The Cassini-Huygens Mission to Saturn
 Cassini-Huygens is a Flagship-class NASA-ESA-ASI robotic spacecraft sent to the Saturn system. It has studied the planet and its many natural satellites since its arrival there in 2004, as well as observing Jupiter and the Heliosphere, and testing the theory of relativity. Launched in 1997 after nearly two decades of gestation, it includes a Saturn orbiter Cassini and an atmospheric probe/lander Huygens that landed in 2005 on the moon Titan. Cassini is the fourth space probe to visit Saturn and the first to enter orbit, and its mission is ongoing as of 2013. It is powered by a plutonium power source, and has facilitated many landmark scientific discoveries in its mission to the stars.
Cassini-Huygens is a Flagship-class NASA-ESA-ASI robotic spacecraft sent to the Saturn system. It has studied the planet and its many natural satellites since its arrival there in 2004, as well as observing Jupiter and the Heliosphere, and testing the theory of relativity. Launched in 1997 after nearly two decades of gestation, it includes a Saturn orbiter Cassini and an atmospheric probe/lander Huygens that landed in 2005 on the moon Titan. Cassini is the fourth space probe to visit Saturn and the first to enter orbit, and its mission is ongoing as of 2013. It is powered by a plutonium power source, and has facilitated many landmark scientific discoveries in its mission to the stars.
Related Articles
The race to put a nuclear reactor on the moon
The “space race” is once again making headlines, with technology worthy of the 21st century. Like the Cold War–era competition, this race too is about showcasing power—but this time...

Surplus plutonium for power reactor fuel: What’s on offer
The Department of Energy has a plan for private companies to “dispose of surplus plutonium”—about 19.7 metric tons in both oxide and metal forms—by “making the materials available...
Orano to supply Zeno with Am-241 to power space missions
Zeno Power, a developer of nuclear batteries, is to receive americium-241 recovered from Orano’s La Hague nuclear fuel recycling site in Normandy, France, under a strategic agreement...

Nuclear power on the moon: What we’re watching
After the Trump administration’s new push to get a nuclear reactor on the moon by 2030 was first reported by Politico last month, media played up the shock value for people new to the...

High-power electricity direct from radiation is the vision of Rads to Watts
You could call it a power contest. Teams picked for a new research program from the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) will compete to design radiovoltaic cells that can...

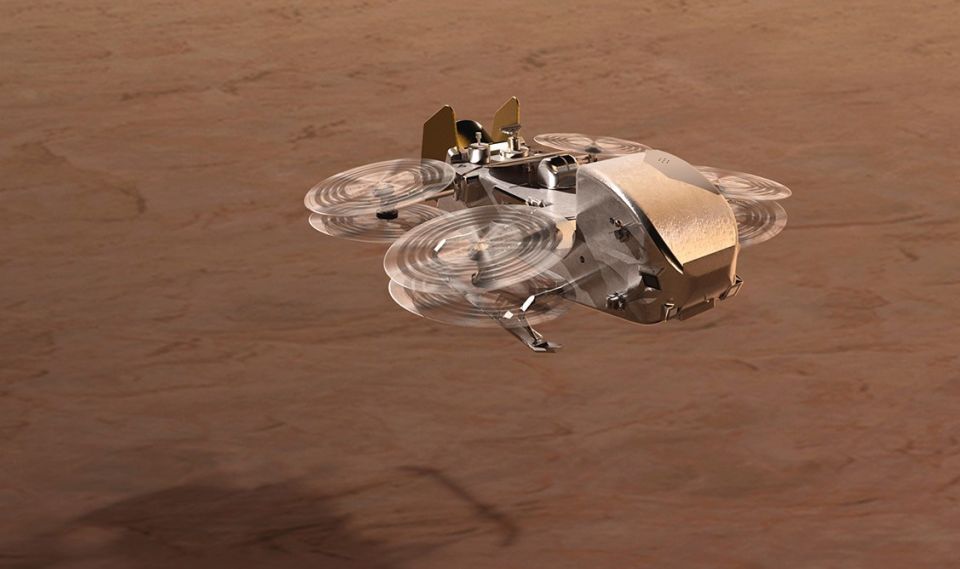
Dragonfly, a Pu-fueled drone heading to Titan, gets key NASA approval
Curiosity landed on Mars sporting a radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG) in 2012, and a second NASA rover, Perseverance, landed in 2021. Both are still rolling across the red planet in...
Former NASA official discusses the need for nuclear power in space
A recent episode of the podcast Space Minds features a discussion about the uses of nuclear power in space with Bhavya Lal, former associate administrator for technology, policy, and strategy...
Looking up: The 2025 NETS conference
The American Nuclear Society’s Nuclear and Emerging Technologies for Space (NETS 2025) conference will take place May 4–8 in Huntsville, Ala. Registration for the meeting is now open, and...

NDA funds Plutonium Ceramics Academic Hub with U.K. universities
The United Kingdom’s Nuclear Decommissioning Authority has announced that it will establish a Plutonium Ceramics Academic Hub with the Universities of Manchester and Sheffield. The...

Senate committee hears from energy secretary nominee Chris Wright
Chris Wright, president-elect Trump’s pick to lead the U.S. Department of Energy, spent hours today fielding questions from members of the U.S. Senate’s committee on Energy and Natural...




 Cassini made its closest approach to Jupiter on December 30, 2000, and made many scientific measurements. About 26,000 images of Jupiter were taken during the months-long flyby. Cassini produced the most detailed global color portrait of Jupiter yet (see image at right), in which the smallest visible features are approximately 60 km (37 mi) across. The New Horizons mission to Pluto captured more recent images of Jupiter, with a closest approach on February 28, 2007.
Cassini made its closest approach to Jupiter on December 30, 2000, and made many scientific measurements. About 26,000 images of Jupiter were taken during the months-long flyby. Cassini produced the most detailed global color portrait of Jupiter yet (see image at right), in which the smallest visible features are approximately 60 km (37 mi) across. The New Horizons mission to Pluto captured more recent images of Jupiter, with a closest approach on February 28, 2007.