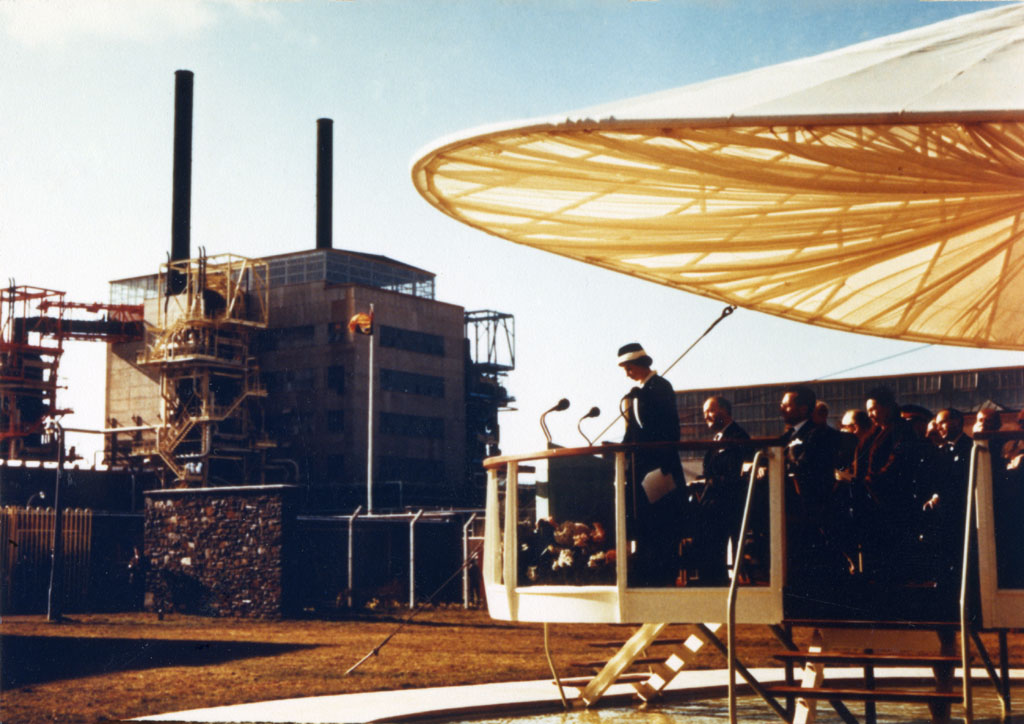
Queen Elizabeth II visits Calder Hall for its ceremonial opening in 1956. (Photo: U.K. Nuclear Decommissioning Authority)
As citizens of the United Kingdom and others around the world mourn the death of Queen Elizabeth II, many have reflected on how the world has changed during the seven decades of the queen’s reign—the same decades that saw the rise of civilian nuclear power.
Calder Hall was already under construction at the Sellafield site in West Cumbria when Princess Elizabeth became queen in 1953. Queen Elizabeth traveled to the site in October 1956 and declared, in a televised ceremony, that “It is with pride that I now open Calder Hall, Britain’s first atomic power station.” Watch the fanfare in a historical clip uploaded to YouTube by Sellafield Ltd below.
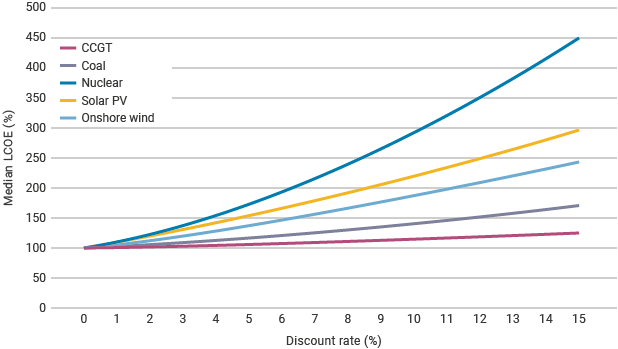
Interest rates have an outsized impact on nuclear power costs compared to those for other methods of power generation. (Source: World Nuclear Association)
In an essay titled “How the Fed will Strangle New Nukes,” published this week by American Thinker, nuclear engineer and writer Joseph Somsel warns that despite current expectations of a nuclear construction boom, “As in the late 1970s, rising interest rates will put the kibosh on new nukes.” Somsel therefore urges the financing and building of new nuclear facilities right now, before ongoing inflation and increasingly high interest rates “kill a lot of the plans” for new nuclear power plants.
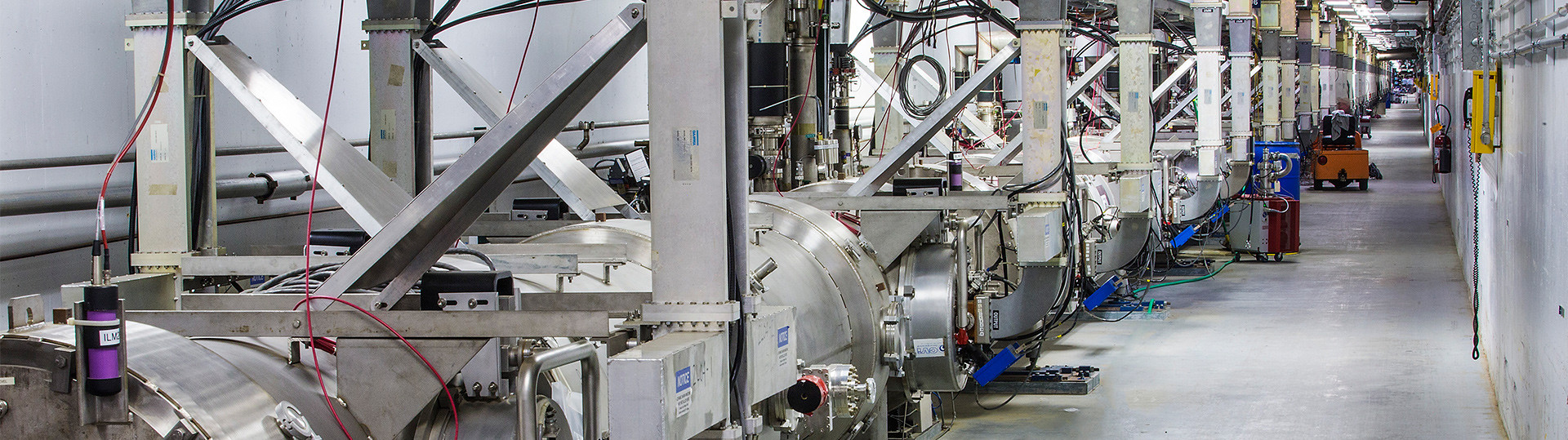
The Continuous Electron Beam Accelerator Facility at Jefferson Lab. (Source: Jefferson Lab)
Research with the Department of Energy’s Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility (Jefferson Lab) has revealed new insights into short-range correlations—the brief pairings of nucleons (protons with neutrons, protons with protons, or neutrons with neutrons) in the nuclei of atoms. The study, published in Nature, used precision measurements to determine that short-range correlations differ depending on the density of the nucleus, that is, how many nucleons it contains.
The Philippine Research Reactor-1 building at the University of the Philippines. (Photo: PNRI)
The research reactor known as SATER (Subcritical Assembly for Training, Education, and Research), housed in at the Philippine Research Reactor-1 building at the University of the Philippines in Quezon City, has become operational. As recently reported by the International Atomic Energy Agency, the core of SATER was loaded with 44 fuel rods, bringing the Philippines its first operational nuclear reactor in 34 years. Through this event, the country has moved a big step closer to meeting the government’s goal of adding nuclear power to its energy resources. The reactor is expected to become fully operational by 2023.
The NNSA’s Savannah Blalock announces that the agency has reallocated $10 million to support peaceful uses. (Photo: NNSA)
The Department of Energy’s National Nuclear Security Administration has redirected about $10 million from the International Atomic Energy Agency’s low-enriched uranium fuel bank to efforts supporting the peaceful uses of nuclear technology and to fight cancer.
Construction of the IAEA’s international training center for nuclear security is expected to be completed by the end of this year. (Photo: C. Daniels/IAEA)
Construction of the International Atomic Energy Agency’s new Nuclear Security Training and Demonstration Centre (NSTDC) is nearing completion in the town of Seibersdorf, Austria, near the capital city of Vienna. The IAEA expects construction to be finished by the end of the year, allowing for the facility to open and be operational by late 2023.
Ed McGinnis, Curio CEO. (Photo: Curio)
Ed McGinnis, the chief executive officer of nuclear innovation startup Curio, is looking to solve the nuclear waste problem. In a profile published by CNBC, McGinnis says that nuclear waste is “a huge, huge unresolved problem representing pretty much the largest ball and chain on the ankle of the U.S. nuclear energy sector [which is] trying to transition itself for the next generation of reactors.” Curio, which has developed its NuCycle technology for chemically processing nuclear waste, is hoping to “rebrand nuclear as a means of unlocking the full potential of human ingenuity and aspiration,” according to the company’s website.
Artist’s rendering of the IMSR Core-Unit. (Credit: Terrestrial Energy)
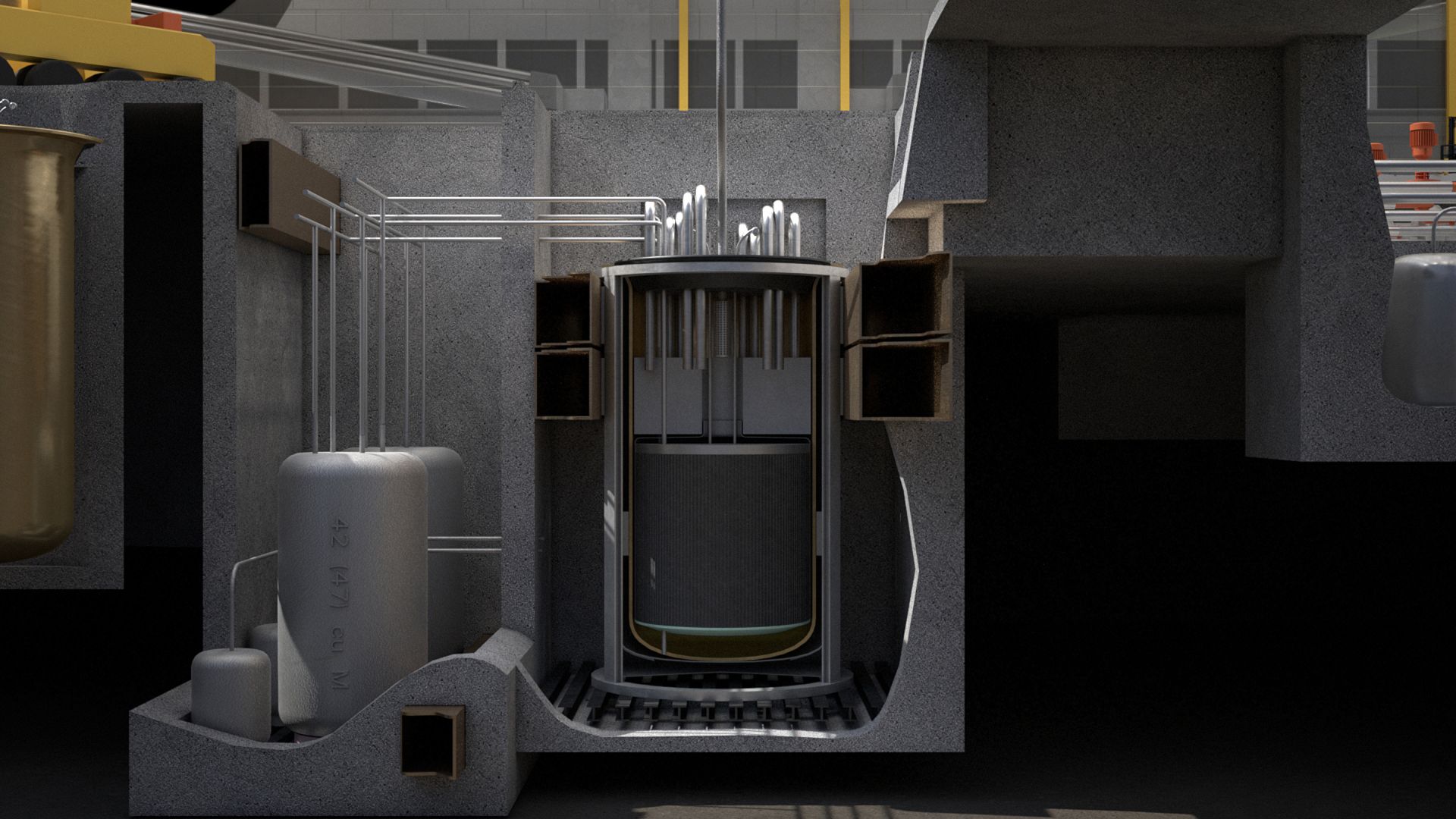
In the ongoing quest to mitigate the effects of climate change, new technology can create new solutions. Even today, however, coal is still a main source of power around the globe, often out of necessity. Many coal-burning plants have already been converted for gas or biomass, but these measures alone are not nearly enough to meet net-zero carbon goals. There is a better solution, however: repowering coal plants with nuclear technology—specifically, Generation IV reactors.
Construction of the new Science and Engineering Research Center is underway on the ACU campus. (Photo: ACU)
The Nuclear Energy eXperimental Testing (NEXT) Laboratory at Abilene Christian University in Texas submitted a construction permit application to the Nuclear Regulatory Commission for its molten salt research reactor (MSRR) on August 15. According to ACU, the move represents the first application for a new U.S. research reactor of any kind in more than 30 years, as well as the first-ever university application for an advanced research reactor.
 The International Atomic Energy Agency, for the second successive year, has revised upward its annual projections of nuclear power’s potential growth over the coming decades as an electricity provider.
The International Atomic Energy Agency, for the second successive year, has revised upward its annual projections of nuclear power’s potential growth over the coming decades as an electricity provider.-3 2x1.jpg)






 The National Association of Regulatory Utility Commissioners (NARUC) has published
The National Association of Regulatory Utility Commissioners (NARUC) has published