Uranium spot price closes out 2024 at $72.63/lb
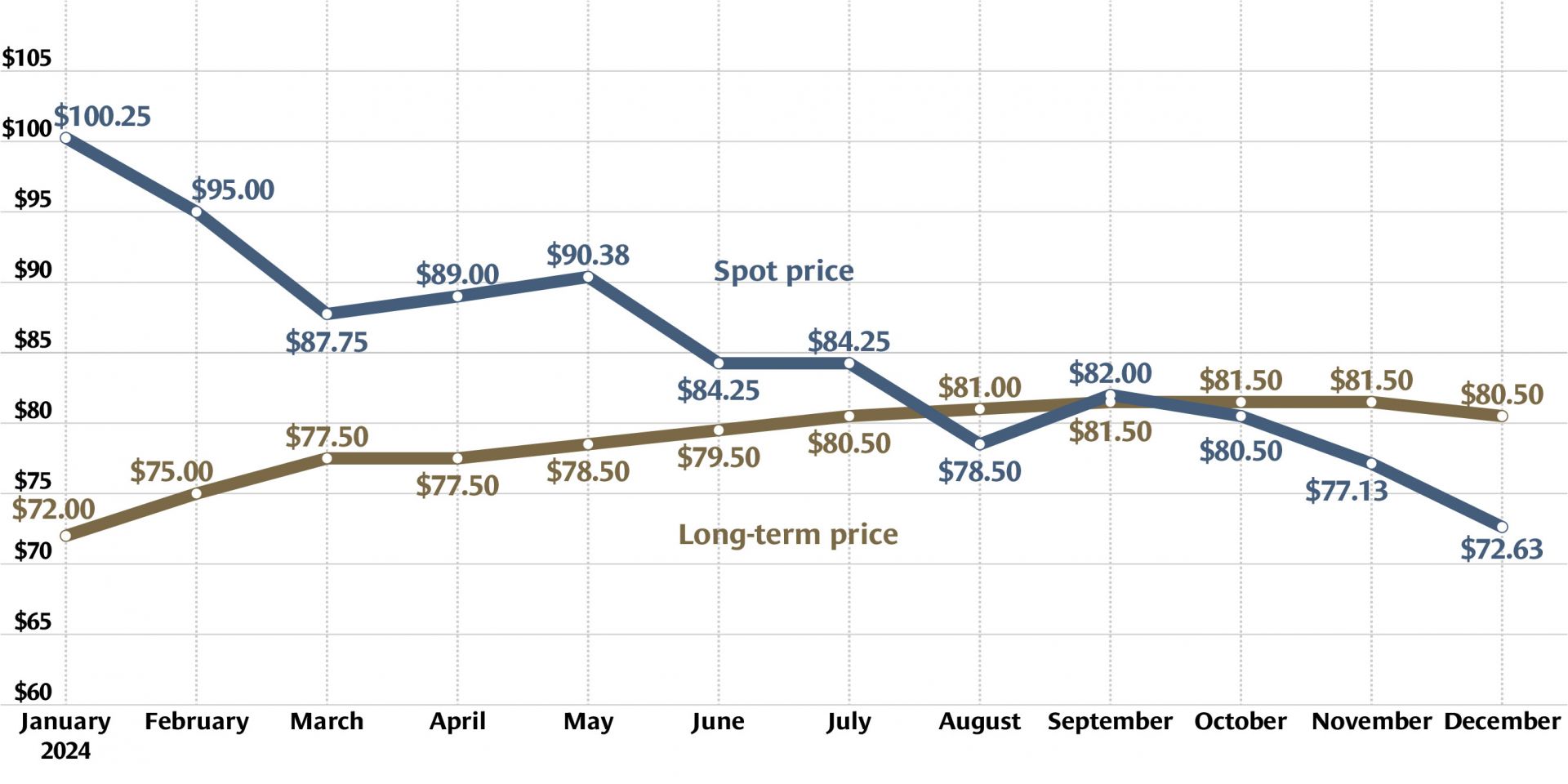
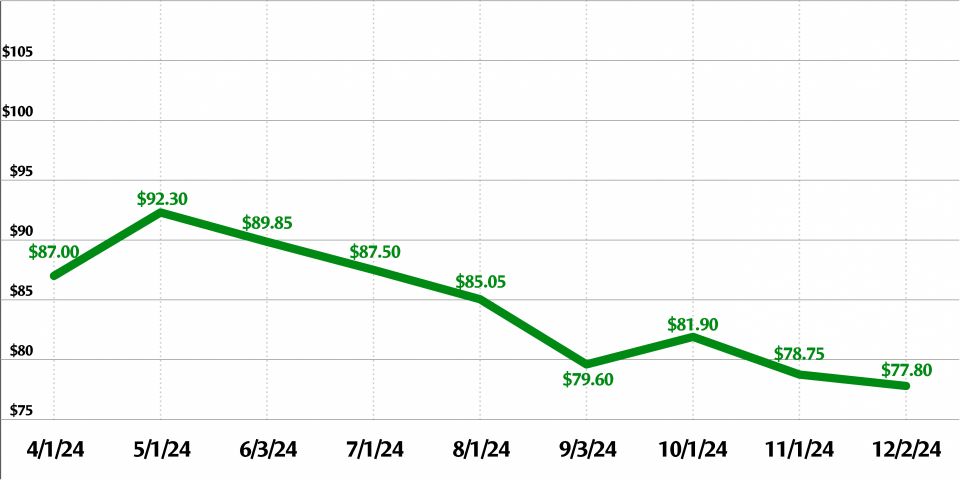
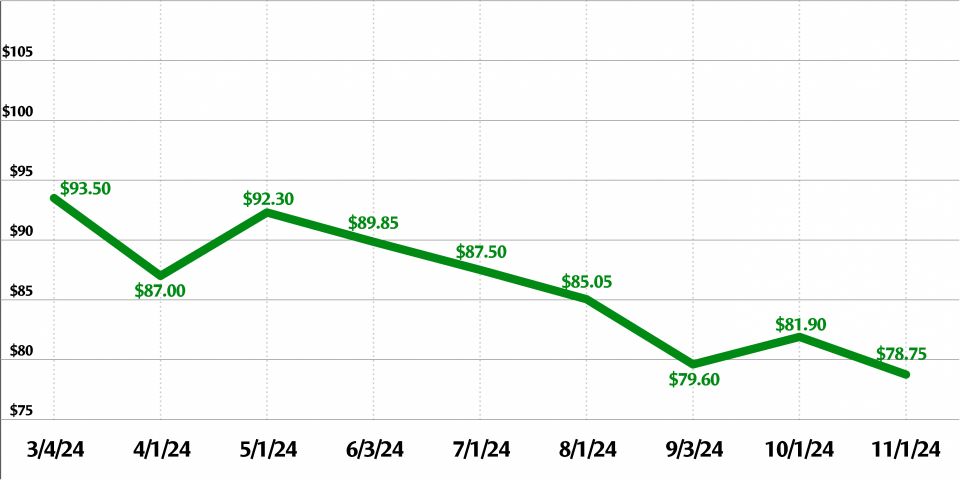
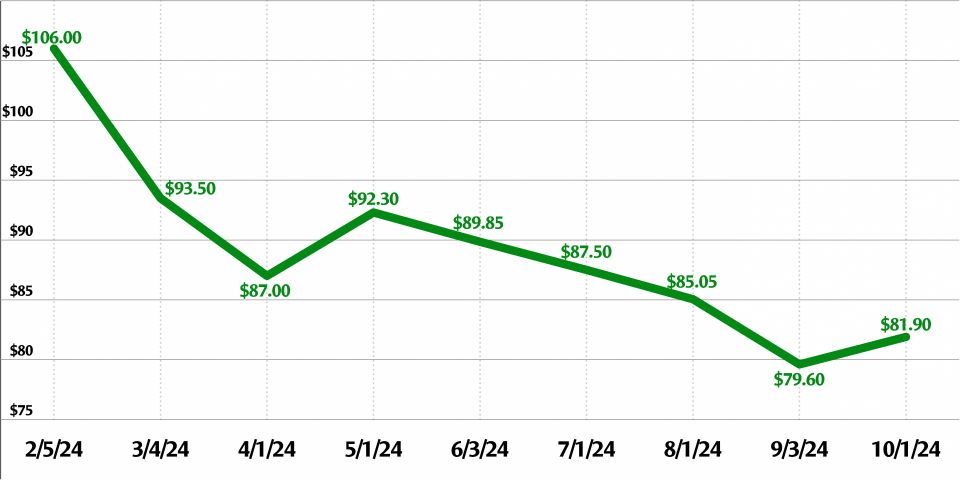
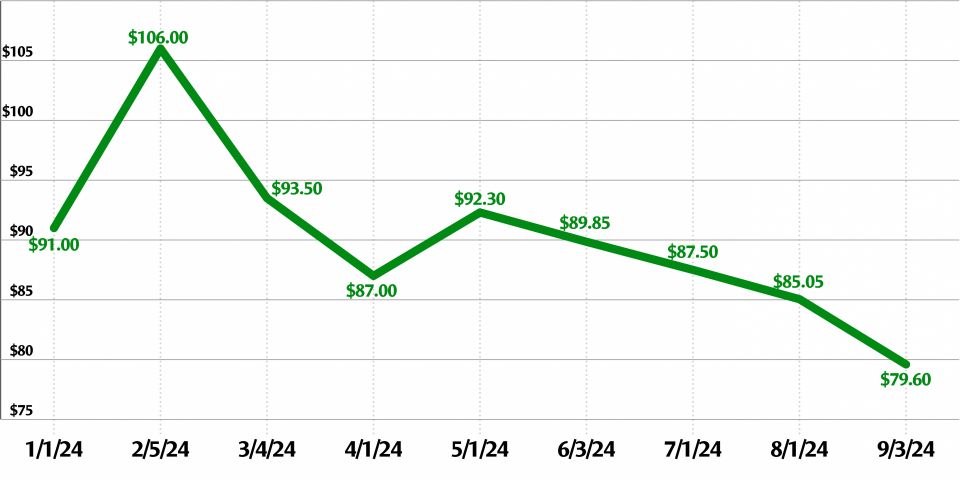
The uranium market closed out 2024 with a spot price of $72.63 per pound and a long-term price of $80.50 per pound, according to global uranium provider Cameco.
The spot price is the current value for which uranium can be bought or sold with an expectation of immediate delivery, while the long-term (or futures) price is the agreed-upon value for delivery at some point in the future.
The spot price has fallen from a peak of $100.25 in January 2024. The long-term price has been gradually rising for years, from $32.50 in January 2020 to the current price.
New year’s increase: Market analysis firm Trading Economics reported that the spot price had risen to $75.00 per pound by January 3 and was expected to trade at $74.62 per pound by the end of the first quarter. Looking forward, Trading Economics is estimating that the spot price will be $79.70 per pound by the end of the year.
Triple challenge: Cameco contrasted the geopolitical uncertainty in uranium supply—caused by such factors as market disruption related to the war in Ukraine and “years of underinvestment in new uranium and fuel cycle service capacities”—with the increasing global demand for uranium.
The increasing demand justifies long-term optimism in the uranium market, according to Cameco. “The benefits of nuclear energy have come clearly into focus with a durability we believe has not been previously seen. This is driven by the accountability created by the net-zero carbon targets being set by countries and companies around the world,” the company noted.
Cameco analysts described a “triple challenge” that these carbon targets present for the energy industry:
- Lift one-third of the global population out of energy poverty by growing clean and reliable baseload electricity.
- Replace 85 percent of the current global electricity grids that run on thermal power with a clean, reliable alternative.
- Grow global power grids by electrifying industries such as private and commercial transportation, home, and industrial heating, largely powered with thermal energy today.