Russia has no current plans to restart Ukraine plant

An official from Russia’s state-owned nuclear power company Rosatom said this week that there are no current plans to reopen the Zaporizhzhia nuclear power plant in Ukraine.
Published since 1959, Nuclear News is recognized worldwide as the flagship trade publication for the nuclear community. News reports cover plant operations, maintenance and security; policy and legislation; international developments; waste management and fuel; and business and contract award news.


An official from Russia’s state-owned nuclear power company Rosatom said this week that there are no current plans to reopen the Zaporizhzhia nuclear power plant in Ukraine.

Duke Energy announced agreements yesterday with Amazon, Google, Microsoft, and Nucor to accelerate clean energy deployments in the Carolinas through a new rate structure proposal.
The company signed memoradums of understanding this month that include proposed Accelerating Clean Energy (ACE) tariffs that would help offset the long-term costs of investing in clean energy technologies, such as new nuclear and energy storage, through early commitments. Duke announced its partnership with the tech and utility giants at this week’s White House Summit on Domestic Nuclear Deployment aimed at strengthening the U.S. nuclear industry.

CPS Energy has become a founding member of the Texas Nuclear Alliance and is also the alliance’s first electric utility provider member. CPS Energy owns 40 percent of the two-unit South Texas Project nuclear power plant, in Bay City, Tex.

James Conca
The term “dirty bomb” surfaces occasionally, usually in the context of nuclear waste, which, while understandable, is incorrect.
Dirty bombs, or radiation dispersal devices (RDDs), use conventional methods like car bombs to disperse radioactive materials in populated economic districts, such as lower Manhattan. The point is to cause great economic and social disruption disproportionate to the actual radiological effects—and well beyond the physical destruction from the conventional bomb components.
Society’s irrational fear of radiation makes the dirty bomb an ultimate weapon of terror. But it is a psychological weapon, not a nuclear one. The public should not be any more afraid of a dirty bomb than they are of an ordinary car bomb.
Nuclear energy advocates attended a White House summit today on domestic nuclear deployment and will help advise a new federal initiative to support building new grid-scale nuclear reactors.
The event showcased recent policy developments and new industry investments that have changed the playing field—for the better—for nuclear during the past few years. The White House is calling it “the largest sustained push to accelerate civil nuclear deployment in the United States in nearly five decades.”

California-based Oklo is partnering with Wyoming Hyperscale to power a state-of-the-art data center campus.
The companies, which announced the partnership last week, signed a nonbinding letter of intent to provide 100 megawatts of carbon-free energy for a 20-year power purchase agreement. Wyoming Hyperscale is building a data center on 58 acres of land on Aspen Mountain, a remote site southeast of Evanston, Wyo., and plans to use Oklo’s Aurora Powerhouse units to provide clean energy at the site.
Utilities need to know months ahead of a scheduled refueling outage that fresh fuel will be on-site and ready to load. Now that the Prohibiting Russian Uranium Imports Act has been signed into law, U.S. utilities with plans to use Russian-origin low-enriched uranium also need to know if they can secure a waiver for imports through December 31, 2027—subject to specific annual limits—if “no alternative viable source of [LEU] is available to sustain the continued operation of a nuclear reactor or a United States nuclear energy company” or if LEU imports from Russia are “in the national interest.”
The United Kingdom has announced a northern Wales site as its preferred location for a third mega-nuclear power station as the nation aims to support long-term energy security.
Following its plans to build nuclear facilities at Hinkley in Somerset and Sizewell in Suffolk, both in England, U.K. officials hope to revive the nuclear history of Wylfa, in Wales, and bring thousands of jobs and major investment to the area. The government is kickstarting talks with global energy firms in hopes of building a nuclear plant in Wylfa that could provide enough energy to power 6 million homes for 60 years.
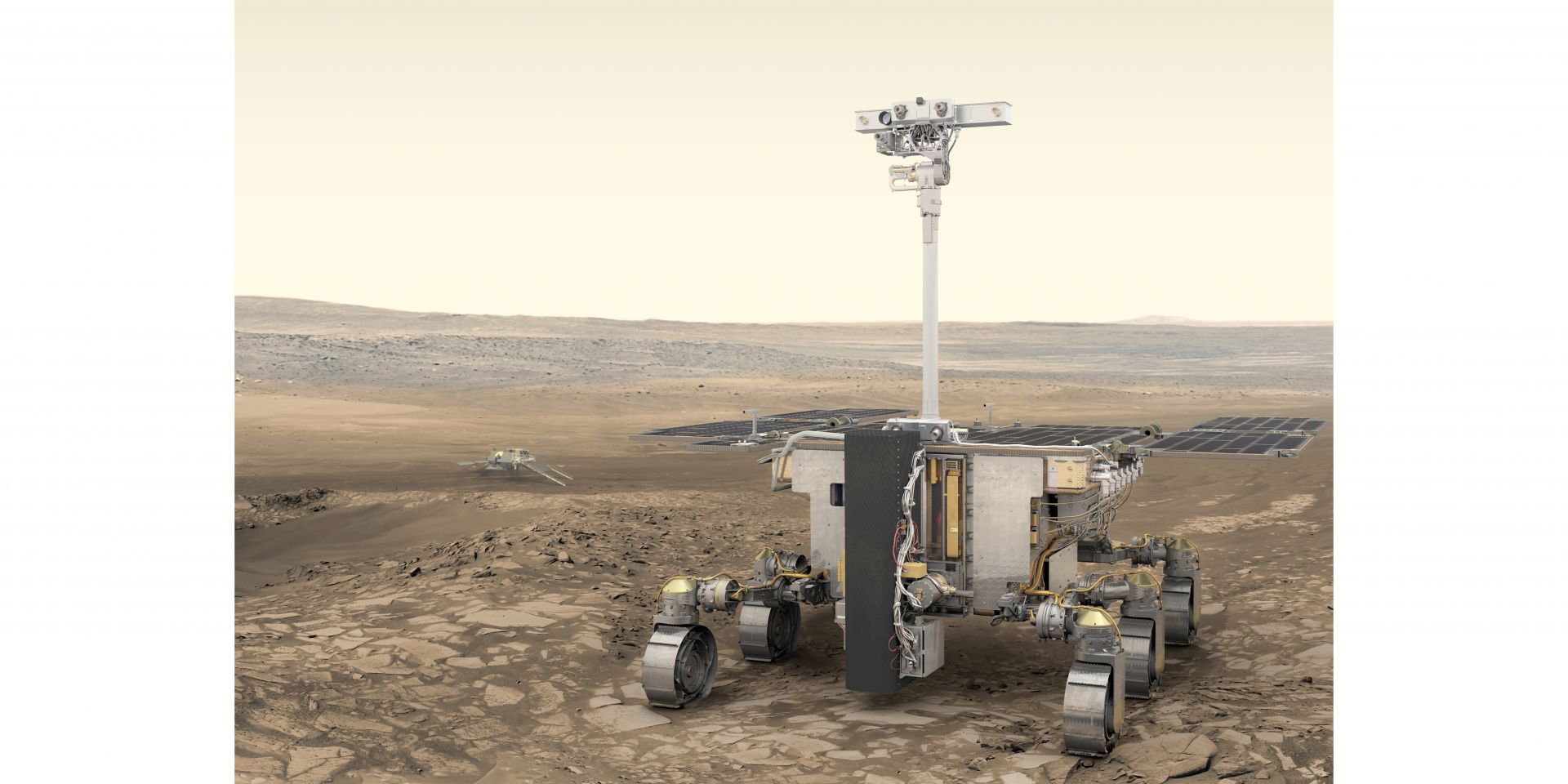
Europe’s first Mars rover—named Rosalind Franklin—was months away from a planned September launch when the European Space Agency (ESA) convened a meeting a few weeks after Russia’s February 2022 invasion of Ukraine. The ESA Council unanimously agreed on “the present impossibility” of working with Roscosmos as its launch partner and later decided to reboot its ExoMars mission with a new lander, new partners, and a new launch date.

Ukraine’s Zaporizhzhia nuclear power plant temporarily lost the connection to its sole remaining 750 kilovolt (kV) off-site power line last week due to a reported short circuit, leaving it reliant on a single backup line for more than three hours.

Ensuring that nuclear technology is used exclusively for peaceful purposes remains a critical challenge for our society today. The global community faces several grave nuclear security threats: nations that attempt to create (such as Iran) or augment (such as Russia, China, and North Korea) their nuclear arsenals, acts of aggression that target civilian nuclear reactors (as seen with Russia in Ukraine), and the looming menace of nuclear weapons deployment (emanating from Russia). Furthermore, addressing climate change necessitates an expansion of nuclear energy for electricity generation, which brings with it the need for safeguarding and regulating the deployment of advanced reactors.

The U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission has formally accepted TerraPower’s small modular reactor construction permit application and is scheduling it for review.
The company’s Natrium reactor demonstration project—the nation’s first commercial advanced reactor of its kind—would be built on land in Wyoming near one of the state’s retiring coal plants. Kemmerer Power Station Unit 1 would operate as a 345-MW sodium-cooled reactor in conjunction with molten salt–based energy storage.
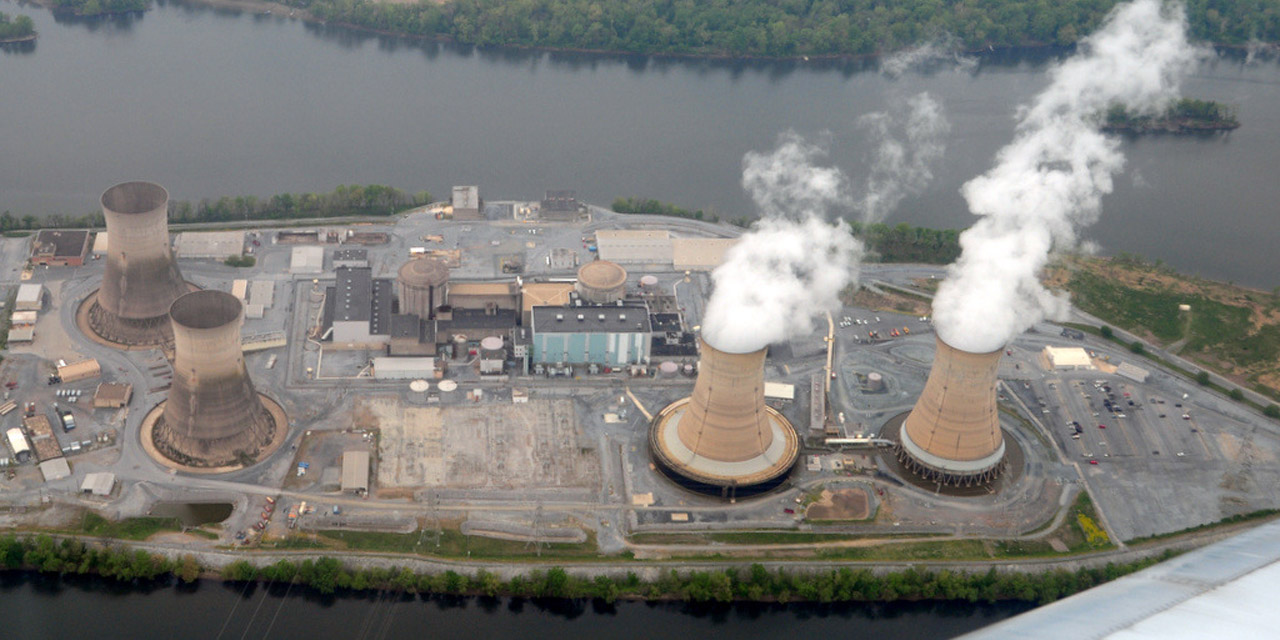

On the company’s earnings call this month, Constellation CEO Joe Dominguez was asked if there is a possibility of restarting the shuttered Three Mile Island plant—as is being proposed for the Palisades nuclear plant in Michigan.
“We’re not unaware that opportunity exists for us,” Dominguez said. “We’re obviously seen what’s happened with Palisades and I think that was brilliant. Brilliant for the nation. … We are doing a good bit of thinking about a number of different opportunities, and that would probably certainly be one of those that we would think about.”

Japan’s Kyoto Fusioneering, a fusion startup spun out from Kyoto University, and Canadian Nuclear Laboratories have announced the formation of Fusion Fuel Cycles Inc., headquartered in Chalk River, Ontario, Canada. The joint venture extends a strategic alliance formed between the two entities in September 2023 and aims to develop and deploy deuterium-tritium (D-T) fusion fuel cycle technologies.

Idaho’s nuclear energy history is deep and rich. The National Reactor Testing Station (NRTS) began its history as an artillery testing range in the 1940s.1 Following World War II, Walter Zinn, Argonne National Laboratory’s founding director and Manhattan Project Chicago Pile-1 project manager, proposed to the Atomic Energy Commission that a remote location be found for building test reactors. In 1949, he and Roger S. Warner, AEC’s director of engineering,2 developed a list of potential sites from which the NRTS was selected. Over the decades, quite a few companies and AEC national laboratories built 52 experimental and test reactors at the NRTS, including 14 by Argonne.3 (For a brief AEC video on the NRTS, see youtube.com/watch?v=C458NsH08TI.)
During the International Atomic Energy Agency’s International Conference on Nuclear Security this week, leaders from the U.S. Department of Energy’s National Nuclear Security Administration and the European Commission made a joint statement on enhancing radioactive source security.

Last week Tennessee Gov. Bill Lee and Stuart McWhorter, commissioner of the state’s Department of Economic and Community Development, announced that the University of Tennessee–Knoxville and Roane State Community College will receive funding from Tennessee’s Nuclear Energy Fund to support existing nuclear programs as well as develop and implement new nuclear education curriculum.
Using its portion of the $50 million Nuclear Energy Fund, the University of Tennessee will establish a new program for non-nuclear engineers to obtain a minor in nuclear engineering at its Knoxville campus. Separate funding for Roane State Community College will allow purchase of laboratory equipment for that school’s inaugural nuclear technology program, which launches in the fall of 2024.

The Nuclear Regulatory Commission hosted a public meeting yesterday to gather comments on its web-based ADAMS (WBA) system—a public document search tool introduced in 2010. It’s a tool that novice users find daunting and frequent users find frustrating, whether they’re searching for a single document or for thousands of documents on a single topic.
Members of the U.S. Senate Energy and Natural Resources Committee on Tuesday included nuclear energy as part of their discussions of the increasing demand for electricity anticipated in the coming decade, spurred in large part by the rise of artificial intelligence, data centers, and public consumption.

Last year, 168 incidents of illegal or unauthorized activities involving nuclear and other radioactive materials were reported to the International Atomic Energy Agency’s Incident and Trafficking Database (ITDB). According to the agency, this number is in line with historical averages. These incidents were reported by 31 IAEA member states; as of 2023, a total of 145 member states have participated in the ITDB.