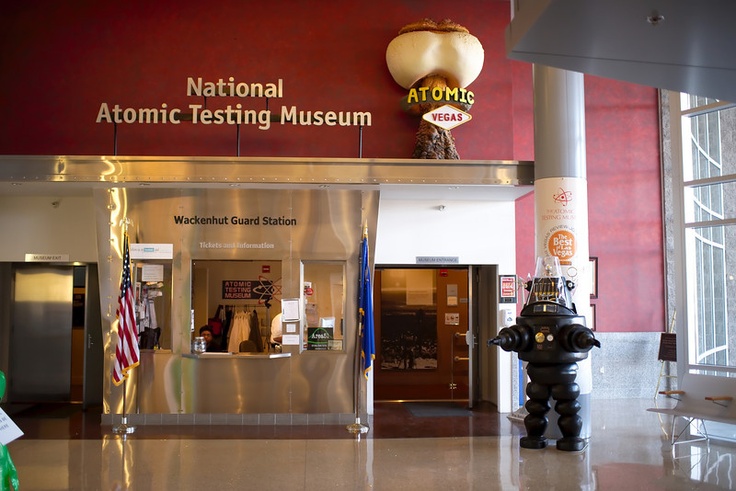
Photo: National Atomic Testing Museum
Longenecker & Associates has announced a $500,000 pledge from John and Bonnie Longenecker to the National Atomic Testing Museum in Las Vegas, Nev. The contribution will strengthen the museum’s missions to inform the public about America’s national security legacy and current programs and to inspire students, educators, and young professionals pursuing careers in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics.
Concept art of a fission surface power system on the surface of the moon. (Image: Lockheed Martin)
The “space race” is once again making headlines, with technology worthy of the 21st century. Like the Cold War–era competition, this race too is about showcasing power—but this time it's nuclear power.
A new article in Power Technology examines the competing efforts of the United States, Russia, and China as they strive to be the first to put a nuclear reactor on the moon to power a lunar base, detailing the technical challenges and international rivalries.
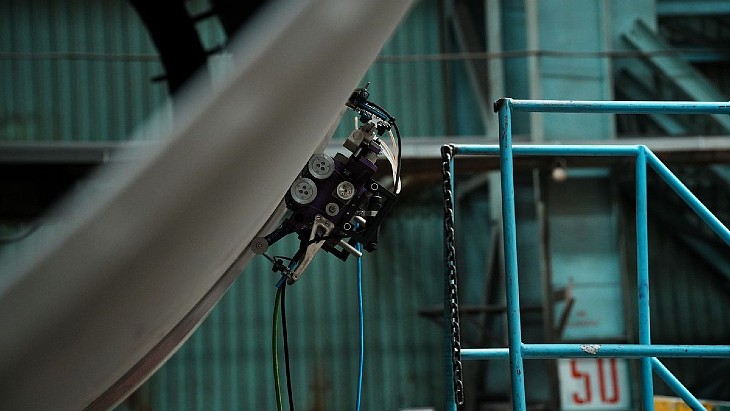
The inspection robot at work. (Photo: Rosatom)
“Nuclear Spider” sounds like the title of a 1950s-era science-fiction movie, but it’s actually a fairly accurate description of a new robotic system deployed by Atommash, the mechanical engineering division of Rosatom, Russia’s state-owned nuclear utility.
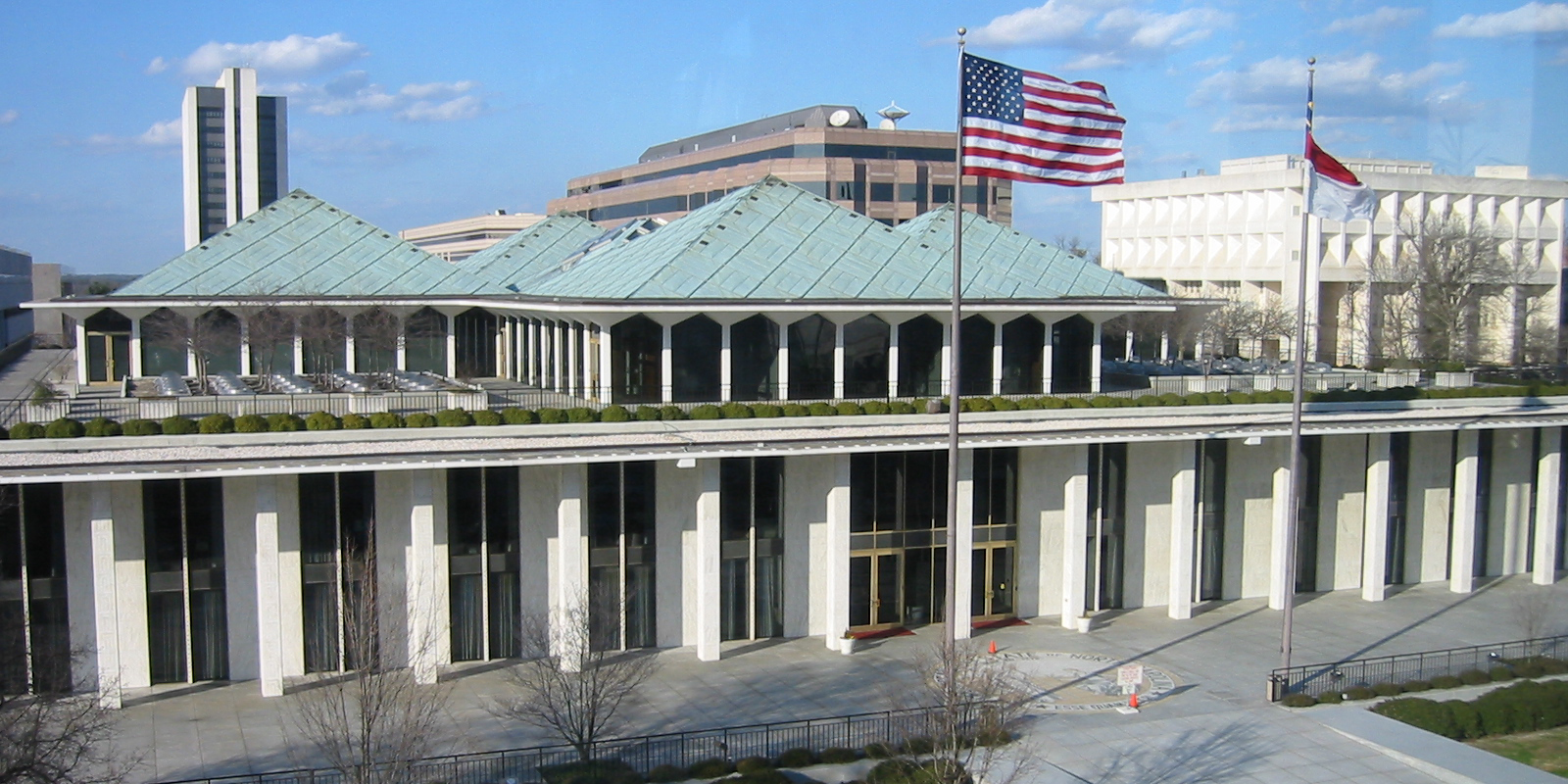
North Carolina's State Legislative Building in Raleigh.
I have been a North Carolinian for 62 years and involved in the state’s nuclear energy industry from my high school days to today. I have seen firsthand how North Carolina has flourished. This growth has been due to the state’s enterprising people and strong leaders. Clean, competitive, and always-on nuclear power has also played an important role.
A commercially irradiated, refabricated test rod in an INL hot cell. (Photo: INL)
An article in the OECD Nuclear Energy Agency’s July news bulletin noted that a first test has been completed for the High Burnup Experiments in Reactivity Initiated Accident (HERA) project. The project aim is to understand the performance of light water reactor fuel at high burnup under reactivity-initiated accidents (RIA).
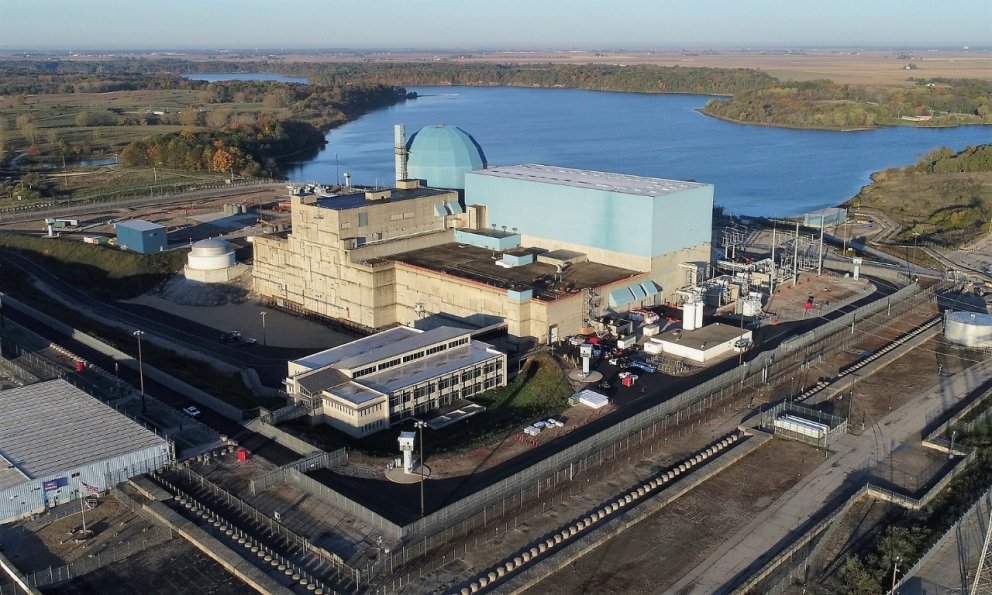
The Clinton nuclear power plant. (Photo: Constellation)
A recent article in the Chicago Tribune explores the benefits and potential drawbacks of the 20-year power purchase agreement (PPA) signed by Constellation Energy and Meta last month.
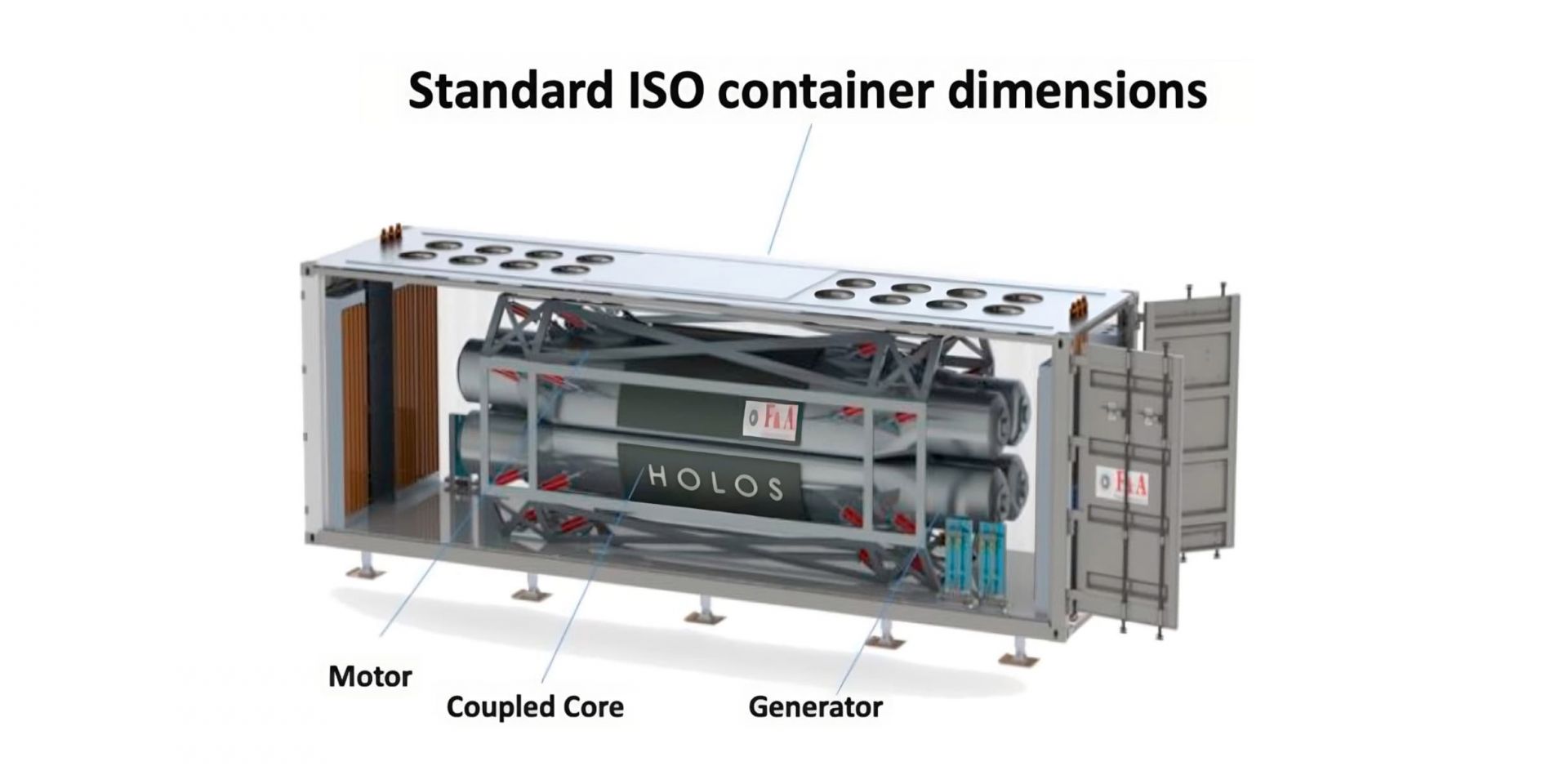
The compact, transportable Holos-Quad microreactor, developed by HolosGen, is shown housed within a standard 40-foot ISO container. (Image: HolosGen)
The University of Michigan’s Department of Nuclear Engineering and Radiological Sciences (NERS) has published a summary of a study on nuclear microreactors and machine learning (ML) that was conducted by researchers from NERS and Idaho National Laboratory. The full paper, “Nuclear Microreactor Transient and Load-Following Control with Deep Reinforcement Learning,” was featured in the July issue of Energy Conversion and Management: X.


-3 2x1.jpg)
 The latest report from the University of Michigan Science, Technology, and Public Policy Program’s
The latest report from the University of Michigan Science, Technology, and Public Policy Program’s