LLNL and Penn State researchers developed a new approach to study and purify medical isotopes, including actinium. (Image: Thomas Reason/LLNL)
Scientists at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory and Pennsylvania State University have demonstrated that a natural protein found bonded to rare earth elements can be recovered and used as a tool to purify and effectively manage radioactive metals that show promise for cancer therapy and the detection of illicit nuclear activities.
Vogtle-4 containment as it appeared last month. Photo: Georgia Power
In what has become for nuclear advocates an all-too-familiar refrain, Georgia Power has made another revision to the Vogtle nuclear expansion project schedule. The company now predicts a Unit 3 in-service date in the third quarter of 2022 and a Unit 4 in-service date in the second quarter of 2023, representing a three-month shift for each unit.
An F-35A Lightning II takes off from Eielson Air Force Base in Alaska on July 1, 2021. (Photo: U.S. Air Force/Airman 1st Class Jose Miguel T. Tamondong)
The Department of the Air Force has selected Eielson Air Force Base as the site of a stationary microreactor that “will provide the installation with a clean, reliable, and resilient nuclear energy supply technology for critical national security infrastructure,” the department announced on October 15.
Physicist Suying Jin with computer-generated images showing the properties of heat pulse propagation in plasma (Image: PPPL/Jin/Kiran Sudarsanan)
Researchers at the Department of Energy’s Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) have developed a new model of how heat flows within plasmas. According to PPPL, the model could improve insights into the behavior of plasmas and may help engineers avoid the conditions that could lead to heat loss in future fusion facilities.
Limerick nuclear power plant. (Photo: Arturo Ramos)
The Department of Energy is providing $50 million in a cost-sharing project with Exelon Generation to digitalize the control room at the company’s Limerick nuclear power plant, the department announced yesterday. Once implemented, the facility will house the first fully digital safety system upgrade at a U.S. nuclear power plant.
SHINE Technologies’ headquarters building in Janesville, Wis. (Photo: SHINE)
The Department of Energy’s National Nuclear Security Administration has issued a cooperative agreement worth $35 million to SHINE Technologies, based in Janesville, Wis., to support the commercial production of molybdenum-99, a critical isotope used in more than 40,000 medical procedures in the United States each day, including the diagnosis of heart disease and cancer.
ORNL’s Benjamin Manard places a swipe on the extraction stage of Advion’s Plate Express, a microextraction tool that has been paired with a mass spectrometer. (Photo: Carlos Jones/ORNL, DOE)
International nuclear safeguards verification relies on a precise count of isotope particles collected on swipes during International Atomic Energy Agency inspections of nuclear facilities and isolated through a series of lengthy chemical separations that can take about 30 days to complete. On October 15, Oak Ridge National Laboratory—a member of the IAEA’s Network of Analytical Laboratories (NWAL)—announced that analytical chemists at the site have developed a faster way to measure isotopic ratios of uranium and plutonium collected on swipes, which could help IAEA analysts detect the presence of undeclared nuclear activities or material.
A PET imaging machine. (Photo: Wikimedia Commons)
ARTMS, a Canadian producer of medical isotopes, announced that it has registered the cyclotron production of gallium-68 with the government of Canada, filing a Type 1 Master File with the Health Products & Food Branch of Health Canada. The Ga-68 radioisotope is used in nuclear medicine diagnostic procedures utilizing positron emission tomography (PET) imaging.
Nuclear power capacity by scenario, 2020–2050 (STEPS: stated policies scenario, APS: announced pledges scenario, NZE: net-zero emissions by 2050 scenario). (Graphic: IEA World Energy Outlook 2021)
The International Energy Agency released its flagship report, World Energy Outlook 2021, on October 13, “at a time when policymakers are contending with the impacts of both climate change and volatile energy markets” and ahead of the COP26 Climate Change Conference in Glasgow, which begins October 31. With a net-zero emissions by 2050 (NZE) scenario that calls for nuclear power capacity to almost double by 2050, the report acknowledges that rapid development of advanced nuclear technologies could expand opportunities for nuclear energy to provide low-carbon electricity, heat, and hydrogen.
October 15, 2021, 3:26PMNuclear NewsMatt Palamara, Ali Fakhar, Stephen Smith, Patrick Fabian, Nathan Lang, and George Holoman Neutron noise monitoring allowed engineers to observe and interpret vibration characteristics captured by neutron flux detectors. (Photo: PSEG/Westinghouse)
The nuclear industry has historically relied on intermittent ultrasonic test and visual inspections of pressurized water reactor components to identify and manage degradation. While this reactive approach has proven to be effective, imagine a scenario in which the degradation could propagate throughout the reactor internals, making a more proactive measure necessary to avoid a major enterprise risk to the plant. Could a utility identify the onset of degradation within the reactor internals during plant operation? If so, could a repair be developed prior to the next refueling outage to prevent additional, cascading degradation? That is exactly the situation that Public Service Enterprise Group (PSEG) and Westinghouse engineers were able to navigate over the course of the 2019–2020 operating cycle at Salem Unit 1, resulting in a tremendous success for the plant and a historic landmark in the nuclear industry, while earning the team a 2021 Nuclear Energy Institute Top Innovative Practice (TIP) award.
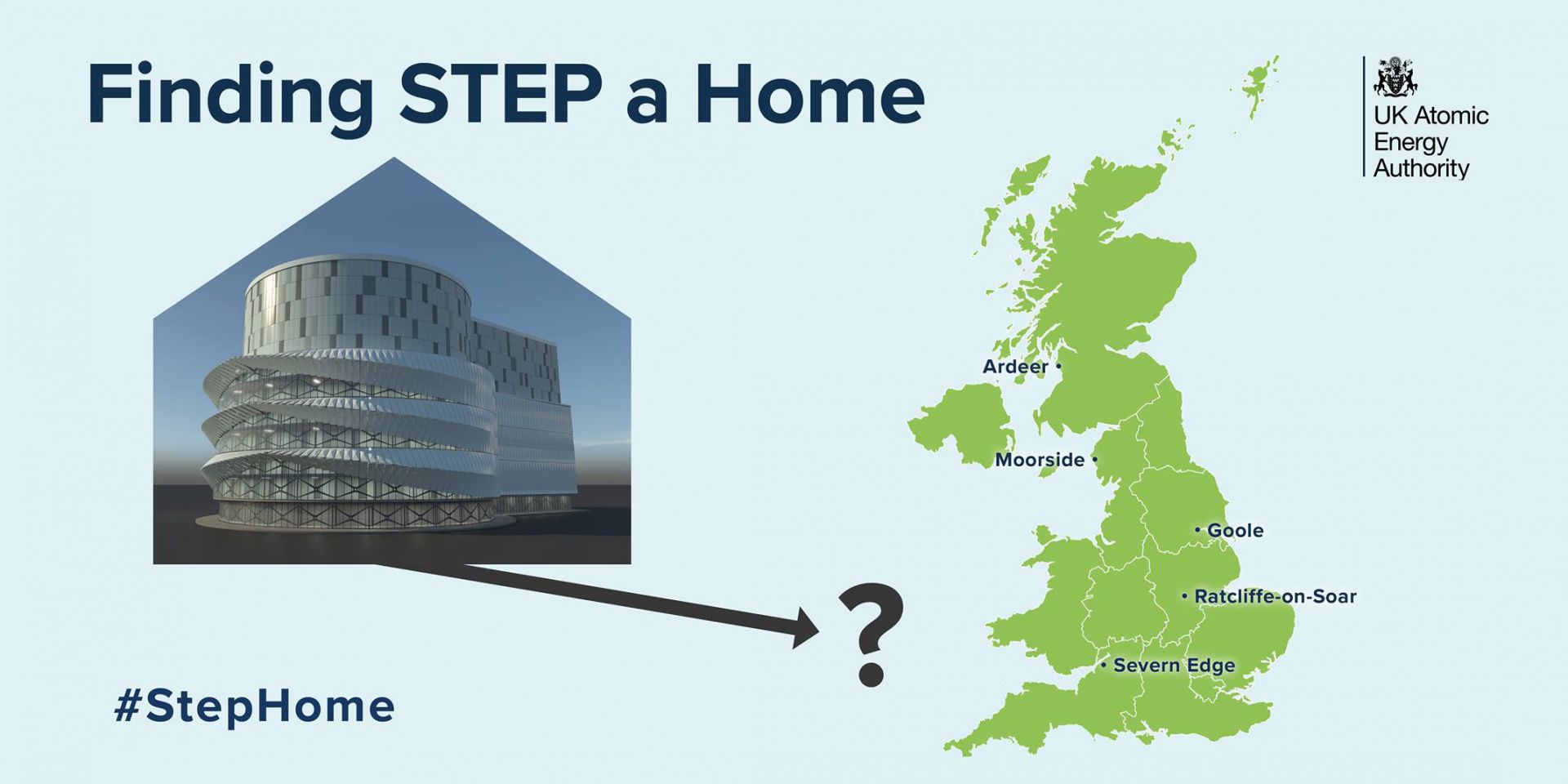
Five sites have been shortlisted for the U.K.’s STEP fusion facility. (Image: UKAEA)
The United Kingdom has announced a shortlist of five sites as the potential future home of the U.K. Atomic Energy Authority’s (UKAEA) prototype fusion energy plant, the Spherical Tokamak for Energy Production (STEP). A final decision on the plant’s location is to be made by the U.K.’s secretary of state for business, energy and industrial strategy around the end of 2022.



 “The price of anti-nuclear psychosis (for that is what it is) will be paid by vulnerable countries and future generations who suffer the escalating damages of climate breakdown,” writes environmentalist and author Mark Lynas in the foreword to a new study,
“The price of anti-nuclear psychosis (for that is what it is) will be paid by vulnerable countries and future generations who suffer the escalating damages of climate breakdown,” writes environmentalist and author Mark Lynas in the foreword to a new study,