July 2, 2021, 2:15PMUpdated December 30, 2021, 7:15AMNuclear NewsSusan Gallier A hot cell at Argonne National Laboratory was used to demonstrate a process for purifying molybdenum-99, an important diagnostic medical isotope. (Photo: Wes Agresta/ANL)
The biggest impact of radiation in our lives may come not from radiation itself, but from regulations and guidelines intended to control exposures to man-made sources that represent a small fraction of the natural radiation around us.
Decades of research have been unable to discern clear health impacts from low levels of ionizing radiation, leading to calls for a new research program—one with a strategic research agenda focused on how the scientific understanding of the health effects of low doses (below 100 millisievert) and low dose rates (less than 5 mSv per hour) can best be augmented, applied, and communicated.
Building instrumentation and control technologies into the design of the next generation of advanced nuclear reactors will help the industry meet zero-carbon-emissions goals.
December 23, 2021, 3:00PMNuclear NewsAlexander Heifetz, Matthew Weathered, Nathan Hoyt, Mark Anderson, Scott Sanders, Anthonie Cilliers Kairos Power’s Instrumentation Test Unit
As a source of carbon-free electricity, nuclear energy currently dominates in the United States. However, the light water reactors in the U.S. are approaching the end of their licensed service lives. Meanwhile, low-cost electricity generated by fossil fuel–based sources (such as natural gas) poses an ongoing challenge to the economic viability of commercial nuclear reactors. To enhance the competitiveness of the nuclear industry, we need to bring down the high operating and maintenance (O&M) costs through savings available from utilizing modern, efficient sensing and automation technologies.
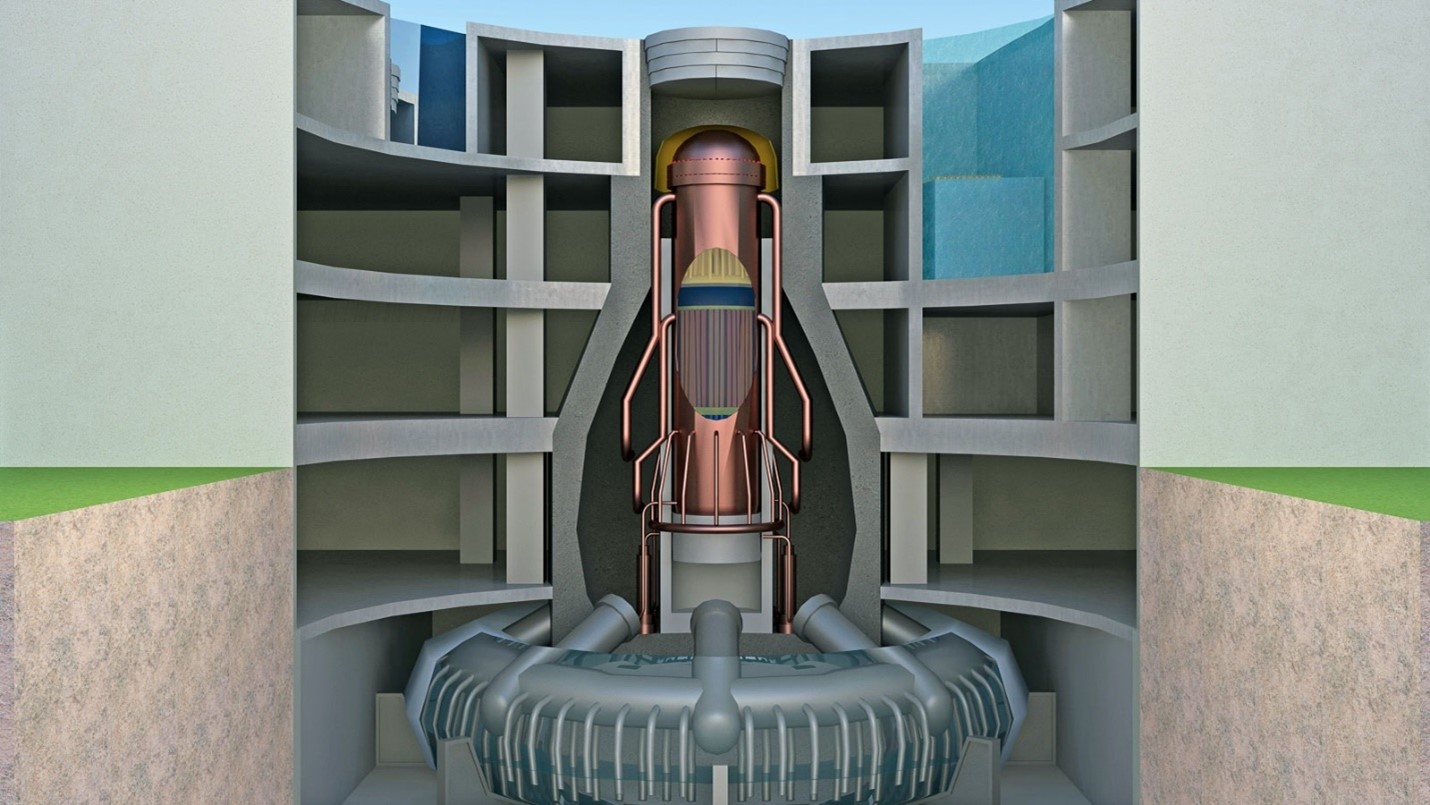
A cutaway view of a nuclear reactor. Its construction consists of two essential material types: fuel, which comprises the rods and cores that hold the fuel (center vertical bands); and structural, those parts of the reactor that house the fuel materials. (Graphic: Shutterstock/petrov-k)
Researchers from the Department of Energy’s Argonne National Laboratory are developing a “tool kit” based on artificial intelligence that will help better determine the properties of materials used in building a nuclear reactor.
The electric power transmission grid of the U.S. consists of thousands of miles of lines operated by hundreds of companies.
To do big things, like building the interstate highway system, or going to the moon, government usually has a plan. Electric companies and grid operators, which are responsible for keeping the lights on, always have a plan. But something unusual has happened in the past few months. About four dozen U.S. utilities, plus the federal government and many states, have promised to do something extremely big: to eliminate carbon dioxide emissions, or cut them drastically. But they are not clear on how.
Diablo Canyon nuclear plant. (Photo: PG&E)
Last April, Entergy had to close its Indian Point nuclear plant. That’s despite the plant’s being recognized as one of the best-run U.S. nuclear plants. That’s also despite its 20-year license extension process having been nearly completed, with full support from the Nuclear Regulatory Commission.
This closure was due in large part to opposition by antinuclear environmental groups. These groups also mobilized existing negative public opinion on nuclear energy to get politicians to oppose the plant’s license extension. Another factor is unfair market conditions. Nuclear energy doesn’t get due government support—unlike solar, wind, and hydro—despite delivering clean, zero-emissions energy.
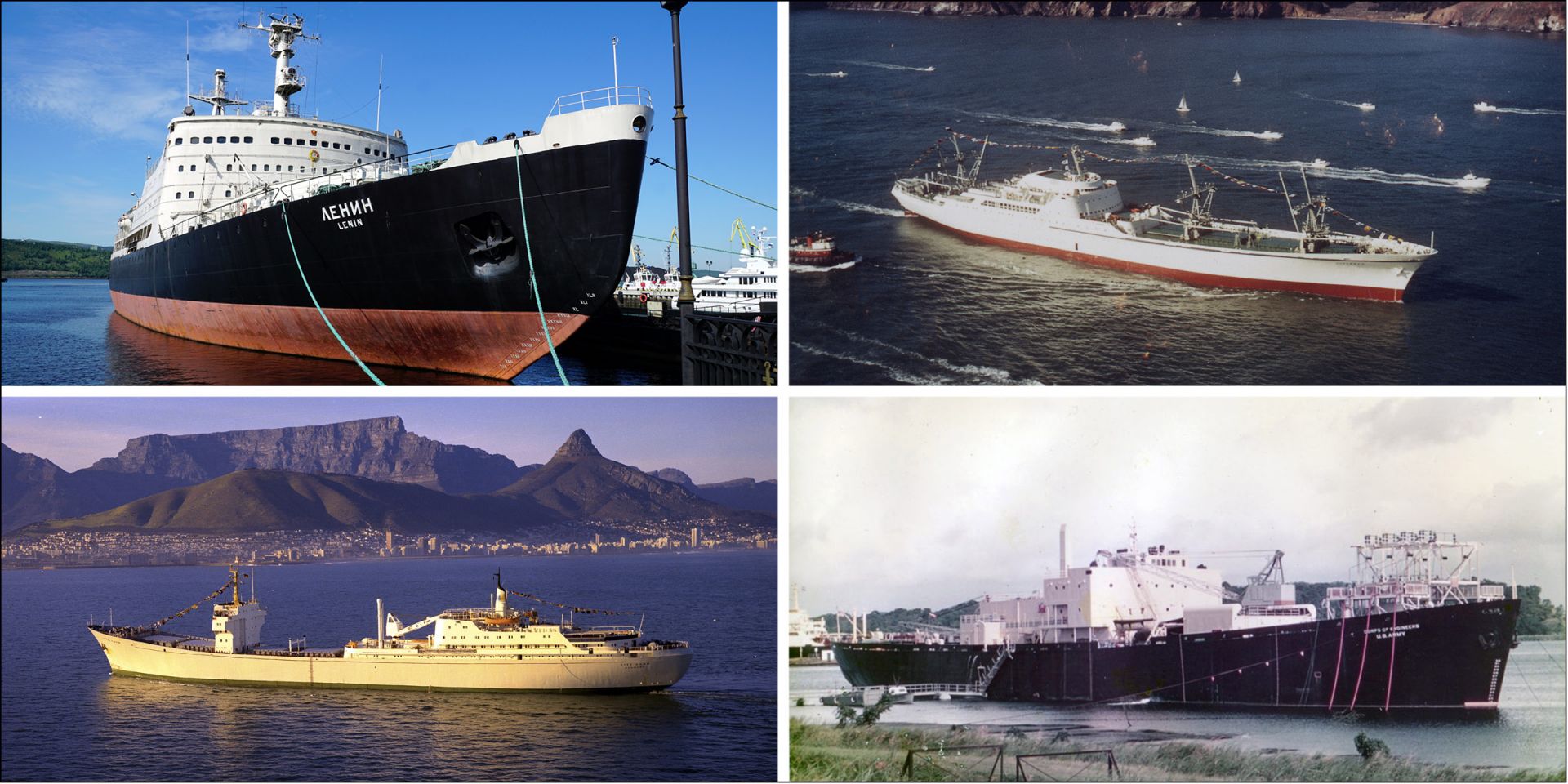
November 24, 2021, 2:30PMNuclear Newsthe U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, Baltimore District, Deactivated Nuclear Power Plant Program staff The Sturgis is towed from the Galveston, Texas, pier to the shipping channel on September 25, 2018, as it heads toward Brownsville, Texas, for final shipbreaking and recycling. Over the past three years in Galveston, the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers has been implementing the challenging and complex effort to decommission the MH-1A—the deactivated nuclear reactor that was onboard the Sturgis vessel.
The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (USACE), Baltimore District, is home to the North Atlantic Division’s Radiological Health Physics Regional (RHPR) Center of Expertise, which is leading the decommissioning of Army reactors.
From 1956 to 1976, the Army’s nuclear power program operated several small nuclear reactors to confirm the feasibility of their meeting military power needs on land. Three Army reactors were deactivated in the 1970s and placed into safe storage awaiting future decommissioning.
Southern California Edison has a plan—and it just might build momentum to solve the nation’s spent nuclear fuel disposal dilemma.
Imagine it’s January 1998. A specially equipped train from the Department of Energy rolls up to the San Onofre Nuclear Generating Station (SONGS) to pick up spent nuclear fuel and take it to the Yucca Mountain repository in Nevada. This scene is repeated thousands of times at nuclear plant sites across the U.S. over the ensuing decades. The solution to permanent spent fuel disposal as outlined in the Nuclear Waste Policy Act (and its amendments) is working as intended. The nation’s commercial spent fuel is safely isolated deep underground for the long term.
But that is not what happened. Work on Yucca Mountain has been stalled for a full decade, and the organization within the DOE that by law is responsible for managing the spent fuel program has been defunded and disbanded.