The origins of The Reactor Safety Study

In March 1972, Stephen Hanauer, a technical advisor with the Atomic Energy Commission, met with Norman Rasmussen, a nuclear engineering professor at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. The AEC had recruited Rasmussen to develop a report, The Reactor Safety Study (WASH-1400), to estimate the probabilities and consequences of a major nuclear power plant accident. With thousands of safety components in a modern reactor, the task was mind-boggling. Rasmussen proposed a novel approach based on more powerful computers, “fault tree” methodology, and an expanding body of operational data. By calculating and aggregating probabilities for innumerable failure chains of components, he believed he could develop a meaningful estimate of overall accident risk. WASH-1400 would be a first-of-its-kind probabilistic risk assessment (PRA).
Hanauer was persuaded, but troubled. “Do we dare undertake such a study till we really know how?” he wondered. Previous estimates of accident probabilities had produced wildly inconsistent results. The AEC’s nuclear power program was mired in controversy, and the report was certain to generate publicity. Proving reactors were safe with an untried methodology might be a fiasco, and it almost was. No regulatory report had a more searing reception than the one that greeted WASH-1400’s publication in 1975. Its unsound risk comparisons, incomplete data sets, flawed calculations, and limited use of peer review prompted criticism so intense that the Nuclear Regulatory Commission issued a partial rejection of it in 1979.
Yet, we now know that the AEC’s daring paid off. WASH-1400’s credibility was restored, prophetically identifying key safety weaknesses that led to the Three Mile Island accident. Today it is remembered as the seminal document of PRA methodology and risk-informed regulation. That happier ending has lent to PRA histories a narrative of inevitability that overshadows the frustrating multi-decade pursuit of accident probabilities that preceded the study and the AEC’s fraught debate on moving forward with it. More than the beginning of PRA, WASH-1400 was the culmination of decades of technical and political dilemmas within the nuclear establishment that made a new quantitative approach to safety imperative.
The burden of WASH-740
The search for accident probabilities began early in the Cold War era. Reactor safety was grounded in a conservative, qualitative philosophy characterized by the alliterative three D’s of safety: design basis accidents, deterministic (conservative) design, and defense in depth. At the AEC’s Hanford production reactors in Washington state, experts on the Reactor Safeguards Committee—the predecessor to the Advisory Committee for Reactor Safeguards (ACRS)—were alarmed by emergent hazards that might cause an explosive reactor runaway more powerful than previously imagined. In 1950, the committee noted that probabilistic assessments of risk were the norm in other technologies, and it would dispel the committee’s concerns if it could be shown that a reactor disaster was just a one in a million (10-6) probability (ML15113A624). General Electric Company, Hanford’s contractor, was confident in the conservatism of its accident consequence estimates, but its forays into probabilistic estimates were foiled by limited operating experience and computing capabilities.
In 1957, Brookhaven National Laboratory came to the same result in its landmark study, WASH-740. Requested by Congress’s Joint Committee on Atomic Energy (JCAE) as part of the pending Price-Anderson indemnity legislation, WASH-740’s consequence estimates were disturbing. A sudden loss of coolant accident (LOCA) coupled with a failure of the emergency core cooling system (ECCS) and containment could cause 3,400 deaths and $7 billion in property damage. Based on a poll of experts, the AEC maintained that this hypothetical accident had an “exceedingly low” probability, in the range of 10-6 per reactor year, but admitted that “no one knows now or will ever know the exact magnitude of this low probability” (ML20086S495).
As the favorite reading of antinuclear critics, WASH-740 was an “albatross around our necks,” AEC chairman Dixy Lee Ray later observed. Refuting it became a priority. In 1964, the JCAE tasked the AEC with updating the study. The request was a major mistake. Brookhaven’s consequence estimates were even worse than the original study, simply because power reactors were larger and produced more fission products.
The AEC tried to put the update’s results in context by contracting a formal probabilistic estimate from Planning Research Corporation. Based on quite limited operating data, Planning Research estimated that a major accident was no more likely than one in 500 years of operation. This was not reassuring. If correct, two major accidents were possible every year in a fleet of 1,000 reactors. A second “quasi-quantitative” estimate relied on a mixture of judgment, failure data, and system block diagrams. It produced very optimistic probabilities, between 10-8 and 10-16 reactor years of operation. Regulatory staff concluded that the estimates were useless. Even the most pessimistic end of the quasi-quantitative approach meant that a reactor operating since the age of the dinosaurs might have just one accident. The AEC did not publish the results of the update. Unable to quantify risk, the AEC made a virtue of its qualitative safety approach. Over the course of the 1960s, advances in risk assessment methodology, regulatory surprises, and the rise of environmentalism compelled the AEC to attempt probabilities again.
Fault tree methodology: Seeing the forest with trees
Risk experts needed a universal visual representation of failure chains that could sort out the most important paths to disaster. “Decision trees” came to the rescue, with contributions from the biological sciences, business scholars, and military think tanks. In 1962, Bell Labs adapted decision trees and Boolean algebra to create fault trees for the U.S. ballistic missile program. Fault trees reduced chains of component failures involving power supplies, valves, and pumps to universal symbols—a visual lingua franca of catastrophe. Combined with component data, they could compute system failure probabilities. If fluent in fault trees, any analyst could see the likeliest paths to a disaster. The use of fault and decision trees spread to nuclear technology, including satellite SNAP reactors, Hanford’s production reactors, and civilian reactor design. Limited data and the possibility of unforeseen mishaps meant that the overall probability estimates from fault trees had a large potential for error, and their application was limited to comparisons of system design variations.
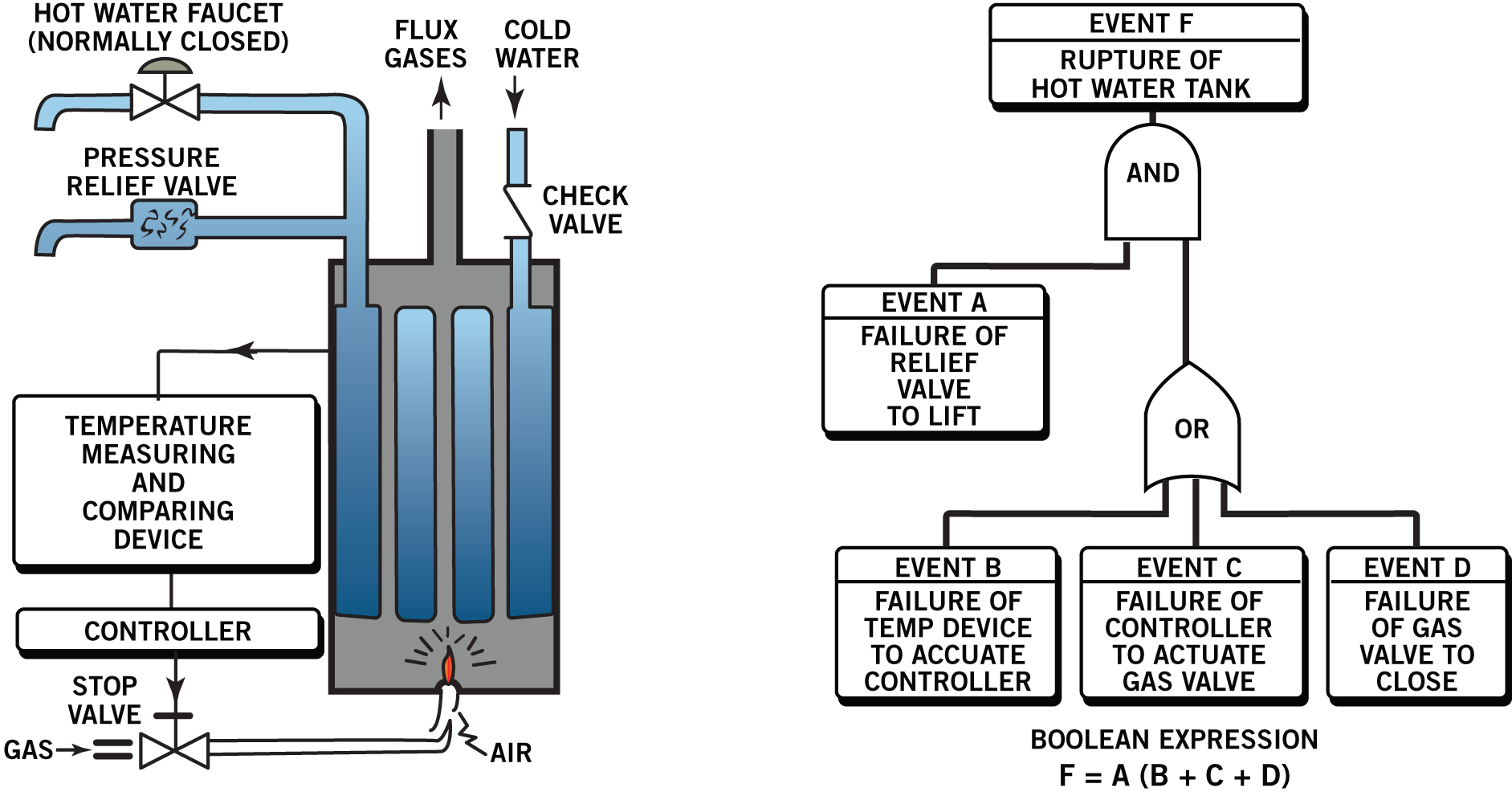
An example of the simplified illustration Bell presented in 1963 depicting the possible failure paths of a household hot water heater. (Diagram adapted from Boeing Corporation, Ref. 5)
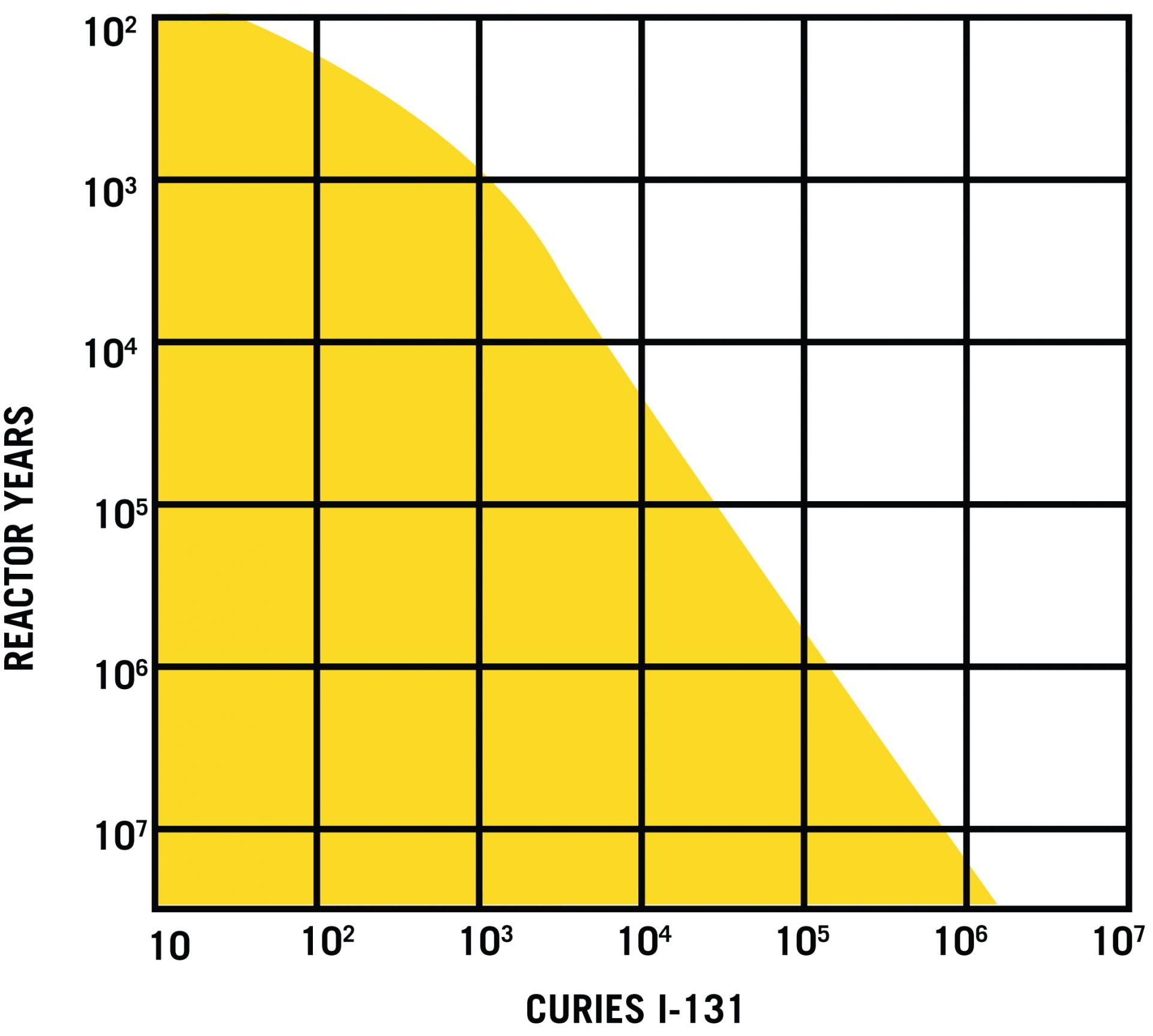
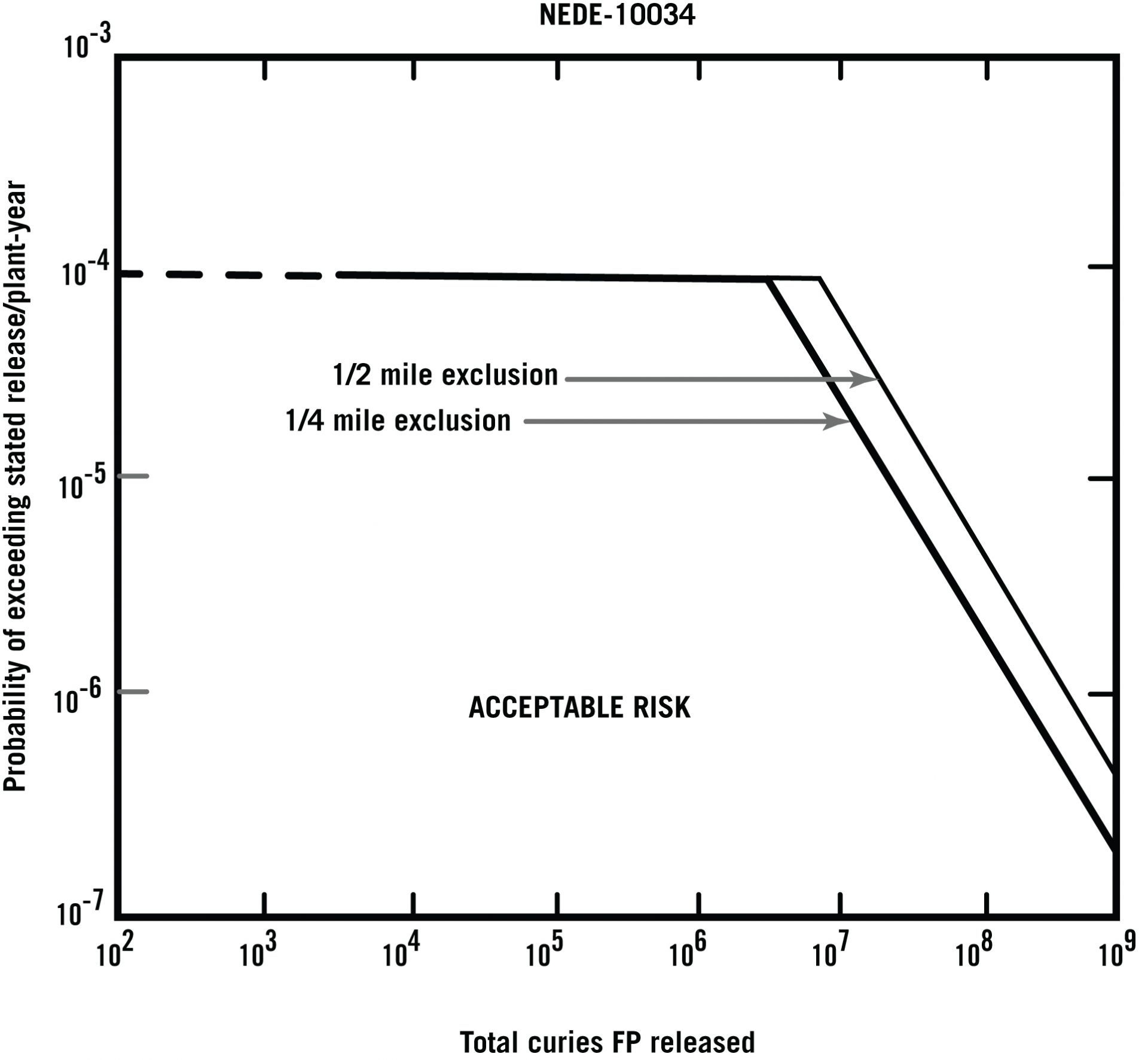
The Farmer curve set a maximum radioactive release criterion for an accident based on its probability. (Graph adapted from IAEA Ref. 6, with permission of the IAEA)
Some risk experts envisioned an ambitious coupling of these bottom-up estimates with top-down quantitative safety goals. In 1967, F. R. Farmer, a British nuclear expert, was dissatisfied with the arbitrariness of regulation by design basis accidents. In 1967, he proposed to analyze “in a quantity-related manner . . . a spectrum of events with associated probabilities and associated consequences.” He established a risk limit curve for reactor design and siting decisions by plotting accident probabilities against international standards for health effects from iodine-131, a radioactive isotope released during an accident. Believing that the public was more averse to one large accident than many small ones, he bent the curve to further reduce the risk of catastrophic accidents. The “Farmer’s curve” influenced risk thinking in the United States, too. For example, Ian Wall, a risk expert with GE and a Standards Service Award recipient in 2019 from the American Nuclear Society, incorporated it into a risk methodology he proposed for reactor siting decisions. GE and the rest of the nuclear industry began to develop expertise in probabilistic approaches to safety.
In 1969, Chauncey Starr, a Manhattan Project veteran and dean of engineering at the University of California–Los Angeles, took Farmer’s model a step further. He proposed a universal model of acceptable risk and benefits across multiple technologies. Excessive caution by nuclear experts, he believed, produced a generation of “nuclear hypochondriacs” with “irrational anxiety.” The key to winning over the public was to quantify and compare the risks and benefits of all technologies. He developed acceptable risk curves based on historical accident and disease data, insurance tables on the value of a life lost, and the risks and benefits of various technologies. Starr’s calculations showed that nuclear power was safer than almost any other technology. In a clear message to the AEC, Starr wrote, “This approach could give a rough answer to the seemingly simple question, ‘How safe is safe enough?’ The pertinence of this question to all of us, and particularly to governmental regulatory agencies, is obvious.”
Starr’s proposal helped inspire a new field of risk analysis. Researchers later identified numerous biases and a lack of trust in experts among the public that made quantification of “safe enough” a task more complex than Starr imagined. Nevertheless, by the late 1960s, the pieces of risk assessment were beginning to coalesce. John Garrick, a future industry leader in PRA, suggested in his 1968 dissertation that experts might soon overcome the obstacles to probabilistic estimates and “arrive at the goal of a figure of merit to quantify safety.”
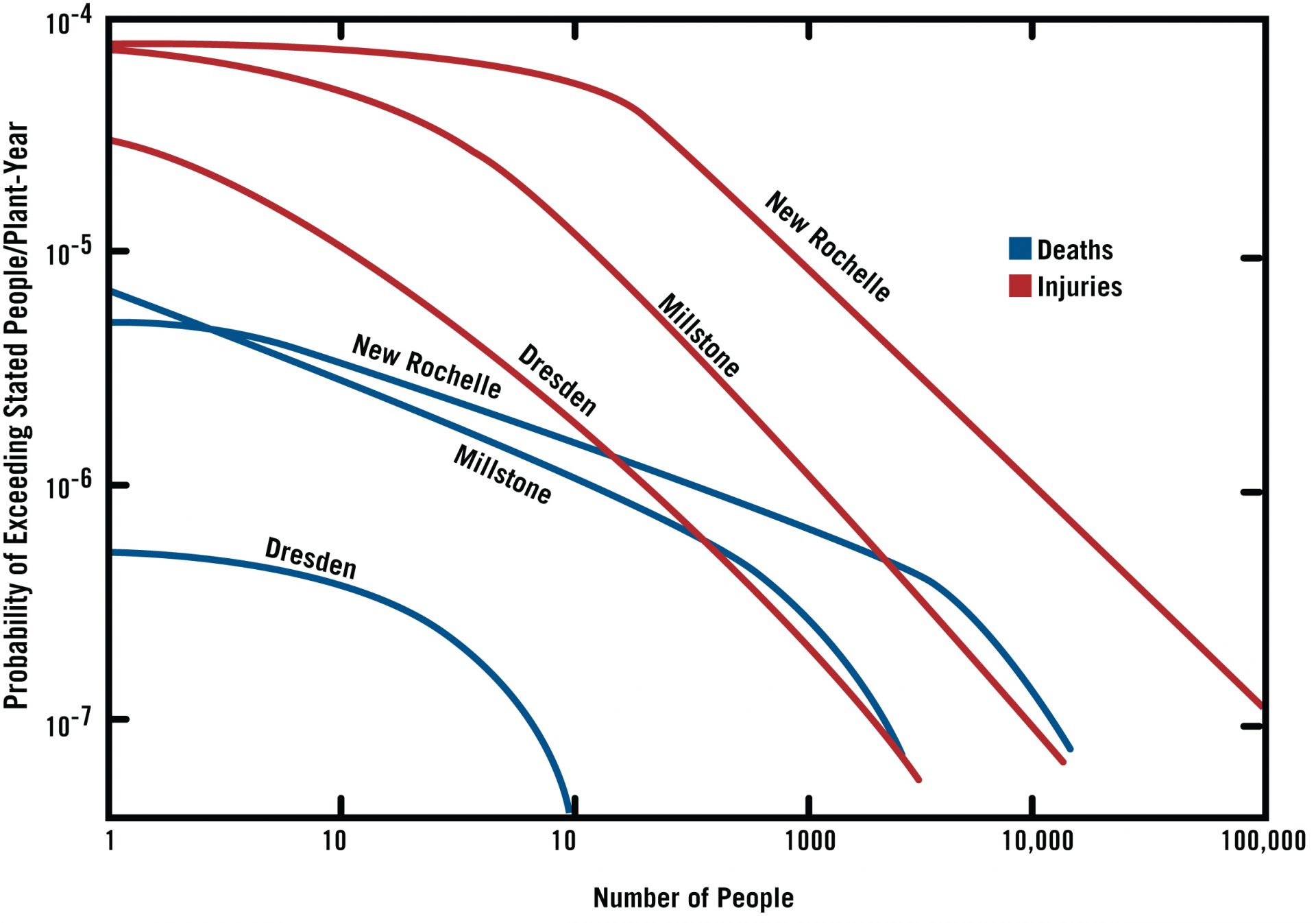
Ian Wall and GE developed a probabilistic approach to nuclear power plant siting decisions based on an analysis of the Dresden and Millstone stations as well as an ill-fated proposal at David’s Island near New Rochelle, N.Y. (Graphs adapted from General Electric Ref. 6)
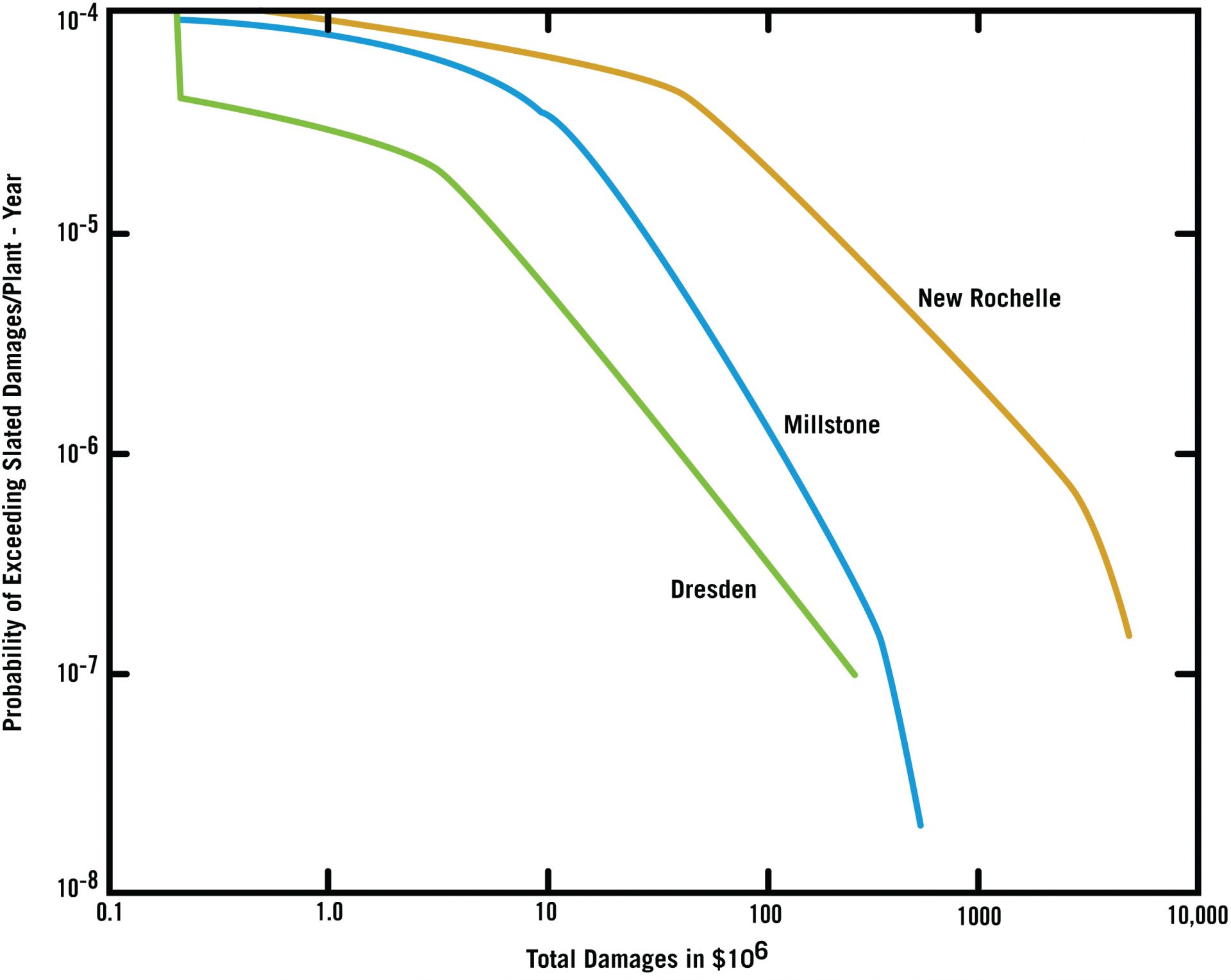
Ian Wall and GE developed a probabilistic approach to nuclear power plant siting decisions based on an analysis of the Dresden and Millstone stations as well as an ill-fated proposal at David’s Island near New Rochelle, N.Y. (Graphs adapted from General Electric Ref. 6)
Ian Wall and GE developed a probabilistic approach to nuclear power plant siting decisions based on an analysis of the Dresden and Millstone stations as well as an ill-fated proposal at David’s Island near New Rochelle, N.Y. (Graphs adapted from General Electric Ref. 6)
The China syndrome revolution
Developments in risk assessment left AEC officials intrigued but unmoved. Hanauer wrote, “We have not yet arrived at the point where probability analysis techniques give adequate assurance that all failure modes are indeed considered, that the probabilistic model for severe accidents corresponds to the actual failures that will occur, and that adequate failure rate data are available for prediction” (ML20235M908). Defense in depth remained the bedrock of light water reactor safety and containment buildings the last line of defense against catastrophe.
“Then a revolution in LWR safety occurred in 1966,” recalled ACRS member David Okrent. During the construction permit review for a General Electric boiling water reactor at Dresden, Ill., and a Westinghouse pressurized water reactor at the Indian Point site in New York, experts recognized that a core meltdown in these large reactors might have sufficient energy to melt through the reactor vessel and breach the containment building. A joke about the molten blob melting all the way to China led to the phenomena’s being dubbed “the China syndrome” (ML090630275).
For some ACRS members, the solution was to require safety system diversity and independence with even more robust containment designs. GE advocated an alternative: Make the ECCS so redundant that it would be the lynchpin of defense in depth. Containment design would assume that the ECCS worked sufficiently to prevent major core damage. GE further called for replacing deterministic safety with a probabilistic approach that emphasized the redundancy and reliability of active safety systems over diversity. Presciently, GE argued the AEC’s design basis events overlooked small mishaps that could lead to a serious accident.Robert Richards, a GE executive, dismissed the AEC’s “almost mystical belief that the containment provided protection” and argued that a core meltdown was only credible during a natural disaster. A careful probabilistic evaluation of a spectrum of accidents could “buy” more safety by optimizing design and providing greater realism to accident analysis (ML20114E664; ML20235C460; ML20114E647).
The AEC did not go along with relaxing containment requirements in exchange for improving ECCS reliability. Clifford Beck, a regulatory technical advisor, responded that GE did not recognize the value of “independent lines of defense which differ in nature and in objective” (ML20118D278). But an AEC task force chaired by William Ergen of Oak Ridge National Laboratory endorsed the industry solution to make ECCS so redundant and reliable that a core meltdown was not credible. The AEC also redirected its safety research program from studies of molten core behavior to focus on tests of ECCS effectiveness. The Atomic Industrial Forum, an industry organization, maintained that research into extreme accidents was unnecessary, since “a major meltdown would not be permitted to occur.” That the industry believed it had the power to forbid a meltdown spoke to its confidence that such accidents were not credible.
Alvin Weinberg, the longtime director of Oak Ridge National Laboratory, recognized the “profound repercussions” of the China syndrome debate. “Up to then, we had counted on containment to keep any radioactivity from escaping in every case: The consequence of even the worst accident was zero. But now . . . we could no longer argue that the widespread damage described in Brookhaven’s WASH-740 was impossible. . . . We had to argue that, yes, a severe accident was possible, but the probability of its happening was so small that reactors must still be regarded as ‘safe.’ Otherwise put, reactor safety became ‘probabilistic,’ not ‘deterministic.’”
The AEC’s probabilistic turn in 1967 was not manifest in quantitative risk criteria, but the change was evident. Defense in depth incorporated more emphasis on the reliability of active safety systems than static physical barriers, as evidenced in revisions to “General Design Criteria for Nuclear Power Plants” (Appendix A to 10 CFR Part 50). Conceived as a high-level constitution of reactor safety, the initial 1965 draft contained about two dozen criteria, including a requirement that containment would not be breached even during a complete ECCS failure. In the wake of the China syndrome debate, the 1967 draft ballooned to 70 criteria. Containment language was softened to require only a “substantial margin” for ECCS failure. Redundancy and reliability requirements were liberally applied to active systems. The 1965 draft specified single-failure criteria for reactor protection systems and control rod malfunctions. In 1967, it was clearly defined and expanded to electric power systems, decay heat, and core and containment cooling systems (ML090630275, chap. 3).
Probabilistic thinking also influenced debates over a new class of hazards—beyond-design-basis events. The first beyond-design-basis event to receive attention was the failure of the scram system after an anticipated transient, such as a loss of the feedwater system. In 1969, E. P. Epler, a consultant to the ACRS, contended that an anticipated transient without scram (ATWS) was far more likely than previously recognized. “The industry, by not attempting to mitigate the ‘China syndrome,’” he argued, “has placed the entire burden of protecting the public on the reactor shutdown system.” Anticipated transients typically occurred every year at nuclear power plants, and, he estimated, failed scrams occurred about once in a thousand demands. If the United States built 1,000 reactors, an ATWS could happen every year (ML090630275). Epler’s estimate included consideration of common-cause failures, such as an electrical fire or a common manufacturing defect that overrode system redundancies. Such a defect had disabled the scram relays at a reactor in West Germany.
ATWSs forced experts to estimate accident probabilities. GE, the most probabilistically minded vendor, claimed that the odds of an ATWS were less than one in 400 trillion. All four reactor vendors argued that an ATWS was not a credible event. Hanauer considered the GE estimate “nonsense” and told his superiors that the vendor was using “fake probabilities.” One ACRS consultant criticized GE’s analysis. “The AEC staff figures of 10–3 [one in 1,000] for the unreliability of reactor scram systems is entirely reasonable. Certainly, the GE value of 2.4 × 10–15 [about one in 400 trillion] is entirely unreasonable.” Experts in the United States, Canada, and Great Britain estimated an ATWS probability between one in 100 to one in 10,000.
The ATWS issue remained unresolved for the next 15 years, but the debate led the staff to spell out for the first time an informal quantitative safety goal of 10-6 for a major accident. Any individual accident scenario, such as an ATWS, LOCA, or damage from a major tornado, should be 10-7, one-tenth of the overall goal. The difficulty with such explicit numerical goals was that they were unverifiable. It would take generations of operating experience to establish with confidence an ATWS probability of 10-7 (ML19352A370; ML13073A158). ACRS consultants urged regulators to develop their own capacity for accident modeling and fault tree methodology.
The political necessity for risk assessment
The 1965 update to WASH-740 was not released to the public, but it was not secret. The AEC refused earlier requests from the antinuclear movement to release it. Harder to ignore was Alaska Sen. Mike Gravel’s request. The commission turned Gravel down but conceded to “an entirely new revision” of WASH-740. In early 1971, the AEC split the study between the Division of Reactor Development and Technology, which would write a report on the AEC’s safety philosophy, and the Office of Regulation, which would attempt a WASH-740 with probabilities to allow for comparisons of nuclear power to other technologies, as Chauncey Starr advocated. While WASH-1400 cost several million dollars and employed nearly 60 experts, the initial study was to be a modest project of a few staffers and a budget of about $200,000. Burdened with dozens of licensing applications, the regulatory staff made no progress on the report (ML20087M293).
Additional prodding followed as the AEC and JCAE confronted new rivals. In January 1970, President Nixon signed the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) and later that year established the Environmental Protection Agency. The EPA assumed authority to set public radiation standards, a potential point of conflict with the AEC in regulating licensees. The AEC came under fire for its limited implementation of NEPA requirements in its environmental impact statements (EIS). The AEC excluded major “Class 9” accidents from EIS consideration on the grounds that the probability of such an event, judged to be 10-8, was not credible (ML19263E348). As a regulator of multiple hazardous substances, the EPA was interested in risk assessment, too, and it pressed the AEC to use more than judgment to justify this claim.
More ominously, the AEC suffered a harshly worded legal defeat in 1971 before the D.C. Circuit Court in the Calvert Cliffs decision. The court ordered the AEC to consider a broader range of nuclear and nonnuclear hazards in environmental impact statements. Appearing insensitive to environmental concerns, a change in AEC leadership followed. Nixon appointed to the commission figures outside the nuclear establishment, including chairman James Schlesinger, an economist; William Doub, a Maryland public utilities commission chairman; and Dixy Lee Ray, a biologist. L. Manning Muntzing, a telephone industry lawyer, was appointed to head the regulatory division. Collectively, the new arrivals were more open to innovative approaches to nuclear safety, including risk assessment.
Environmental turf wars also distracted the JCAE. Until 1970, the Joint Committee was unchallenged in its control over atomic weapons, nuclear energy, and AEC oversight. Environmentalism empowered related congressional committees to challenge its monopoly. The JCAE faced an existential threat from legislative proposals in Congress and by the White House to break up the AEC and roll it into a super energy and resources agency.
To take back the initiative, Saul Levine, an AEC staffer on loan to the Joint Committee, recommended that the committee request an AEC study of its safety approach and the probabilities and consequences of major accidents—the key elements of the report the AEC had already promised to Gravel. The report would allow the committee to hold hearings and propose its own legislation. In October, the Joint Committee requested that the Reactor Development and Technology Division begin its stalled study on the AEC’s approach to safety. In December 1971, committee staff pressed regulatory leadership to get moving on their accident study.
Before the AEC could bring Rasmussen in for his interview in March 1972, the agency took further hits. In January, it began rulemaking hearings to establish performance criteria for emergency core cooling systems (ECCSs). Opponents accused the AEC of stifling the staff witness who disagreed with its position, and the agency appeared as a zealous promoter of nuclear power that lacked a commitment to safety. Even members of the JCAE stated their interest in breaking up the powerful agency. The AEC needed a fresh approach to making the safety case for nuclear power.
The Reactor Safety Study

Norman Rasmussen at MIT
With its credibility under scrutiny, the AEC sought an outsider to lead the study. In March 1972, Hanauer met with Rasmussen to map out the report’s tasks. Several covered the traditional ground of consequence studies like WASH-740—estimates of fission product release, dispersion, and health consequences. The hard part would be two groundbreaking tasks—to construct fault trees and estimate accident probabilities. Rasmussen cautioned, “There will be a significant lack of precision in our final result.” Hanauer admitted that the report team might have to “learn by trying,” but these new tasks were what the AEC wanted. “We want the whole package,” Hanauer wrote. “Doing [accident consequences without probabilities] would be another WASH-740 with the risk still unquantified. We might have to settle for that but want to try to do probabilities.”
Rasmussen was hired, but the AEC was not united on what he was hired to do. Tom Murley, a commission staffer who later served in the NRC as the director of the Office of Nuclear Reactor Regulation, was assigned to help Rasmussen in cajoling resources from an overburdened regulatory staff. To history’s benefit, he began to keep a notebook that chronicled the hope and foreboding with which AEC leadership approached the report over the next year (ML20087N390).
On the side of hope was AEC general manager R. E. Hollingsworth. He thought the new report would “bury WASH-740,” as Murley summarized. In a meeting with industry leaders, Schlesinger seconded the argument that the study would put WASH-740 into perspective for the public, and he was optimistic that a probabilistic study would reveal that current designs were grossly conservative.
Less sanguine was commissioner James Ramey. A former JCAE staff member, Ramey was a New Deal Democrat, a passionate supporter of nuclear power, and perhaps the most influential commissioner in AEC history. He remembered well the WASH-740 struggle and flawed accident probability results that doomed the 1965 update. He did not want Rasmussen to study accident consequences until he convincingly developed probability estimates. His concerns mirrored those of the nuclear industry. If Rasmussen’s analysis confirmed that accident probabilities were low, they asked, why study consequences at all? The commission initially agreed to restrict the investigation of consequences and described WASH-1400 as a study of accident probabilities and an “exploration of implications.”

Left to right: AEC commissioner James Ramey; AEC chairman Glenn Seaborg; President Lyndon B. Johnson; and AEC commissioner Samuel Nabrit at the Experimental Breeder Reactor-1 in Idaho. (Photo: U.S. DOE)
Ramey was also drawn to the study’s public relations possibilities. He gave the report a pronuclear tone by adding a Starr-like section that compared nuclear to nonnuclear risks. Of this new section, the staff noted, “The public daily accepts risks to its health and safety when it uses automobiles, airplanes, subways, elevators, and so on. Many of these activities have risks that are precisely known or can be computed. The risks associated with nuclear plants would then be placed in the context of other risks of the modern world” (ML20087M548). This section became the final report’s controversial executive summary, which was heavily criticized for comparing well-quantified risks, such as airplane accidents, to Rasmussen’s highly uncertain accident probabilities.

Saul Levine
“Get Saul Levine full time!” Schlesinger commanded Murley. Rasmussen served the AEC on a part-time basis, and the unwieldy study needed a strong hand. Levine had a temper so ferocious that some staffers summoned to his office remained standing to dodge the desk items he might throw at them. But he possessed navy discipline and attracted loyalty from staffers who adapted to his temper and aim. Levine brought to the study a regulator’s perspective on the value of risk assessment that transcended the commission’s focus on public relations. Risk assessment, he believed, could solve knotty problems, such as ATWSs, and improve regulatory staff capability. Under Levine’s leadership, the AEC later created a group organized around a cadre from the Rasmussen study to explore PRA applications in regulations.
As the study gained coherence in late 1972, it still needed unified commission support to expand it to include probabilities and consequences. Ramey’s influence with the JCAE made it difficult to move forward without him, and he micromanaged numerous aspects of the study and staff assignments. Schlesinger urged Rasmussen to “go make peace with Ramey.” Ramey held out. At a January 1973 meeting, he said the study might be a “nice theoretical work, but it could be like a successful operation where the patient died.” Commissioner Dixy Lee Ray countered that even if Rasmussen did not estimate consequences, someone else could do the same by using WASH-740’s results. Ramey quipped, “If it shows just one human life [lost], I’m against it.”
Pressure outside the agency grew. In March, the AEC met with representatives of the President’s Council on Environmental Quality. CEQ reported that the EPA wanted the AEC to make its case that major Class 9 accidents should be excluded from EIS risk-benefit analysis. “The AEC is telling the world that Class 9 accidents are incredible—they should tell the world why they think so.” The EPA could not force the AEC to analyze Class 9 accidents, but it might outflank it. The EPA, the AEC learned, was working on its own study of risk that would include a Farmer’s curve as a proposed safety standard.
Myron Cherry, a lawyer for antinuclear groups, threatened a lawsuit to obtain the 1965 update to WASH-740. AEC leadership concluded that they had no choice but to release it. Despite Ramey’s efforts, a worst-case estimate of perhaps 45,000 deaths was about to make headlines anyway. The Rasmussen report began to look more like a solution than a problem.
In a conclusive commission meeting at the end of May 1973, Rasmussen carried the day with a rough probabilistic estimate. Based on reactor vessel failure probabilities, a core-melt accident with serious health consequences was 10-6. A worst-case scenario of 1,400 acute (early) fatalities had a probability of one in 10 billion years. These were limited consequences for such an improbable accident. At last, Ramey agreed. “OK to go ahead!” Murley wrote in this his last journal entry. Ramey even permitted Rasmussen to choose his own staff for low-level team assignments. His term at an end, Ramey left the commission a month later.
Satisfied that WASH-1400 would bury WASH-740 and its update, the commission unleashed Rasmussen. The charismatic professor was deployed to counter the fallout from the release of the WASH-740 update. At a JCAE hearing in September 1973, Rasmussen dismissed WASH-740’s “upper-limit” calculations as “far from reality.” He expected his report would be “fairly favorable” to nuclear power. Delighted, Congressman Craig Hosmer said the report was “one of the most significant things that we have been presented in a number of years in reactor safety.” Holding the EPA at bay, the AEC inserted into its EISs a statement that Class 9 accident probabilities would be addressed by The Reactor Safety Study (ML082830088). The industry press reported, “If one thing is clear . . . the Atomic Energy Commission is counting rather heavily on the results of the Rasmussen risk quantification study to confirm . . . that the operation of nuclear reactors poses no undue risk to the health and safety of the public.”
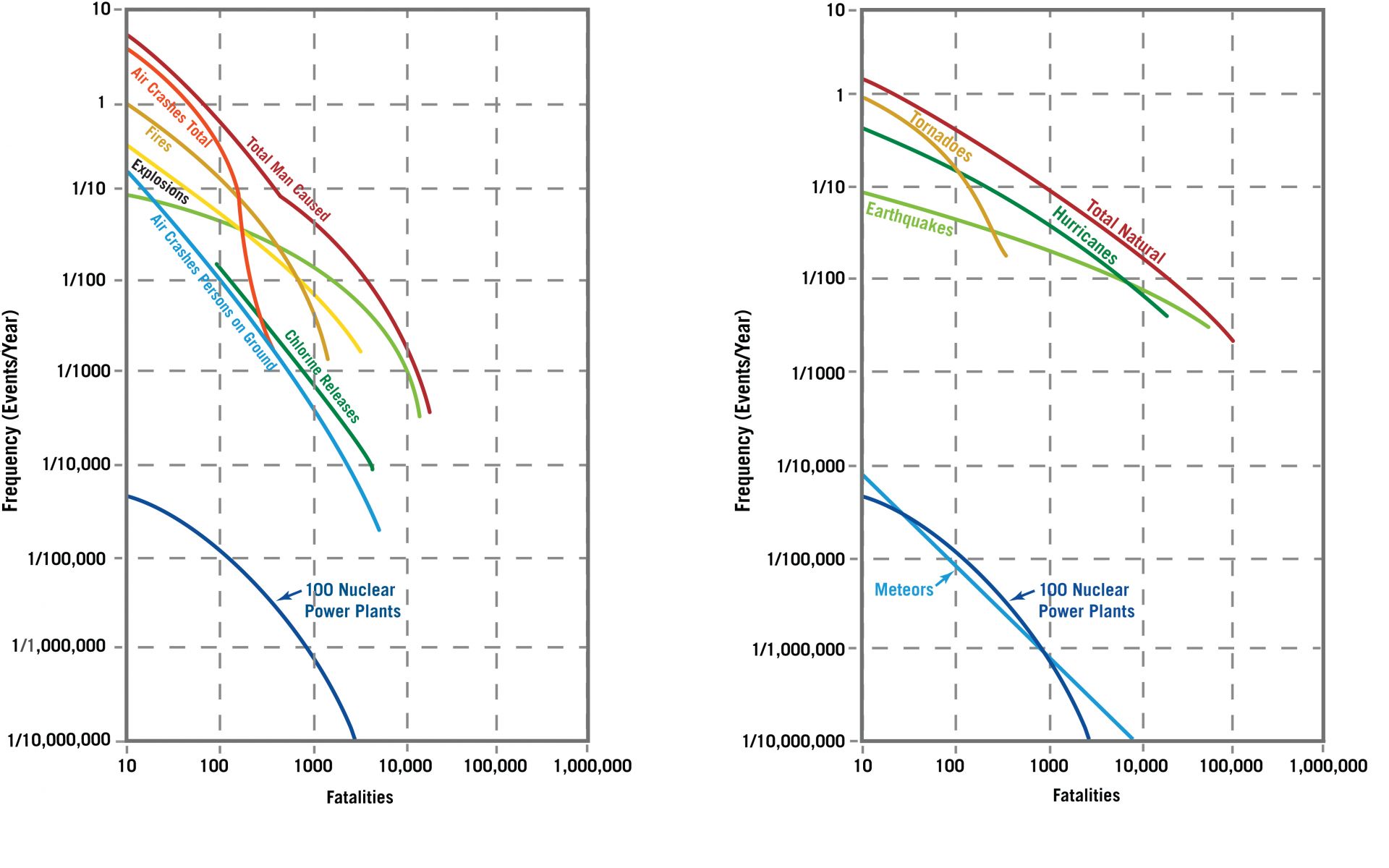
Comparisons of natural and human-made hazards as depicted in WASH-1400’s executive summary. (Graphs adapted from The Reactor Safety Study, NUREG-75/014)
Conclusion
The year of internal AEC debate revealed the disparate motives behind WASH-1400. For the commissioners and AEC leadership, the study might rid the agency of WASH-740’s ghost, persuade the public that nuclear power was safe, and restore the agency’s authority. In this hope, WASH-1400 was not successful. The Energy Reorganization Act of 1974 dissolved the agency and created in the NRC an independent safety regulator. Unpersuaded by quantitative assessments of risks and benefits, public support for nuclear power eroded throughout the 1970s. The study was more successful as the regulatory tool envisioned by Levine, Hanauer, and the nuclear industry, although the road to risk-informed regulation has been long.
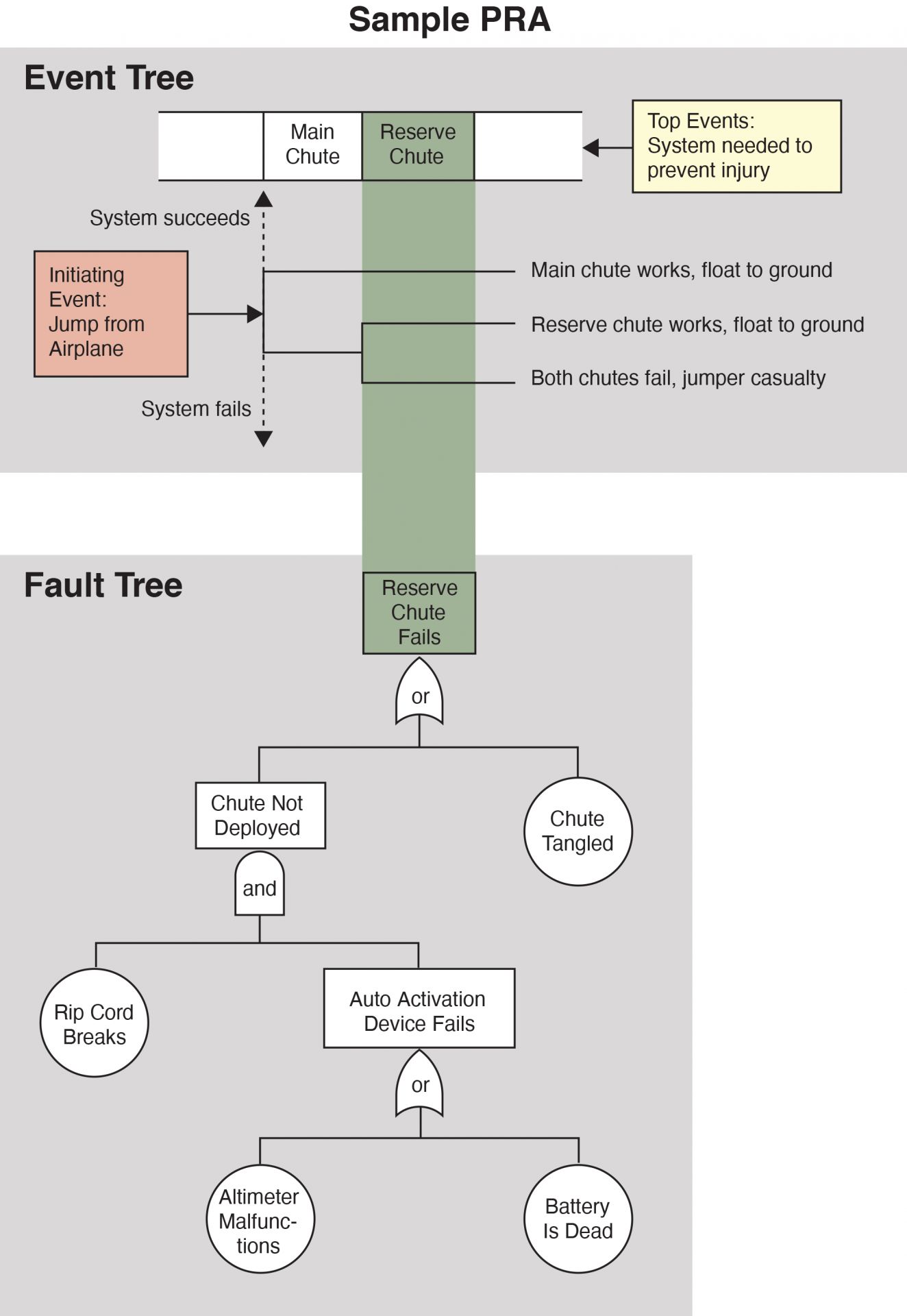
The key innovation of WASH-1400 was its integration of fault and event trees into one methodology, as depicted in this sample PRA for a parachute failure. (Diagram: U.S. NRC)
WASH-1400’s importance, however, exceeds this simple summation of failed and fulfilled expectations. The results were a revelation, even to Rasmussen. Comfortable in the assurance that he would confirm the old saw that a meltdown was a one-in-a-million probability, the commission gave Rasmussen the go-ahead in May 1973. His estimate was wide of the mark, more judgment than method, since he had yet to do much fault-tree work.
By the time the draft study was published in August 1974, Rasmussen and Levine had uncovered something unexpected. While it confirmed that accident consequences would be low, its overall accident probability estimate of one in 17,000 was so high that it broke the spell one-in-a-million held in the regulatory imagination. The major contributors to overall risk came not from a design basis accident or catastrophic vessel failure, but seemingly minor events such as small-break LOCAs, human error, and common-cause events. Despite the flaws in its calculations, WASH-1400’s insights found application in NRC regulations after the Three Mile Island accident in 1979.
The significance of WASH-1400 today is quite different than that envisaged by the AEC or its authors. Conceived of as a public relations tool that would confirm what experts thought they already knew about safety, it revealed what they did not know. Making accident risk knowable is PRA’s greatest legacy. As Saul Levine wrote in 1982, “It seems that the United States nuclear power community is finally taking to heart the words of Cicero (circa 40 B.C.): ‘Probabilities direct the conduct of wise men.’”
Thomas R. Wellock (Thomas.Wellock@nrc.gov) is the historian for the Nuclear Regulatory Commission and the author of Safe Enough? A History of Nuclear Power and Accident Risk (University of California Press).
This work was authored as part of the contributor’s official duties as an employee of the United States government and is therefore a work of the United States government. In accordance with 17 USC. 105, no copyright protection is available for such works under U.S. law.
This article reflects the views of the author. It does not represent an official position of the NRC.