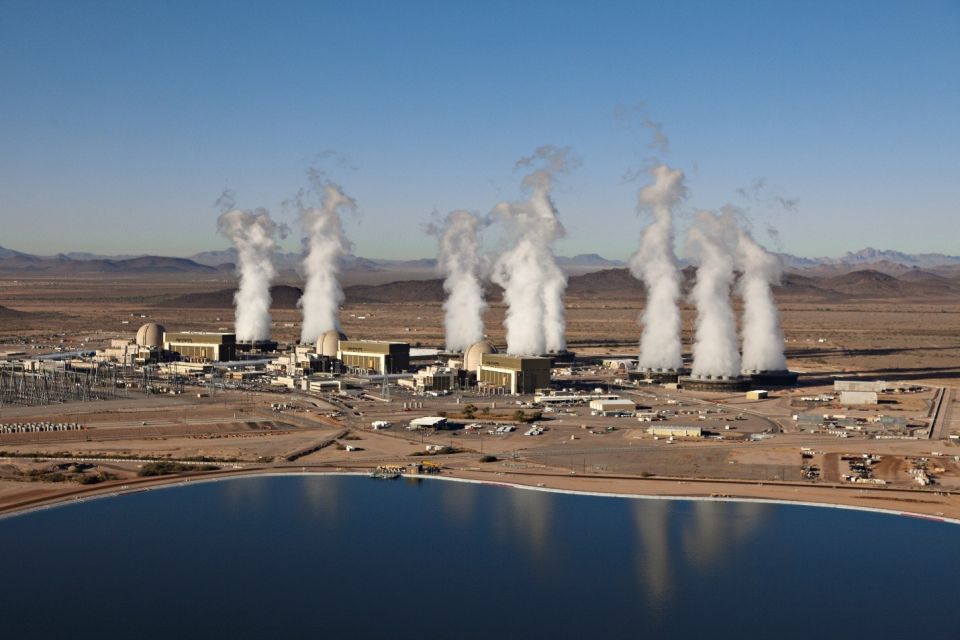
The report, A Multidimensional Nuclear Resurgence: Differing Drivers and Challenges, contrasted developments in the American, European, and Chinese investments in and construction of new nuclear energy technologies and infrastructure. The motivator for those differing investments is the same across the market: a sharp rise in the demand for energy security in the midst of growing electrification (in part driven by the AI boom) alongside a need for decarbonization through firm power sources.
Quotable: “As the world grapples with climate change and energy security challenges alongside steepening AI-related load forecasts, nuclear power is experiencing a global resurgence in interest,” said Emmanuel Dubois-Pelerin, EMEA utilities managing director at S&P Global Ratings, adding that “technological maturity, construction costs and financing . . . must be addressed for a true nuclear renaissance.”
European development: In line with a goal set at the 2023 UN Climate Change Conference to triple nuclear capacity by 2050, numerous European countries have announced and are in the planning stages of significant traditional reactor projects, broadly leaving small modular reactor development to the future. Spain's, Belgium's, and Germany’s intentions to reduce their nuclear capacity, however, bely a lack of commitment from the entirety of the EU on nuclear.
AI epicenter: While the rest of the world slowly expands into the datacenter sector, the United States is currently the world leader in infrastructural AI investments. The incredible energy intensity of server-housing facilities is pushing already high U.S. energy needs even higher. The excitement around AI is spurring both American industry and the public to look to nuclear to energize the boom.
Taking action: In contrast to numerous new-build announcements across the U.S. and Europe, China is accelerating construction, pushing a more aggressive plan to nuclearize in the short term. Their successful maintenance of a healthy project pipeline supported by strong supply chains and advancing technologies has led to an impressive increase in nuclear power generation. The report details that “China’s installed nuclear capacity is expected to more than triple by 2050 to reach over 260 GW.”