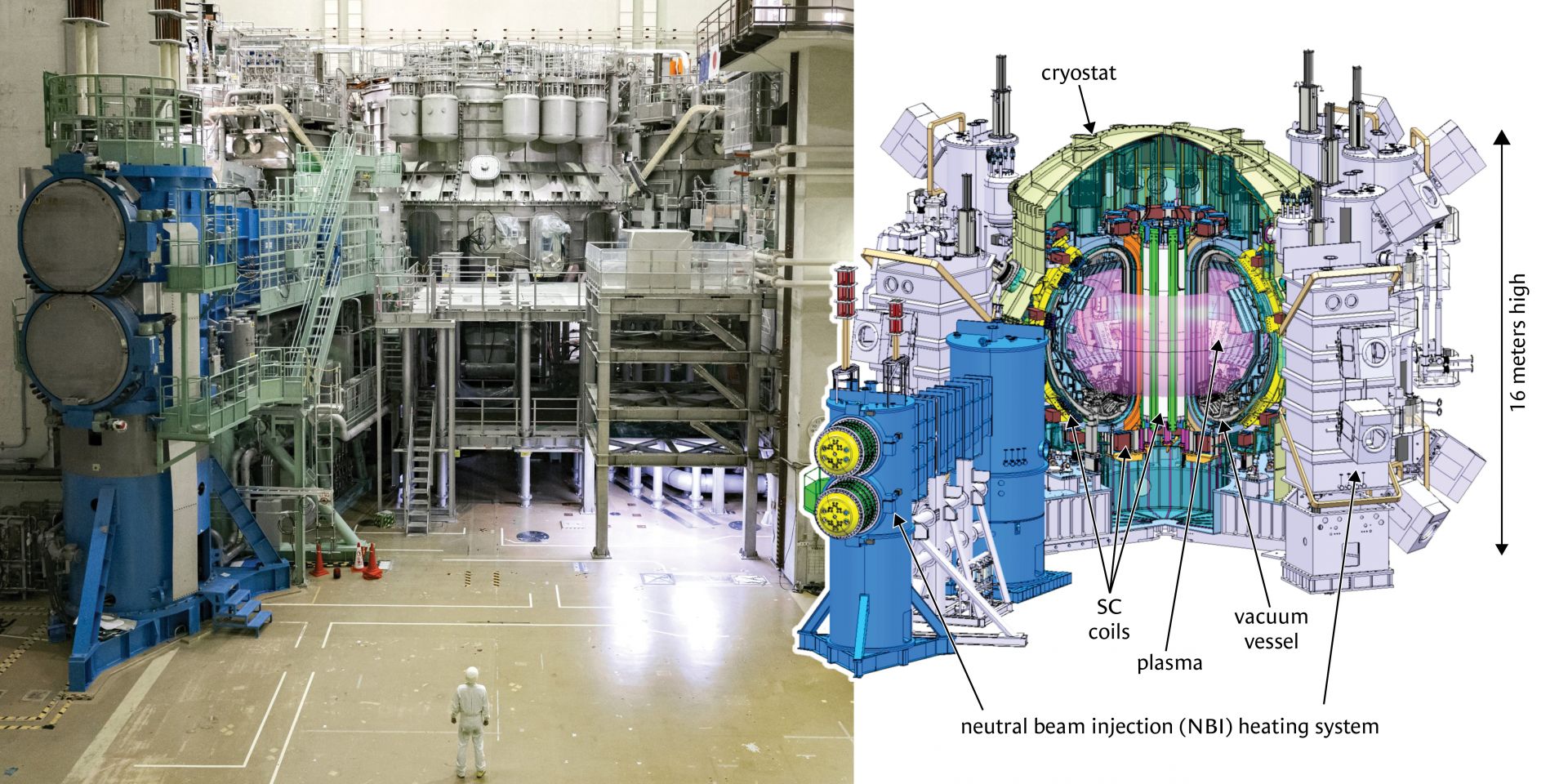
Fig. 1. A photograph (left) and schematic figure (right) of JT-60SA.
(Source: Naka Institute)
JT-60SA (Japan Torus-60 Super Advanced) is the world’s largest superconducting tokamak device. Its goal is the earlier realization of fusion energy (see Fig. 1). Fusion is the energy that powers the Sun, and just 1 gram of deuterium-tritium (D-T) fuel produces enormous energy—the equivalent of 8 tons of crude oil.
Last fall, the JT-60SA project announced an important milestone: the achievement of the tokamak’s first plasma. This article describes the objectives of the JT-60SA project, achievements in the operation campaign for the first plasma, and next steps.
The company has awarded nearly $6 million for STEM education and research programs since the program launched in 2010
Constellation is taking applications for its 2024 E2 Energy to Educate grant program, which provides funding for student projects focusing on energy innovation.
Educators and students in grades 6–12 can apply for program grants of up to $25,000, and those in two- and four-year colleges can apply for grants of up to $50,000.
Company celebrates Browns Ferry’s 50 years in service
Bellefonte nuclear power plant. (Photo: TVA)
The Tennessee Valley Authority this week discussed the potential for new nuclear technology at its sites during its second-quarter earnings call.
TVA and GE Hitachi signed an agreement in 2022 to develop and deploy a BWRX-300 small modular reactor at the Clinch River site near Oak Ridge, Tenn.
Urenco’s Capenhurst enrichment site in the U.K. (Photo: Urenco)
A plan to build up a high-assay low-enriched uranium fuel cycle in the United Kingdom to support the deployment of advanced reactors is still in place after the Labour party was voted to power on July 4, bringing 14 years of conservative government to an end. A competitive solicitation for grant funding to build a commercial-scale HALEU deconversion facility opened days before the election, and the support of the new government was confirmed by a set of updates on July 19. But what does the U.K. HALEU program entail, and how does it differ from the U.S. HALEU Availability Program?
Rendition of a Rolls-Royce SMR site.(Image: Rolls-Royce)
The small modular reactor design from Rolls-Royce has cleared step two of the United Kingdom’s generic design assessment (GDA) and is moving to the third and final step.
The company announced its progress and lauded “Rolls-Royce SMR’s position ahead of any other SMR in Europe” in a July 30 press release. Rolls-Royce SMR touts its ability to deliver new nuclear power based on proven technology, providing a “factory-built” power station to provide enough energy for a million homes for a 60-year stretch.
Comanche Peak nuclear power plant. (Photo: Meranda Cohn/Vistra)
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission has renewed the operating licenses of Comanche Peak Units 1 and 2 for an additional 20 years.
Unit 1’s operating license now expires on February 8, 2050, and Unit 2’s on February 2, 2053.
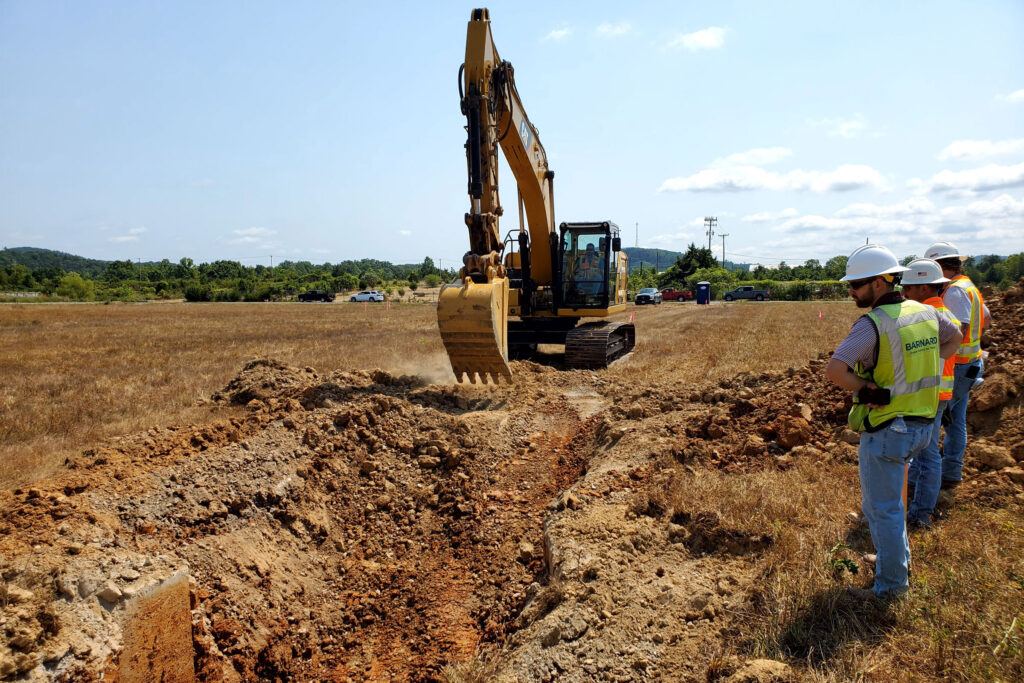
Workers begin construction at the Hermes site in Oak Ridge, Tenn. (Photo: Kairos Power)
Earlier today, on a site in Oak Ridge, Tenn., that was formerly home to the K-33 Gaseous Diffusion Plant, Kairos Power marked the start of construction on its low-power demonstration reactor. Named Hermes, the 35-MWt test reactor claims status as the first Gen IV reactor to be approved for construction by the Nuclear Regulatory Commission and the first non–light water reactor to be permitted in the United States in more than 50 years.
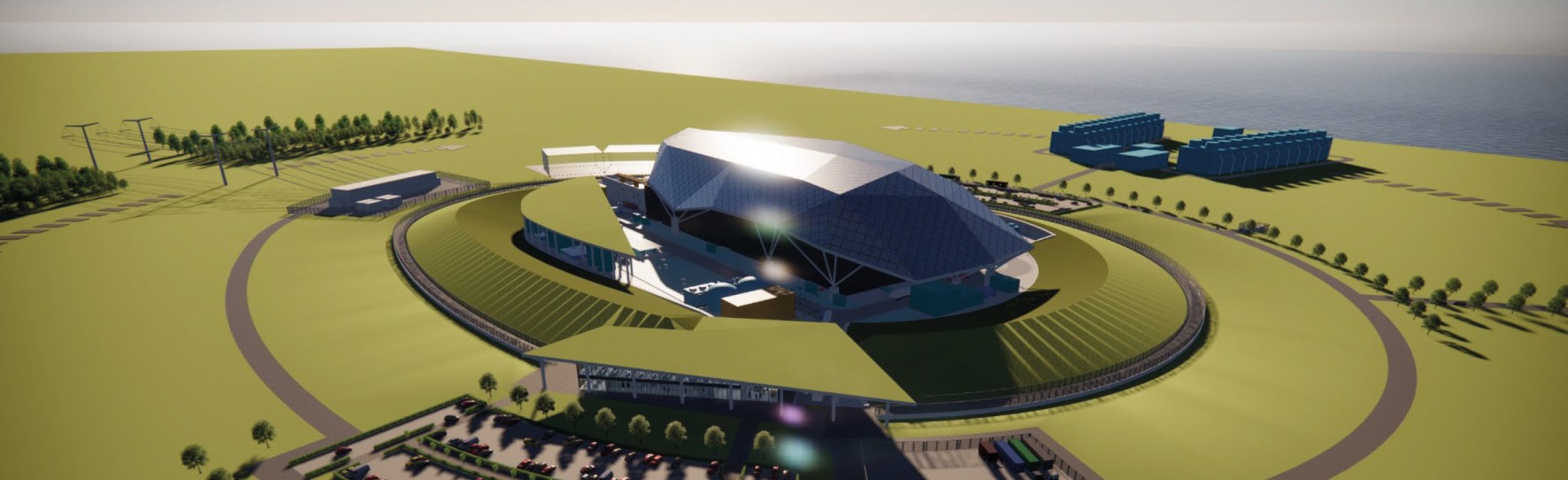
A screengrab from a video released by the STEP program on July 23 illustrating the future home of the prototype fusion power plant. (Image: UKAEA/STEP)
Japan’s recent moves to boost fusion power in the nation’s energy plan and accelerate the timeline for a prototype fusion power plant come in response to increased global attention on fusion energy. Even as ITER faces delays, more than 40 private fusion developers are pursuing different technologies and competing for attention. And so are other countries, including the United Kingdom, which announced its plans for a fusion pilot plant back in 2019. Fusion companies and nations alike are responding to a growing sense that there is a race—or at least collective momentum—to commercialize fusion energy.






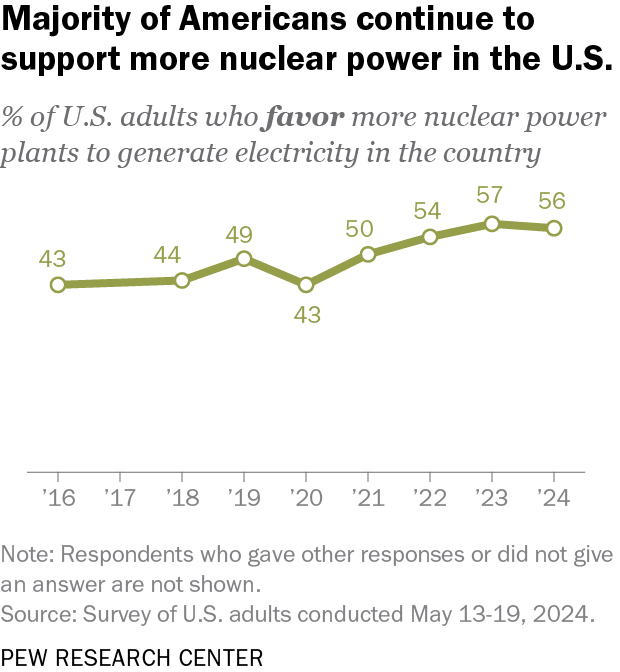 A number of surveys and polls, such as
A number of surveys and polls, such as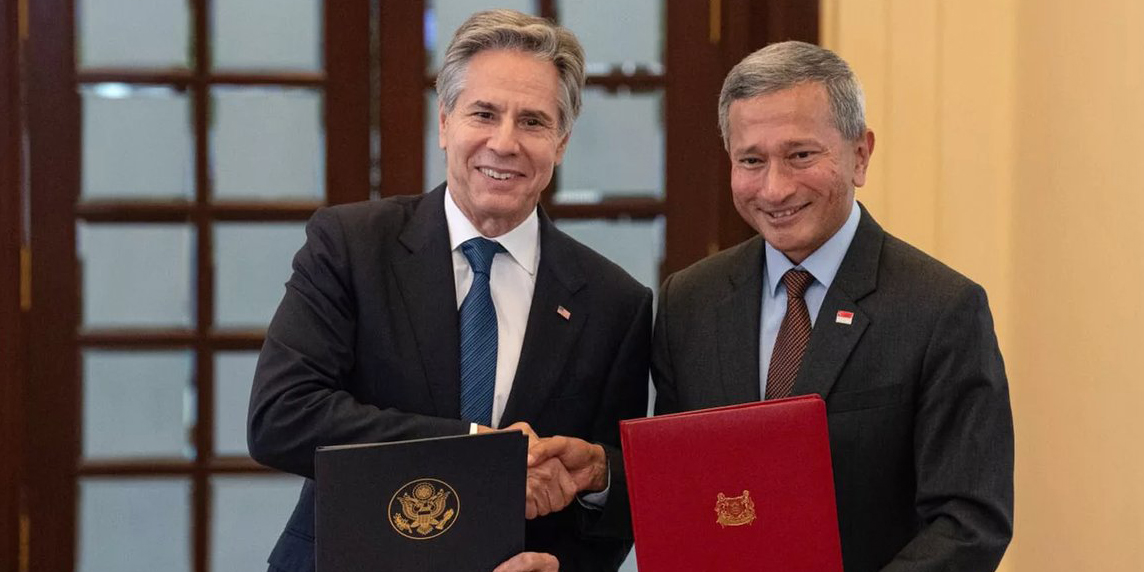 


.png)